Abstract
Summary
This study investigated the alterations of mineral metabolism in patients with Graves’ disease (GD) who achieved euthyroidism. They had higher fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and phosphorus as compared with healthy subjects. Serum FGF23 was negatively correlated with serum phosphorus. These indicated abnormal mineral metabolism even after 1.6 years of euthyroid status.
Introduction
FGF23 is involved in the mineral homeostasis, especially the regulation of serum phosphorus. Graves’ disease (GD) is associated with accelerated bone turnover, hyperphosphatemia, and elevated serum FGF23. Evidence suggested that serum FGF23 decreased after a 3-month treatment of GD. However, it remains unclear whether serum FGF23, serum phosphorus, and other markers of mineral metabolism will be normalized after euthyroid status achieved.
Methods
A total of 62 patients with euthyroid GD and 62 healthy control subjects were enrolled, and the median duration of euthyroid status was 1.6 years. Endocrine profiles including thyroid function test, autoantibodies, serum FGF23, and bone turnover markers were obtained and compared between the two groups.
Results
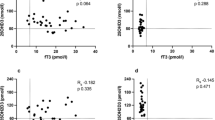
Euthyroid GD patients had significantly higher serum FGF23 and phosphorus, and lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) levels as compared with the control group. Serum FGF23 was significantly and negatively correlated with phosphorus level after adjusted for age, gender, calcium, iPTH, and 25(OH)D in the euthyroid GD group.
Conclusion
Serum phosphorus and FGF23 levels remain higher in GD patients even after euthyroid status has been achieved for a median of 1.6 years. Serum FGF23 was negatively correlated with serum phosphorus in euthyroid GD patients. Underlying mechanisms warrant further investigations.
Trial registration
Registration number: NCT01660308 and NCT02620085

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith TJ, Hegedus L (2016) Graves’ disease. N Engl J Med 375 (16):1552–1565. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1510030
Mirza F, Canalis E (2015) Management of endocrine disease: secondary osteoporosis: pathophysiology and management. Eur J Endocrinol 173(3):R131–R151. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-15-0118
Brandt F, Thvilum M, Almind D, Christensen K, Green A, Hegedus L, Brix TH (2013) Morbidity before and after the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism: a nationwide register-based study. PLoS One 8(6):e66711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066711
Cho SW, Bae JH, Noh GW, Kim YA, Moon MK, Park KU, Song J, Yi KH, Park do J, Chung JK, Cho BY, Park YJ (2015) The presence of thyroid-stimulation blocking antibody prevents high bone turnover in untreated premenopausal patients with Graves’ disease. PLoS One 10(12):e0144599. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144599
Lucidarme N, Ruiz JC, Czernichow P, Leger J (2000) Reduced bone mineral density at diagnosis and bone mineral recovery during treatment in children with Graves’ disease. J Pediatr 137(1):56–62. https://doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2000.106219
Park SE, Cho MA, Kim SH, Rhee Y, Kang ES, Ahn CW, Cha BS, Lee EJ, Kim KR, Lee HC, Lim SK (2007) The adaptation and relationship of FGF-23 to changes in mineral metabolism in Graves’ disease. Clin Endocrinol 66(6):854–858. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02824.x
Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L (2003) Hyperthyroidism, bone mineral, and fracture risk--a meta-analysis. Thyroid 13(6):585–593. https://doi.org/10.1089/105072503322238854
Yamashita H, Yamazaki Y, Hasegawa H, Yamashita T, Fukumoto S, Shigematsu T, Kazama JJ, Fukagawa M, Noguchi S (2005) Fibroblast growth factor-23 in patients with Graves’ disease before and after antithyroid therapy: its important role in serum phosphate regulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(7):4211–4215. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-2498
Pantazi H, Papapetrou PD (2000) Changes in parameters of bone and mineral metabolism during therapy for hyperthyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(3):1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.85.3.6457
Burch HB, Cooper DS (2015) Management of Graves disease: a review. JAMA 314(23):2544–2554. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.16535
Ma WY, Yang CY, Shih SR, Hsieh HJ, Hung CS, Chiu FC, Lin MS, Liu PH, Hua CH, Hsein YC, Chuang LM, Lin JW, Wei JN, Li HY (2013) Measurement of waist circumference: midabdominal or iliac crest? Diabetes Care 36(6):1660–1666. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-1452
