Abstract
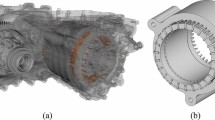
Axial field machines are available in a wide range of configurations. It has flexible design restrictions. Several research efforts were performed to discover machine performance and design horizons. However, the common design process of axial field machines depends on numerical field analysis, due to the lack of trusted and generalized analytical and/or empirical formulas especially for field distribution. This paper aims to present the essential analytic formulation for dimension selection. In addition, it provides the normalized relations between dimensions and airgap flux density using 3D-FEM as an alternative for empirical formulas. The paper describes a design procedure for coreless stator axial flux permanent magnet synchronous machine. Definite equations are derived to help the designer select the proper number of PM poles and concentrated coils to get balanced multi-phase voltage out of the generator. Moreover, the paper defines the necessary limitations of the span of the concentrated coil for a certain pole pitch to reduce the harmonic content of the output voltage waveform. The paper proposes a new approach for selecting the dimensions of the magnetic circuit using proposed data curves instead of struggling with the 3D-FEM along with its high time consumption and the need for high computational power. The loss calculations and the armature reaction are also investigated as a performance analysis criteria for the designed generator. The paper investigates the design for small-scale wind applications. The design procedure is validated using both 3D-FEM simulations and experimental results. The results show the consistency of the proposed procedure. The procedure is described and applied for a certain configuration and materials. However, it is solely extendable to several other configurations.























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(e_{\mathrm{cond}}\) :
-
Induced voltage in a single conductor (V)
- \(e_{\mathrm{coil}}\) :
-
Induced voltage in a single coil (V)
- \(e_{\mathrm{ph}}\) :
-
Induced voltage per phase (V)
- \(E_{\mathrm{ph}}\) :
-
RMS-induced voltage per phase (V)
- \(v_{\mathrm{ph}}\) :
-
Stator terminal voltage per phase (V)
- \(B_{\mathrm{ag}}\) :
-
Average flux density in the airgap (T)
- \(l_{\mathrm{cond}}\) :
-
Active length of the conductor (m)
- \(\omega _{\mathrm{m}}\) :
-
Angular speed of the rotor (rad/s)
- \(N_{\mathrm{rpm}}\) :
-
Speed of the rotor (r/min)
- \(r_{\mathrm{m}}\) :
-
Mean radius of the rotor disc (m)
- \(T_{\mathrm{coil}}\) :
-
Number of turns in each coil
- q :
-
Number of coils per phase
- \(P_{\mathrm{in}}\) :
-
Input power (kW)
- \(P_{\mathrm{o}}\) :
-
Output power (kW)
- T :
-
Developed torque (Nm)
- m :
-
Number of phases
- cos(\(\phi \)):
-
Power factor
- \(i_{\mathrm{ph}}\) :
-
Induced current per phase (A)
- \(\eta \) :
-
Machine overall efficiency
- \(D_{\mathrm{in}}\) :
-
Inner diameter of rotor disc (m)
- \(D_{\mathrm{o}}\) :
-
Outer diameter of rotor disc (m)
- \(r_{\mathrm{i}}\) :
-
Inner radius of rotor disc (m)
- \(r_{\mathrm{o}}\) :
-
Outer radius of rotor disc (m)
- \(\tau \) :
-
Pole arc-to-pole pitch ratio
- \(\delta \) :
-
Current density in stator winding (\(\hbox {A/m}^{2}\))
- \(a_{\mathrm{c}}\) :
-
Cross-sectional area of stator conductor (\(\hbox {m}^{2}\))
- \(l_{\mathrm{tot}}\) :
-
Total length of stator conductors (m)
- \(N_{\mathrm{c}}\) :
-
Number of stator coils
- p :
-
Number of PM poles
- \(h_{\mathrm{m}}\) :
-
Magnet height (mm)
- \(l_{\mathrm{m}}\) :
-
Magnet length (mm)
- \(w_{\mathrm{m}}\) :
-
Magnet width (mm)
- \(h_{\mathrm{y}}\) :
-
Height of rotor yoke (mm)
References
Saifee A, Mittal A (2014) Design of novel axial flux permanent magnet generator (AFPMG) for wind energy applications. Int J Electr Electr Eng Res 4(3):35–42
Jo W, Lee I, Cho Y, Koo D, Chun Y (2007) Design and analysis of axial flux permanent magnet synchronous machine. J Electr Eng Technol 2(1):61–67
Price G, Batzel T, Comanescu M, Muller B (2008) Design and testing of a permanent magnet axial flux wind power generator. In: Proceedings of IAJC-IJME international conference, p 190
Huang S, Luo J, Leonardi F, Lipo T (1999) A comparison of power density for axial flux machines based on general purpose sizing equations. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 14(2):185–192
Gerlando A, Foglia G, Iacchetti M, Perini R (2011) Axial flux PM machines with concentrated armature winding: design analysis and test validation of wind energy generators. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(9):3795–3805
Choi J, Lee S, Ko K, Jang S (2011) Improved analytical model for electromagnetic analysis of axial flux machines with double-sided permanent magnet rotor and coreless stator winding. IEEE Trans Magn 47(10):2760–2763
Kamper M, Wang R, Rossouw G (2008) Analysis and performance of axial flux permanent-magnet machine with air-cored nonoverlapping concentrated stator windings. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 44(5):1495–1504
Mahmoudi A, Rahim N, Ping H (2012) Axial-flux permanent-magnet motor design for electric vehicle direct drive using sizing equation and finite element analysis. Progr Electromagn Res 22:467–496
Wang R, Kamper MJ, Van der Westhuizen K, Gieras JF (2005) Optimal design of a coreless stator axial flux permanent-magnet generator. IEEE Trans Magn 41(1):55–64
Virtic P, Vrazic M, Papa G (2016) Design of an axial flux permanent magnet synchronous machine using analytical method and evolutionary optimization. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 31(1):150–158
Chan TF, Lai LL (2007) An axial-flux permanent-magnet synchronous generator for a direct-coupledwind-turbine system. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 22(1):9
Fasil M, Mijatovic N, Jensen BB, Holboll J (2016) Finite-element model-based design synthesis of axial flux PMBLDC motors. IEEE Trans Appl Supercond 26(4):1–5
Kim Ju Hyung, Wooyoung Choi, Sarlioglu Bulent (2016) Closed-form solution for axial flux permanent-magnet machines with a traction application study. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 52(2):1775–1784
Gieras JF, Wang R-J, Kamper MJ (2004) Axial flux permanent magnet brushless machines. Norwell, MA: Kluwer, 1-4020- 2661-7(HB)
Carter GW (1954) Electromagnetic field in its engineering aspects. Longmans
Serway Raymond A (1986) Physics for scientists and engineers, 2nd edn. Saunders College Publishing, Orlando, p 202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almozayen, M.A., El-Nemr, M.K. & Rashad, E.M. Design procedure of coreless stator PM axial field synchronous machine for small-scale wind applications. Electr Eng 100, 877–894 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0540-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0540-4