Abstract
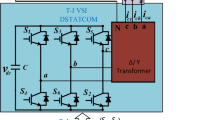
This paper proposes a new normalized Huber adaptive control algorithm for shunt compensation. A 5-level cascaded multilevel inverter (CHB-MLI) is controlled as a shunt active power filter (SAPF) unit for a medium voltage distribution system. The proposed algorithm is designed, modelled, and tested to control the SAPF unit under normal and distorted grid conditions. It is employed to extract the fundamental active power component of load current. This extracted effective component is used to generate source reference currents by multiplying with the unit vector template. Furthermore, the switching of CHB-MLI is performed using phase-shifted PWM scheme. The algorithm helps to mitigate the reactive power and unwanted harmonics generated by the nonlinear load. A single-phase scale-down prototype model is developed for experimental investigation and testing purpose in the laboratory. The associated voltage and current sensors and control circuits are controlled by the dSpace 1104 digital microprocessor. Simulation and experimental results show good performance of the proposed algorithm in steady-state and dynamic load conditions. A fair performance comparison is also done with other conventional adaptive algorithms.












source current (is), load current (iL) and compensating current (ic) wrt PCC voltage (Vs) THD of 2.8%, 30.1% and 1.8% in is, il, Vs


source voltage (Vs), source current (is), load current (iL) and compensating current (ic)


