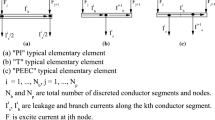
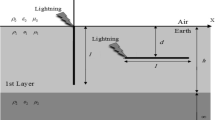
Abstract
In this article, transient behaviour of grounding systems buried in multilayer soil structure is analysed under the influence of lightning discharge. Vertical grounding rods, horizontal conductors and grounding grids are considered in the analysis. The computation of transient behaviour is performed in the frequency domain and obtained in time domain using inverse Fourier transform (IFT). The presented method is a hybrid approach based on PEEC technique that represents an equivalent circuit of grounding system buried in multilayer soil structure. Inductive, capacitive and conductive effects of grounding electrodes due to current leaking into the soil are also considered in the analysis. A procedure is adopted that simplifies the computation process of Sommerfeld method using small number of sample points over the grid. Also impulse impedance for horizontal grounding electrode, vertical rod and grounding grid is evaluated in two-layer soil structures. Simulated results are validated with the experimental and theoretical results reported in the literature and good agreements are found. Proposed method will help to improve the modelling of simple as well as complex grounding system buried in multilayer soil structure.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({Y}_{GC}\) :
-
Admittance matrix accounting for conductive and capacitive coupling
- \({Y}_{RL}\) :
-
Admittance matrix accounting internal impedance
- \({\omega}\) :
-
Angular frequency
- \( {{\phi}_{b}} \) :
-
Average branch potential
- \( \sigma _{i} \) :
-
Electric conductivity of ith layer of soil
- \({{h}_{1} }\) :
-
First layer soil depth
- \({{\tilde{G }}_{vv}^{A}, {\tilde{G }}_{zz}^{A},{\tilde{G }}_{zu}^{A}} \) :
-
Green’s function in spectral domain
- \({A}\) :
-
Incidence matrix of branch and node
- \({I}_{bl}\) :
-
Leakage current of branch
- \({I}_{nl}\) :
-
Leakage current of node
- \({G}_{A}\) :
-
Magnetic vector potential
- \({\phi }_{n}\) :
-
Nodal potential
- \({G}_{\phi }\) :
-
Scalar electric potential
- \({K}^{\phi }\) :
-
Scalar potential component
- \({h}_{2}\) :
-
Second layer soil depth
- \({\upmu }_{0}\) :
-
Vacuum permeability
- \({\upvarepsilon }_{0}\) :
-
Vacuum permittivity
References
Gua Z, Wu G, Chen S (2018) Transient behavior of common grounding grids to artificially triggered lightning. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 61(2):426–433
Mazzetti C (2003) Principles of protection of structures against lightning. In: Cooray V (ed) The lightning flash. IEE, London, U.K., pp 503–548
Sengar KP, Chandrasekaran K (2019) Designing of cost minimum substation grounding grid system using DE, SCA, and HDESCA techniques. IET Sci Meas Technol 13(9):1260–1267
Sengar KP, Chandrasekaran K (2018) Effects of cost optimised grid configuration on earthing system performance: a comparative assessment. IET Sci Meas Technol 14(5):610–620
Ramamoorty M, Narayanan BM, Parameswaran S, Mukhedkar D (1989) Transient performance of grounding grids. IEEE Trans Power Del 4(4):2053–2059
Feng Z, Wen X, Tong X, Lu H, Lan L, Xing P (2015) Impulse characteristics of tower grounding devices considering soil ionization by the time-domain difference method. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 30(4):1906–1913
Zhang B, He J, Lee JB, Cui X, Zhao Z, Zou J (2005) Numerical analysis of transient performance of grounding systems considering soil ionization by coupling moment method with circuit theory. IEEE Trans Magn 41(5):1440–1443
Liu Y, Theethayi N, Thottappillil R (2005) An engineering model for transient analysis of grounding system under lightning strikes: nonuniform transmission-line approach. IEEE Trans Power Del 20(2):722–730
Sunde ED (1968) Earth conduction effects in transmission systems. Bell Telephone Laboratories incorporated, New York, NY, USA
Qi L, Cui X, Zhao Z, Li H (2007) Grounding performance analysis of the substation grounding grids by finite element method in frequency domain. IEEE Trans Magn 43(4):1181–1184
Olsen RG, Grcev L (2015) Analysis of high frequency grounds: comparison of theory and experiment. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 51(6):4889–4899
Karami H, Sheshyekani K, Rachidi F (2017) Mixed-potential integral equation for full-wave modeling of grounding systems buried in a lossy multilayer stratified ground. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 59(5):1505–1513
Grcev L, Dawalibi F (1990) An electromagnetic model for transients in grounding systems. IEEE Trans Power Del 5(4):1773–1781
Popov M, Grcev L, Hoidalen HK, Gustavsen B, Terzija V (2015) Investigation of the overvoltage and fast transient phenomena on transformer terminals by taking into account the grounding effects. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 51(6):5218–5227
Alípio R, Visacro S (2014) Impulse efficiency of grounding electrodes: Effect of frequency-dependent soil parameters. IEEE Trans Power Del 29(2):716–723
Grcev L (2009) Time- and frequency-dependent lightning surge characteristics of grounding electrodes. IEEE Trans Power Del 24(4):2186–2196
Chen H, Du Y (2019) Lightning grounding grid model considering both the frequency dependent behavior and ionization phenomenon. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 61(1):157–165
Liew AC, Darveniza M (1974) Dynamic model of impulse characteristics of concentrated earths. IEE Proc 121(2):123–135
Elzowawi A, Haddad A, Griffiths H, Clark D (2015) Investigation of soil ionization propagation in two-layer soil samples. In: Proceedings of the International University Power Engineering Conference Stoke on Trent. pp. 1-5
He J, Zhang B, Zeng R, Zhang B (2011) Experimental studies of impulse breakdown delay characteristics of soil. IEEE Trans Power Del 26(3):1600–1607
