Abstract:
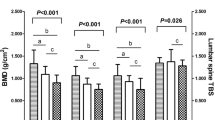
Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) may result in greater cortical than trabecular bone loss. Ultrasound is able to predict osteoporotic fracture risk independent of densitometric measurements, but little is known about the changes in ultrasound variables with PHPT. The aim of our study was to examine the effect of PHPT on ultrasound variables and bone density measurements at cortical (hand) and trabecular (lumbar spine and heel) sites, and to evaluate their reversibility following surgical treatment. We recruited 25 postmenopausal women diagnosed with PHPT ages 51–76 years (mean 62 years) and 95 postmenopausal controls ages 57–80 years (mean 67 years). Measurements were made at baseline and 1 year. Speed of sound (SOS) and broadband ultrasound attenuation (BUA) of the heel were measured using the Lunar Achilles (LA+) and McCue CUBA Clinical (CC). Amplitude-dependent speed of sound (AD-SoS) and ultrasound bone profile index (UBPI) of the fingers were measured using the IGEA DBM Sonic. Bone mineral density (BMD) of the hand and lumbar spine (LS) were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). At baseline, hand BMD, LS BMD and heel BUA were significantly lower and finger UBPI significantly higher in the PHPT patients compared with controls (p<0.001). There were no differences in Stiffness Index, heel SOS or finger AD-SoS between control and PHPT subjects. At 1 year postoperatively, there was a mean (±SD) increase in LS and hand BMD of 3 ± 1% (p<0.01). BUA at the heel increased (11 ± 5%, p<0.001), and UBPI of the fingers decreased (17 ± 7%, p<0.001) probably reflecting different modes of attenuation in trabecular (scattering) and cortical (absorption) bone. Stiffness Index, SOS of the heel and AD-SoS of the fingers did not change. BUA, UBPI and BMD returned towards normal postmenopausal values following surgery. There were no changes in BMD or QUS variables at 1 year in the control group. Quantitative ultrasound (QUS) measurements provide different information about bone structure than densitometric measurements and cannot be regarded as simply reflecting bone density. With further research the combined use of BMD and QUS could improve the assessment of skeletal status in patients with PHPT before and after surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 September 2001 / Accepted: 31 January 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingle, B., Thomas, W. & Eastell, R. Differential Effects of Primary Hyperparathyroidism on Ultrasound Properties of Bone . Osteoporos Int 13, 572–578 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980200075
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980200075