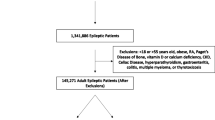
Abstract
Summary
People with epilepsy who take certain medications are at risk for developing osteoporosis and fractures of the vertebrae that commonly go undiagnosed. By using technology available in a bone density scan, we observed at least one fracture in many subjects with bone density in the normal and osteopenic range.
Purpose/Introduction
Chronic use of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), both enzyme-inducing (phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and primidone) and non-enzyme-inducing (i.e., valproate), is recognized as a cause of secondary osteoporosis. Vertebral compression fractures (VF) are the most common type of osteoporotic fractures and may confer an increased risk of future hip, wrist, and vertebral fractures. Vertebral compression fractures in the general population are frequently asymptomatic, and under-diagnosed. The purpose of this study is to describe the prevalence of VF in a cohort of male veterans with epilepsy on chronic AEDs.
Methods
The cohort for this study consisted of 146 male veterans who carried a diagnosis of epilepsy and were chronic users of AEDs known to cause osteoporosis (phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone, and valproate). Chronic AED use was defined as receiving an AED for at least 2 years. Subjects were previously seen in the osteoporosis clinic and had been evaluated by a dual-energy X-Ray absormetry (DXA) instrument including morphometric studies following a standard vertebral fracture assessment (VFA) protocol during the same DXA imaging acquisition session.
Results
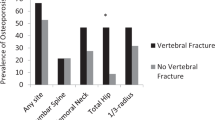
The mean age was 63 years. Low bone mineral density defined as osteoporosis or osteopenia was observed in 29% and 43% respectively. We observed at least one VF in 41 % of the subjects who had normal BMD, 54% in the osteopenic range, and 75% in the osteoporotic range.
Conclusions
By performing a VFA in addition to standard bone densitometric studies, we disclosed a large prevalence of compression fractures in individuals with epilepsy chronically treated with AEDs who had BMDs in the normal and osteopenic ranges. The addition of VFA or other imaging methods to evaluate VF should be included in the evaluation of bone health in individuals with epilepsy receiving AEDs since it may modify treatment recommendations to prevent future osteoporotic fractures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Espinosa PS, Perez DL, Abner E, Ryan M (2011) Association of antiepileptic drugs, vitamin D, and calcium supplementation with bone fracture occurrence in epilepsy patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 113:548–551
Meier C, Kraenzlin ME (2011) Antiepileptics and bone health. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 3:235–243
Beerhorst K, Schouwenaars FM, Tan IY, Aldenkamp AP (2012) Epilepsy: fractures and the role of cumulative antiepileptic drug load. Acta Neurol Scand 125:54–59
Ensrud KE, Walczak TS, Blackwell T, Ensrud ER, Bowman PJ, Stone KL (2004) Antiepileptic drug use increases rates of bone loss in older women: a prospective study. Neurology 62:2051–2057
Ensrud KE, Walczak TS, Blackwell TL, Ensrud ER, Barrett-Connor E, Orwoll ES (2008) Antiepileptic drug use and rates of hip bone loss in older men: a prospective study. Neurology 71:723–730
Cosman F (2017) Spine fracture prevalence in a nationally representative sample of US women and men aged >/=40 years: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2014---supplementary presentation. Osteoporos Int 28:2319–2320
Ginther JP, Ginther AW, Brodersen LD (2017) Adding Vfa to Dxa identifies fracture risk in a way not duplicated by other measures. Endocr Pract 23:1375–1378
McClung M, Harris ST, Miller PD, Bauer DC, Davison KS, Dian L, Hanley DA, Kendler DL, Yuen CK, Lewiecki EM (2013) Bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis: benefits, risks, and drug holiday. Am J Med 126:13–20
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki EM, Tanner B, Randall S, Lindsay R (2014) Clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 25:2359–2381
Lazzari AA, Dussault PM, Thakore-James M, Gagnon D, Baker E, Davis SA, Houranieh AM (2013) Prevention of bone loss and vertebral fractures in patients with chronic epilepsy--antiepileptic drug and osteoporosis prevention trial. Epilepsia 54:1997–2004
Jin YZ, Lee JH, Xu B, Cho M (2019) Effect of medications on prevention of secondary osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture, non-vertebral fracture, and discontinuation due to adverse events: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20:399
Lewiecki EM (2010) Bone densitometry and vertebral fracture assessment. Curr Osteoporos Rep 8:123–130
Bazzocchi A, Diano D, Battista G, Albisinni U, Rossi C, Guglielmi G (2012) New dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry equipment in the assessment of vertebral fractures: technical limits and software accuracy. Skelet Radiol 41:823–829
Binkley N, Krueger D, Gangnon R, Genant HK, Drezner MK (2005) Lateral vertebral assessment: a valuable technique to detect clinically significant vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int 16:1513–1518
El Maghraoui A, Mounach A, Rezqi A, Achemlal L, Bezza A, Ghozlani I (2012) Vertebral fracture assessment in asymptomatic men and its impact on management. Bone 50:853–857
Schousboe JT, Vokes T, Broy SB, Ferrar L, McKiernan F, Roux C, Binkley N (2008) Vertebral Fracture Assessment: the 2007 ISCD Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 11:92–108
Vokes TJ, Dixon LB, Favus MJ (2003) Clinical utility of dual-energy vertebral assessment (DVA). Osteoporos Int 14:871–878
Zeytinoglu M, Jain RK, Vokes TJ (2017) Vertebral fracture assessment: enhancing the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of osteoporosis. Bone 104:54–65
Li Y, Yan L, Cai S, Wang P, Zhuang H, Yu H (2018) The prevalence and under-diagnosis of vertebral fractures on chest radiograph. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 19:235
