Abstract
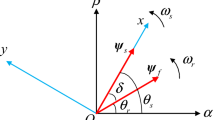
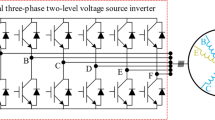
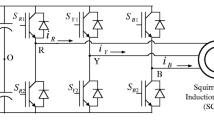
This paper proposes a deadbeat controller applied to direct torque control strategy for a three-phase induction motor. The deadbeat control method uses the discretized dynamic model of the machine to calculate the theoretical stator voltage vector required to reach the references of torque and flux in a single switching period. In this proposal controller, it is used the stator flux and current vectors in the machine model. The induction motor is powered by a three-phase inverter, which is modulated through a vector modulation technique. The experimental results are presented to validate the proposed controller, including low-speed operation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siemens (2003) Seminarios tecnicos 2003, engenheiros e projetistas. Siemens, Technical Report
Vitorino M, Beltrao de Rossiter Correa M, Jacobina C, Lima A (2011) An effective induction motor control for photovoltaic pumping. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(4):1162–1170
Filho AJS, Ruppert E (2010) A deadbeat active and reactive power control for doubly-fed induction generators. Electr Power Compon Syst 38(5):592–602
Costa F, Filho AS, Capovilla C, Casella I (2014) Morphological filter applied in a wireless deadbeat control scheme within the context of smart grids. Electr Power Syst Res 107:175–182
Takahashi I, Noguchi T (1986) A new quick-response and high-efficiency control strategy of an induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl IA-22(5):820–827
Depenbrock M (1988) Direct self-control (dsc) of inverter-fed induction machine. IEEE Trans Power Electron 3:420–429
Blaschke F (1972) The principle of field orientation as applied to the new transvector closed-loop control system for rotating field machines. Siemens Rev 39(5):217–220
Kang J-K, Sul S-K (1999) New direct torque control of induction motor for minimum torque ripple and constant switching frequency. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 35:1076–1082
Casadei D, Serra G, Tani A, Zarri L (2013) Direct torque control for induction machines: a technology status review. In: IEEE workshop on electrical machines design control and diagnosis (WEMDCD) 2013, pp 117–129
Rodriguez J, Pontt J, Silva C, Kouro S, Miranda H (2004) A novel direct torque control scheme for induction machines with space vector modulation. In: Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Aachen, pp 1392–1397
Stojic D, Vukosavic S (2005) A new induction motor drive based on the flux vector acceleration method. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 20(1):173–180
Shyu K-K, Lin J-K, Pham V-T, Yang M-J, Wang T-W (2010) Global minimum torque ripple design for direct torque control of induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(9):3148–3156
Zhang Z, Tang R, Bai B, Xie D (2010) Novel direct torque control based on space vector modulation with adaptive stator flux observer for induction motors. IEEE Trans Magn 46(8):3133–3136
Zaid S, Mahgoub O, El-Metwally K (2010) Implementation of a new fast direct torque control algorithm for induction motor drives. Electr Power Appl IET 4(5):305–313
Kumar T, Rao S (2010) Direct torque control method for induction motor drives based on modified amplitude and angle decoupled control of stator flux. In: 2010 Joint international conference on power electronics, drives and energy systems (PEDES) 2010 Power India, pp 1–6
Vinay Kumar T, Srinivasa Rao S (2011) Direct load angle control of three phase induction motor drives. In: 2011 IEEE ninth international conference on power electronics and drive systems (PEDS), pp 513–516
Metidji B, Taib N, Baghli L, Rekioua T, Bacha S (2012) Low-cost direct torque control algorithm for induction motor without ac phase current sensors. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(9):4132–4139
Geyer T (2013) Model predictive direct torque control: derivation and analysis of the explicit control law. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 49(5):2146–2157
Hafeez M, Uddin M, Rahim N, Hew W (2013) Self–tuned NFC and adaptive torque hysteresis based DTC scheme for IM drive. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 50(2):1410–1420
Habetler T, Profumo F, Pastorelli M, Tolbert L (1992) Direct torque control of induction machines using space vector modulation. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 28(5):1045–1053
Kenny B, Lorenz R (2003) Stator- and rotor-flux-based deadbeat direct torque control of induction machines. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 39(4):1093–1101
Neves F, Menezes B, Silva S (2004) A stator flux oriented induction motor drive with deadbeat direct torque and flux control. Electr Power Compon Syst 32:1319–1330
West N, Lorenz R (2009) Digital implementation of stator and rotor flux-linkage observers and a stator-current observer for deadbeat direct torque control of induction machines. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 45(2):729–736
Xu W, Lorenz R (2014) Reduced parameter sensitivity stator flux linkage observer in deadbeat-direct torque and flux control for IPMSMS. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 50(4):2626–2636
Vas P (1998) Sensorless vector and direct torque control. Oxford University Press Inc, Oxford. ISBN 0198564651
Golnaraghi F, Kuo BC (2009) Automatic control systems. Wiley, New York
Filho AJS (2007) O controlador complexo aplicado ao controle vetorial do motor de inducao. Master’s thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas
Bim E (2009) Mequinas Eletricas e Acionamento. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hu J, Wu B (1998) New integration algorithms for estimating motor flux over wide speed range. IEEE Trans Power Electron 13(5):969–977
Filho AJS, Filho ER (2009) The complex controller for three-phase induction motor direct torque control. SBA Mag 20:256–262
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by FAPESP and CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altuna, J.A.T., Jacomini, R.V., Puma, J.L.A. et al. Deadbeat controller applied to induction motor direct torque control with low-speed operation. Electr Eng 100, 123–128 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0494-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-016-0494-y