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodriguez J, Franquelo LG, Kouro S et al (2009) Multilevel converters: an enabling technology for high-power applications. Proc IEEE 97(11):1786–1817. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030235
Franquelo LG, Rodriguez J, Leon JI, Kouro S, Portillo R, Prats MAM (2008) The age of multilevel converters arrives. Ind Electron Mag IEEE 2(2):28–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIE.2008.923519s
Nabae A, Takahashi I, Akagi H (1980) Neutral-point-clamped PWM inverter. In: Conference on record IEEE IAS annual meeting, Cincinnati, OH, vol 3, pp 761–766. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.1981.4503992
Meynard TA, Foch H (1992) Multi-level conversion: high voltage choppers and voltage-source inverters. In: Proceedings of the IEEE power electronics specialist conference, pp 397–403. https://doi.org/10.1109/PESC.1992.254717
Lavieville JP, Carrere P, Meynard T (1997) Electronic circuit for converting electrical energy and a power supply installation making use thereof, U.S. Patent 5,668,711
Malinowski M, Gopakumar K, Rodriguez J, Perez MA (2010) A survey on cascaded multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(7):2197–2206. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2009.2030767
Tsunoda A, Hinago Y, Koizumi H (2014) Level-and phase-shifted PWM for seven-level switched-capacitor inverter using series/parallel conversion. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61:4011–4021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2286559
Akagi H, Watanabe EH, Aredes M (2017) Instantaneous power theory and applications to power conditioning. Wiley, NJ
Gonzalez-Espin F, Figueres E, Garcera G (2012) An adaptive synchronous reference-frame phase-locked loop for power quality improvement in a polluted utility grid. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(6):2718–2731. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2011.2166236
Herrera RS, Salmerón P, Kim H (2008) Instantaneous reactive power theory applied to active power filter compensation: different approaches, assessment, and experimental results. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(1):184–196. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2007.905959
Singh A, Singh B, Mittal AP (2010) Performance and control of converter interfaced distribution resources. In: Proceedings of the IEEE IICPE conference, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/IICPE.2011.5728124
Pouresmaeil E, Montesinos-Miracle D, Gomis-Bellmunt O, Sudrià-Andreu A (2011) Instantaneous active and reactive current control technique of shunt active power filter based on the three-level NPC inverter. Eur Trans Electr Power 21(7):2007–2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/etep.536
Singh B, Arya S, Verma P (2014) An implementation of double-frequency oscillation cancellation technique in control of DSTATCOM. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst 24:796–807. https://doi.org/10.1002/etep.1735
Singh B, Arya S (2013) Composite observer-based control algorithm for distribution static compensator in four-wire supply system. IET Power Electron 6(2):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2012.0412
Valdez-Fernandez A, Martinez P, Escobar G, Limones-Pozos C, Sosa J (2013) A model-based controller for the cascade H-bridge multilevel converter used as a shunt active filter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60(11):5019–5028. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2012.2218558
Arya S, Singh B (2015) Implementation of kernel incremental learning algorithm in distribution static compensator. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(3):1157–1169. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2014.2315495
Chittora P, Singh A, Singh M (2016) Performance evaluation of a new Kalman filter based least mean square algorithm for power quality improvement. In: International conference on power electronics, intelligent control and energy systems (ICPEICES), Delhi, India, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPEICES.2016.7853382
Badoni M, Singh A, Singh B (2016) Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system least-mean-square-based control algorithm for DSTATCOM. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 12(2):483–492. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2016.2516823
Chittora P, Singh A, Singh M (2017) Simple and efficient control of DSTATCOM in three phase four wire polluted grid system using MCCF-SOGI based controller. IET Gener Trans Distrib 12(5):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1049/ietgtd.2017.0901
Badoni M, Singh A, Singh B (2016) An implementation of variable step-size least-mean-square based control algorithm for DSTATCOM. Int Trans Electr Energ Syst 26:1540–1554. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2017.0901
Naidu TA, Arya SR, Al-Durra A, El-Fouly THM (2020) Comparative performance of dynamic voltage restorer using adaptive control algorithms with optimized error regulator gains. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst 2020:e12696. https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12696
Alam SJ, Arya SR (2020) Control of UPQC based on steady state linear Kalman filter for compensation of power quality problems. Chin J Electr Eng 6(2):52–65. https://doi.org/10.23919/CJEE.2020.000011
Patel SK, Arya SR, Maurya R (2019) Optimal step LMS-based control algorithm for DSTATCOM in distribution system. Electr Power Components Syst 47(8):675–691. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2019.1602797
Badoni M, Alka S, Bhim S, Hemant A (2020) Real-time implementation of active shunt compensator with adaptive SRLMMN control technique for power quality improvement in the distribution system. IET Gener Transm Distrib 14(8):1598–1606. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-gtd.2019.0929,10.1049/iet-gtd.2019.0929
Badoni M, Singh A, Singh B (2020) Power quality enhancement using Euclidean direction search based control technique. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(3):2231–2240. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2019.2905835
Shyu K, Yang M, Chen Y, Lin Y (2008) Model reference adaptive control design for a shunt active-power-filter system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2006.347931
Modi G, Kumar S, Singh B (2020) Improved Widrow-Hoff based adaptive control of multi objective PV-DSTATCOM system. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 56(2):1930–1939. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2019.2960732
Jayasankar VN, Vinatha U (2020) Backstepping controller with dual self-tuning filter for single-phase shunt active power filters under distorted grid voltage condition. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 56(6):7176–7184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2020.3025520
Trilochan P, Mrutyunjaya M, Kumar PA, Kumar SS (2016) Sparse LMS control algorithm for fuel cell based SAPF. In: 2016 IEEE Uttar Pradesh section international conference on electrical, computer and electronics engineering (UPCON), Varanasi, pp 72–77. https://doi.org/10.1109/UPCON.2016.7894627
Lee H-S, Yim S-H, Song W-J (2017) z2-proportionate diffusion LMS algorithm with mean square performance analysis. Sig Process 131:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.06.011
Li Z, Guan S (2018) Diffusion normalized Huber adaptive filtering algorithm. J Frankl Inst 355(8):3812–3825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.03.001
Waware M, Agarwal P (2012) Hardware realization of multilevel inverter-based active power filter. IETE J Res Sep 58(5):356–366. https://doi.org/10.4103/0377-2063.104152
Ray S, Gupta N, Gupta RA (2018) Hardware realization of proportional-resonant regulator based advanced current control strategy for cascaded H-bridge inverter-based shunt active power filter. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst 66:e2714. https://doi.org/10.1002/etep.2714
Petrus P (1999) Robust Huber adaptive filter. IEEE Trans Signal Process 47(4):1129–1133. https://doi.org/10.1109/78.752610
Ciobotaru M, Teodorescu R, Blaabjerg F (2006) A new single-phase PLL structure based on second order generalized integrator. In: 2006 37th IEEE power electronics specialists conference, Jeju, Korea (South), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/pesc.2006.1711988
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to Department of Science and Technology, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Simulation parameters
Grid supply voltage, Vs = 110 V, nonlinear load of resistance and inductance, R = 10Ω and L = 50mH, dc bus capacitance = 2500 μF, kp = 1.2, ki = 0.1, Vdc-ref = 200 V, interfacing inductor Lf = 3mH, switching frequency fsw = 10 kHz, sampling time = 4 μs.
1.2 Experimental parameters
Grid supply voltage, Vs = 110 V, 1-phase 2-leg diode rectifier as nonlinear load of resistance and inductance, R = 40Ω and L = 8mH, dc bus capacitance = 3000 μF, kp = 1.2, ki = 0.1, Vdc-ref = 200 V, interfacing inductor, Lf = 3mH, switching frequency fsw = 10 kHz, sampling time = 50 μs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, P., Singh, A. Nonlinear adaptive normalized Huber control algorithm for 5-level distribution static compensator. Electr Eng 104, 1635–1648 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01424-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01424-0