Abstract
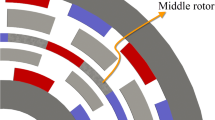
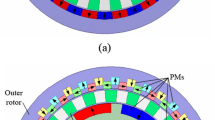
The dual-stage magnetically geared machine (DSMGM) has a high gear ratio. The first stage is a Vernier machine (VM), and the second stage is a coaxial magnetic gear (CMG). These two components share a common rotor (CR), and they are partially flux coupled. Two DSMGMs with different PM arrangements are fabricated and tested. The DSMGM-I with gear ratio 34 can work smoothly, while the DSMGM-II with gear ratio 14.875 is hard to be started up. The purpose of this paper is to reveal the failure of the DSMGM-II. Due to the magnetic flux coupling, there is a recessive CMG in DSMGM structure. The recessive CMG in DSMGM-II prototype is activated and results in high cogging torque and high torque ripple. The thickness of CR yoke controls the portion of flux penetrating through stator. When the thickness of CR yoke is large enough, the cogging torque of the DSMGM-II can be improved. Moreover, another effective method to improve the cogging torque is designing a flux barrier to magnetically decouple the VM and CMG components. For direct-drive robotic application, a DSMGM with Halbach-PM-array is presented. It has a high gear ratio, high torque capability and low cogging torque.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Komiyama H, Uchimura Y (2013) Contactless magnetic gear for robot control application. Electr Eng Jpn 184(4):32–41
Huang DJ, Yao LG, Li W, Zhang J (2017) Design and realization of a novel magnetic nutation drive for industry robotic wrist reducer. Ind Robot 44(1):58–63
Atallah K, Howe D (2001) A novel high-performance magnetic gear. IEEE Trans Magn 37(4):2844–2846
Jian L, Chau KT (2010) A coaxial magnetic gear with Halbach permanent magnet arrays. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 25(2):319–328
Uppalapati KK, Bomela WB, Bird JZ, Calvin MD, Wright JD (2014) Experimental evaluation of low-speed flux-focusing magnetic gearboxes. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 50(6):3637–3643
Uppalapati KK, Calvin MD, Wright JD, Pitchard J, Williams WB, Bird JZ (2018) A magnetic gearbox with an active region torque density of 239 N·m/L. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 54(2):1331–1338
Shen J, Li H, Hao H, Jin M (2017) A coaxial magnetic gear with consequent-pole rotors. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 32(1):267–275
Aiso K, Akatsu K, Aoyama Y (2019) A novel reluctance magnetic gear for high-speed motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 55(3):2690–2699
Chau KT, Zhang D, Jiang J, Liu C, Zhang Y (2007) Design of a magnetic-geared outer-rotor permanent-magnet brushless motor for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans Magn 43(6):2504–2506
Wang J, Atallah K, Carvley SD (2011) A magnetic continuously variable transmission device. IEEE Trans Magn 47(10):2815–2818
Shi Y, Wei J, Deng Z, Jian L (2017) A novel electric vehicle powertrain system supporting multi-path power flows: its architecture, parameter determination and system simulation. Energies 10:216
Atallah K, Rens J, Mezani S, Howe D (2008) A novel “pseudo” direct-drive brushless permanent magnet machine. IEEE Trans Magn 44(11):4349–4352
Wang LL, Shen JX, Luk PCK, Fei WZ, Wang CF, Hao H (2009) Development of a magnetic-geared permanent-magnet brushless motor. IEEE Trans Magn 45(10):4578–4581
Bai J, Liu J, Zheng P, Tong C (2019) Design and analysis of a magnetic-field modulated brushless double-rotor machine—part I: pole pair combination of stator, pm rotor and magnetic blocks. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(4):2540–2549
Ding S, Cheng M, Hang J, Sun L (2020) Segment design of the complementary magnetic-geared dual-rotor motor for hybrid electric vehicles. Electr Eng 102:2109–2122
Niu S, Sheng T, Zhao X, Zhang X (2019) Operation principle and torque component quantification of short-pitched flux-bidirectional-modulation machine. IEEE Access 7:136676–136685
Yu J, Liu C (2018) Design of a double-stator magnetless vernier machine for direct-drive robotics. IEEE Trans Magn 54(11):8105805
Zhu ZQ, Li HY, Deodhar R, Pride A, Sasaki T (2018) Recent developments and comparative study of magnetically geared machines. CES Trans Electr Mach Syst 2(1):13–22
Floris A, Serpi A, Porru M, Fois G, Damiano A (2018) Design of a double-stage magnetic gear for high-speed electric propulsion systems. In: Proceedings of XIIIth international conference on electrical machines, pp 670–676
Filippini M, Alotto P (2017) Coaxial magnetic gear design and optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(12):9934–9942
Zhang J, Zhang Q (2020) Design and analysis of a two-stage transmission magnetic-geared machine. IEEJ Trans Electr Electron Eng 15(1):151–156
Gerber S, Wang RJ (2018) Cogging torque definitions for magnetic gears and magnetically geared electrical machines. IEEE Trans Magn 54(4):8103209
Niguchi N, Hirata K (2012) Cogging torque analysis of magnetic gear. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(5):2189–2197
Niguchi N, Hirata K (2012) Cogging torque characteristics of magnetic-geared motor. COMPEL Int J Comput Math Elect Electron Eng 31(5):1470–1481
Fang H, Song R, Cai X (2019) Analysis and reduction of cogging torque for magnetic-gear pmsg used in wave energy conversion. In: 22nd international conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS), pp 1–6
Zhang J, Zhang Q (2020) Optimal PM arc ratio determination and vector-control of vernier machine with consequent pole rotor. Int J Appl Electromagn Mech 62:845–860
Liu G, Jiang Y, Ji J, Chen Q, Yang J (2014) Design and analysis of a new fault-tolerant magnetic-geared permanent-magnet motor. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 24(3):0503205
Johnson M, Gardner MC, Toliyat HA, Englebretson S, Ouyang W, Tschida C (2018) Design, construction, and analysis of a large-scale inner stator radial flux magnetically geared generator for wave energy conversion. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 54(4):3305–3314
Hao X, Zhu X, Zhang H (2015) Free vibration of the electromechanical integrated magnetic gear system. J VibroEng 17(3):1120–1132
Li X, Cheng M, Wang Y (2018) Analysis, design and experimental verification of a coaxial magnetic gear using stationary permanent magnet ring. IET Electr Power Appl 12(2):231–238
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 51575236, and in part by the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province under Grant KYCX18_1839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhang, Q. Analysis of cogging torque in dual-stage magnetically geared devices considering magnetic flux coupling. Electr Eng 103, 853–863 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01123-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01123-2