Abstract
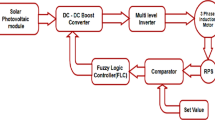
This paper describes a new control method for the integrated of six current rectifiers—seven-level diode-clamped inverter feeding induction motor considering dc-link capacitors voltage balancing problem. The proposed controller uses type-2 fuzzy systems to compensate the fluctuations of capacitors voltage, draw a sinusoidal line current with nearly unity power factor, and ensure the motor speed control. The performance of dc-link voltages control is evaluated in comparison to the conventional PI control scheme. The overall system and the control algorithm are presented and a set of simulations is carried out in order to prove the good performances of the proposed solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai JS and Peng FZ (1996). Multilevel converters—a new breed of power converters. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 32: 509–517
Tolbert LM, Peng FZ and Habetler TG (1999). Multilevel converters for large electric drives. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 35: 36–44
Sinha G and Lipo T (2000). Four-level inverter based drive with a passive front end. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 15: 285–294
Zhou D and Rouad DG (2001). Experimental comparisons of space vector neutral point balancing strategies for three-level topology. IEEE Trans Power Electron 16: 872–879
Marchesoni M and Tenca P (2002). Diode-clamped multilevel converters: a practicable way to balance dc-link voltages. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49: 752–765
Pan Z and Peng FZ (2006). Harmonics optimization of the voltage balancing control for multilevel converter/inverter systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron 21: 211–218
Chen Y, Mwinyiwiwa B, Wolanski Z and Ooi BT (2000). Unified power flow controller (UPFC) based on chopper stabilized diode-clamped multilevel converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 15: 258–267
Rodriguez JR, Dixon JW, Espinoza JR, Pontt J and Lezana P (2005). PWM regenerative rectifiers: state of the art. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52: 5–22
Komurcugil H and Kukrer O (1998). Lyapunov-based control for three-phase PWM AC/DC voltage-source converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 13: 801–813
Jung J, Lim S and Nam K (1999). A feedback linearizing control scheme for PWM converter-inverter having a very small dc-link capacitor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 35: 1124–1131
Lee DC, Lee GM and Lee KD (2000). DC-bus voltage control of three-phase AC/DC PWM converters using feedback linearization. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 36: 826–833
Perez M, Ortega R and Espinoza JR (2004). Passivity-based PI control of switching power converters. IEEE Trans Contr Syst Tech 12: 881–890
Chibani R and Berkouk EM (2005). Five-level PWM current rectifier–five-level NPC VSI–permanent magnet synchronous machine cascade. Euro Phys J Appl Phys 30: 1–14
Jasinski M, Liserre M, Blaaberg F, Cishowlas M (2002) Fuzzy logic current controller for PWM rectifiers. In Proceedings of IECON 1300–1305
Cecati C, Dell’Aquilla A, Liserre M and Ometto A (2003). A fuzzy-logic-based controller for active rectifier. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 39: 105–112
Cecati C, Dell’Aquilla A, Lecci A and Liserre M (2005). Implementation issues of a fuzzy-logic-based three-phase active rectifier employing only voltage sensors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52: 378–385
Zadeh LA (1975). The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Inf Sci 8: 199–249
Karnik NN, Mendel JM and Liang Q (1999). Type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 7: 643–658
Liang Q and Mendel JM (2000). Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8: 535–550
Liang Q, Karnik NN and Mendel JM (2000). Connection admission control in ATM networks using survey-based type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C 30: 329–339
Lin PZ, Lin CM, Hsu CF and Lee TT (2005). Type-2 fuzzy controller using a sliding–mode approach for application to DC–DC converters. IEE Proc. Electr Power Appl 152: 1482–1488
Vas P (1994). Vector Control of AC machines. Oxford Science publication, Oxford
Leonhard W (1990). Control of electrical drives, 2nd ed. Springer, Germany
Peresada S, Tilli A and Tonielli A (2003). Theoretical and experimental comparison of indirect field-oriented controllers for induction motors. IEEE Tans Power Electron 18: 151–163
Heber B, Xu L and Tang Y (1997). Fuzzy logic enhanced speed control of an indirect field-oriented induction machine drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 12: 772–778
Zhen L and Xu L (1998). On-line fuzzy tuning of indirect field-oriented induction machine drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 13: 134–141
Cupertino F, Lattanzi A and Salvatore L (2000). A new fuzzy logic-based controller design method for DC and AC impressed-voltage drives. IEEE Trans Power Electron 15: 974–982
Zhao J, Bose BK (2002) Evaluation of membership functions for fuzzy logic controlled induction motor drive. In: ICON 02, IEEE 28th annual conference of the industrial electronics society, pp 229–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barkati, S., Berkouk, E.M. & Boucherit, M.S. Application of type-2 fuzzy logic controller to an induction motor drive with seven-level diode-clamped inverter and controlled infeed. Electr Eng 90, 347–359 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-007-0087-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-007-0087-x