Yutthagowith P, Ametani A, Nagaoka N, Baba Y (2011) Application of the partial element equivalent circuit method to analysis of transient potential rises in grounding systems. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 53(3):726–736
Chen H, Du Y (2019) Lightning grounding grid model considering both the frequency-dependent behavior and ionization phenomenon. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 61(1):157–165
Visacro S, Alipio R, Vale MHM, Pereira C (2011) The response of grounding electrodes to lightning currents: the effect of frequency-dependent soil resistivity and permittivity. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 53(2):401–406
De Conti A, Emdio MPS (2016) Extension of a modal domain transmission line model to include frequency-dependent ground parameters. Electric Power Syst Res 138:120–130
Tarasov A, Titov K (2013) On the use of the Cole-Cole equations in spectral induced polarization Geophys. J Int 195(1):352–356
Alipio R, Visacro S (2017) Time-domain analysis of frequency- dependent electrical parameters of soil. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 59(3):873–878
Seidel M, Tezkan B (2017) 1D Cole-Cole inversion of TEM transients influenced by induced polarization. J Appl Geophys 138:220–232
Li ZX, Rao SW (2018) Frequency domain soil parameters inversion of horizontally multilayered earth model with considering high-frequency field. IET Gen Trans Distrib 12(21):5690–5699
Li ZX, Rao SW (2019) Estimation of frequency domain soil parameters of horizontally multilayered earth by using Cole-Cole model based on the parallel genetic algorithm. IET Gen Trans Distrib 13(9):1746–1754
Ruehli AE (1974) Equivalent circuit models for three-dimensional multi conductor systems. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 22(3):216–221
Yutthagowith P, Ametani A, Nagaoka N, Baba Y (2009) Lightning induced voltage over lossy ground by a hybrid electromagnetic-circuit model method with Cooray-Rubinstein formula. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 51(4):975–985
Visacro S, Soares A (2005) HEM: a model for simulation of lightning related engineering problems. IEEE Trans Power 20(2):1206–1208
Araneo R, Celozzi S (2002) Extraction of equivalent lumped circuits of discontinuities using the finite-difference time-domain method. Proc IEEE Electromagn Compat Symp 1:119–122
Celozzi S, D’Amore M (1996) Magnetic field attenuation of nonlinear shields. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 38(3):318–326
Li Z-X, Yin Y, Zhang C-X, Zhang L-C (2014) A mathematical model for the transient lightning response from grounding systems. Prog Electromagn Res 57:47–61
Poljak D, Doric V (2006) Wire antenna model for transient analysis of simple grounding systems, part I: the vertical grounding electrode. Progress Electromagn Res 64:149–166
Kherif O, Chiheb S, Teguar M, Mekhaldi A, Harid N (2018) Time-domain modeling of grounding systems impulse response incorporating nonlinear and frequency-dependent aspects. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 60(4):907–916
Harrington RF (1968) Field computation by moment methods. Macmillan, New York
Cidras J, Otero AF, Garrido C (2000) Nodal frequency analysis of grounding systems considering the soil ionization effect. IEEE Trans Power Del 15(1):103–107
Li Z, Fan J (2008) Numerical calculation of grounding system in low frequency domain based on the boundary element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 73:685–705
Grover FW (1962) Inductance calculations [M]. Dover Publications, New York
Ruehli AE, Antonini G, Jiang LJ (2013) Skin-effect loss models for time-and frequency domain PEEC solver. Proc IEEE 101(2):451–472
Araneo R, Lovat G, Celozzi S (2011) Shielding effectiveness of periodic screens against finite high-impedance near-field sources. IEEE Trans Electromagn Compat 53(3):706–716
Kourkoulos V, Cangellaris AC (2006) Accurate approximation of Green’s functions in planar stratified media in terms of a finite sum of spherical and cylindrical waves. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 54(5):1568–1576
Merheim, B (1992) Modellierung von hochspannungs erdersystemen und vergleich mit messungen ihres dynamischen verhaltens,” (in English), Dipl.Ing. thesis, Diplomaufgabe, Inst. Allgemeine ochspannungstechnik, Technischen Hochschule, Aachen, Germany
Rochereau H, Merheim B (1993) Application of the transmission lines theory and EMTP program for modelisation of grounding systems in high frequency range. In: Collection de notes internes de la Direction des Etudes et Recherches Electricité de France. 93NR00059: 1–31
Markovski B, Grcev L, Arnautovski-Toseva V (2020) Fast and accurate transient analysis of large grounding systems in multilayer soil. IEEE Trans Power Deliv. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2020.2985926
Harid N, Griffiths H, Mousa S, Clark D, Robson S, Haddad A (2015) On the analysis of impulse test results on grounding systems. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 51(6):5324–5334
Grcev L (1996) Computer analysis of transient voltages in large grounding systems. IEEE Trans Power Del 11(2):8–823
Jamali M, Niasati M, Jazaeri M (2019) A two-layer soil model for the calculation of electrical parameters of grounding systems under lightning strikes. Electric Power Compon Syst 47(1):181–191
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the respected reviewers for their valuable suggestions to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengar, K.P., Chandrasekaran, K. Transient behaviour of grounding systems in multilayer soil under lightning strikes. Electr Eng 104, 1205–1218 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01367-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01367-6