Kendler DL, Bauer DC, Davison KS et al (2016) Vertebral fractures: clinical importance and management. Am J Med 129:221.e221–221.e210
Schousboe JT, Lix LM, Morin SN, Derkatch S, Bryanton M, Alhrbi M, Leslie WD (2019) Vertebral fracture assessment increases use of pharmacologic therapy for fracture prevention in clinical practice. J Bone Miner Res 34:2205–2212
Kanis JA, Oden A, Johansson H, Borgstrom F, Strom O, McCloskey E (2009) FRAX and its applications to clinical practice. Bone 44:734–743
Steuart Richards J, Lazzari AA, Teves Qualler DA, Desale S, Howard R, Kerr GS (2014) Validation of the osteoporosis self-assessment tool in US male veterans. J Clin Densitom 17:32–37
Buehring B, Krueger D, Checovich M, Gemar D, Vallarta-Ast N, Genant HK, Binkley N (2010) Vertebral fracture assessment: impact of instrument and reader. Osteoporos Int 21:487–494
Pearson D, Horton B, Green DJ, Hosking DJ, Goodby A, Steel SA (2006) Vertebral morphometry by DXA: a comparison of supine lateral and decubitus lateral densitometers. J Clin Densitom 9:295–301
Vokes T, Bachman D, Baim S, Binkley N, Broy S, Ferrar L, Lewiecki EM, Richmond B, Schousboe J (2006) Vertebral fracture assessment: the 2005 ISCD Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 9:37–46
Genant HK, Jergas M (2003) Assessment of prevalent and incident vertebral fractures in osteoporosis research. Osteoporos Int 14 Suppl 3:S43–S55
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Genant HK (1997) Assessment of vertebral fractures in osteoporosis research. J Rheumatol 24:1212–1214
Zmuda JM, Cauley JA, Glynn NW, Finkelstein JS (2000) Posterior-anterior and lateral dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of vertebral osteoporosis and bone loss among older men. J Bone Miner Res 15:1417–1424
Schousboe JT (2016) Epidemiology of Vertebral Fractures. J Clin Densitom 19:8–22
Souverein PC, Webb DJ, Petri H, Weil J, Van Staa TP, Egberts T (2005) Incidence of fractures among epilepsy patients: a population-based retrospective cohort study in the General Practice Research Database. Epilepsia 46:304–310
Beerhorst K, Tan IY, De Krom M, Verschuure P, Aldenkamp AP (2013) Antiepileptic drugs and high prevalence of low bone mineral density in a group of inpatients with chronic epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand 128:273–280
Lotfizadeh HTM, Montouris G (2004) Bone health in males with epilepsy scientific meeting. American Society of Epilepsy, New Orleans
Cosman F, Krege JH, Looker AC, Schousboe JT, Fan B, Sarafrazi Isfahani N, Shepherd JA, Krohn KD, Steiger P, Wilson KE, Genant HK (2017) Spine fracture prevalence in a nationally representative sample of US women and men aged >/=40 years: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2013-2014. Osteoporos Int 28:1857–1866
Waterloo S, Ahmed LA, Center JR, Eisman JA, Morseth B, Nguyen ND, Nguyen T, Sogaard AJ, Emaus N (2012) Prevalence of vertebral fractures in women and men in the population-based Tromso Study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 13:3
Popp AW, Buffat H, Eberli U, Lippuner K, Ernst M, Richards RG, Stadelmann VA, Windolf M (2014) Microstructural parameters of bone evaluated using HR-pQCT correlate with the DXA-derived cortical index and the trabecular bone score in a cohort of randomly selected premenopausal women. PLoS One 9:e88946
Bastos LA, Tavares DRB, Okazaki JEF, Gazoni FM, Fonte FK, Maeda SS, Lazaretti-Castro M, Cendoroglo MS, Santos FC (2019) High prevalence of vertebral fracture in a very elderly community-dwelling: "longevous project". J Clin Densitom 23:497–502
Hagemann G, Lemieux L, Free SL, Krakow K, Everitt AD, Kendall BE, Stevens JM, Shorvon SD (2002) Cerebellar volumes in newly diagnosed and chronic epilepsy. J Neurol 249:1651–1658
Shorvon SD, Reynolds EH (1982) Anticonvulsant peripheral neuropathy: a clinical and electrophysiological study of patients on single drug treatment with phenytoin, carbamazepine or barbiturates. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:620–626
Engelke K (2012) Assessment of bone quality and strength with new technologies. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 19:474–482
Dussault PM, Lazzari AA (2017) Epilepsy and osteoporosis risk. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 24:395–401
Delmas PD, van de Langerijt L, Watts NB, Eastell R, Genant H, Grauer A, Cahall DL (2005) Underdiagnosis of vertebral fractures is a worldwide problem: the IMPACT study. J Bone Miner Res 20:557–563
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Linda Niesner, PharmD for proof reading and assisting with editing the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Philip M. Dussault, David McCarthy, Samuel A. Davis, Manisha Thakore-James, and Antonio A. Lazzari declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
• Vertebral compression fractures are frequently underdiagnosed and are the most common type of osteoporotic fracture and known to confer an increased risk of future hip, wrist, and vertebral fractures.
• By performing a VFA, we disclosed a large prevalence of compression fractures in male veterans with epilepsy chronically treated with AEDs.
• Detection of previously undiagnosed compression fractures may expedite a more focused treatment with the goal of improving bone health in the epileptic patient population.
• Based on these results, we recommend performing a lateral vertebral assessment in addition to bone densitometric studies when evaluating bone health in people with chronic epilepsy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dussault, P., McCarthy, D., Davis, S. et al. High prevalence of vertebral fractures in seizure patients with normal bone density receiving chronic anti-epileptic drugs. Osteoporos Int 32, 2051–2059 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-021-05926-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-021-05926-2