Hung CS, Lee JK, Yang CY, Hsieh HR, Ma WY, Lin MS, Liu PH, Shih SR, Liou JM, Chuang LM, Chen MF, Lin JW, Wei JN, Li HY (2014) Measurement of visceral fat: should we include retroperitoneal fat? PLoS One 9(11):e112355. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112355
Yu TY, Wei JN, Kuo CH, Liou JM, Lin MS, Shih SR, Hua CH, Hsein YC, Hsu YW, Chuang LM, Lee MK, Hsiao CH, Wu MS, Li HY (2017) The impact of gastric atrophy on the incidence of diabetes. Sci Rep 7:39777. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39777
Chong WH, Molinolo AA, Chen CC, Collins MT (2011) Tumor-induced osteomalacia. Endocr Relat Cancer 18(3):R53–R77. https://doi.org/10.1530/erc-11-0006
Sanders J, Oda Y, Roberts S, Kiddie A, Richards T, Bolton J, McGrath V, Walters S, Jaskolski D, Furmaniak J, Smith BR (1999) The interaction of TSH receptor autoantibodies with 125I-labelled TSH receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(10):3797–3802. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.10.6071
Cabral HW, Andolphi BF, Ferreira BV, Alves DC, Morelato RL, Chambo AF, Borges LS (2016) The use of biomarkers in clinical osteoporosis. Rev Assoc Med Bras 62(4):368–376. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.62.04.368
Cardoso LF, Maciel LM, Paula FJ (2014) The multiple effects of thyroid disorders on bone and mineral metabolism. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 58(5):452–463
Alcalde AI, Sarasa M, Raldua D, Aramayona J, Morales R, Biber J, Murer H, Levi M, Sorribas V (1999) Role of thyroid hormone in regulation of renal phosphate transport in young and aged rats. Endocrinology 140(4):1544–1551. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.140.4.6658
Ishiguro M, Yamamoto H, Masuda M, Kozai M, Takei Y, Tanaka S, Sato T, Segawa H, Taketani Y, Arai H, Miyamoto K, Takeda E (2010) Thyroid hormones regulate phosphate homoeostasis through transcriptional control of the renal type IIa sodium-dependent phosphate co-transporter (Npt2a) gene. Biochem J 427(1):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20090671
Zhou M, Li S, Pathak JL (2019) Pro-inflammatory cytokines and osteocytes. Current osteoporosis reports 17(3):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-019-00507-z
Pathak JL, Bakker AD, Luyten FP, Verschueren P, Lems WF, Klein-Nulend J, Bravenboer N (2016) Systemic inflammation affects human osteocyte-specific protein and cytokine expression. Calcif Tissue Int 98(6):596–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-016-0116-8
Pedro AB, Romaldini JH, Takei K (2011) Changes of serum cytokines in hyperthyroid Graves’ disease patients at diagnosis and during methimazole treatment. Neuroimmunomodulation 18(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1159/000311519
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357(3):266–281. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra070553
Minisola S, Peacock M, Fukumoto S, Cipriani C, Pepe J, Tella SH, Collins MT (2017) Tumour-induced osteomalacia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 13(3):17044. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.44
Bringhurst F, Demay M, Kronenberg H (2016) Hormones and disorders of mineral metabolism. In: Melmed S, Polonsky K, Larsen P, Kronenberg H (eds) Williams textbook of endocrinology. 13 edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1254–1322
Olauson H, Lindberg K, Amin R, Sato T, Jia T, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Andersson G, Lanske B, Larsson TE (2013) Parathyroid-specific deletion of klotho unravels a novel calcineurin-dependent FGF23 signaling pathway that regulates PTH secretion. PLoS Genet 9(12):e1003975. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003975
Silver J, Naveh-Many T (2012) FGF23 and the parathyroid. Adv Exp Med Biol 728:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0887-1_6
Mosekilde L, Lund B, Sorensen OH, Christensen MS, Melsen F (1977) Serum-25-hydroxycholecalciferol in hyperthyroidism. Lancet 1(8015):806–807
Salvatore D, Davies T, Schlumberger M, Hay I, Larsen P (2016) Thyroid physiology and diagnostic evaluation of patients with thyroid disorders. In: Melmed S, Polonsky K, Larsen P, Kronenberg H (eds) Williams texbook of endocrinology, 13th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 334–368
Bhattoa HP (2018) Laboratory aspects and clinical utility of bone turnover markers. Ejifcc 29(2):117–128
Ercolano MA, Drnovsek ML, Silva Croome MC, Moos M, Fuentes AM, Viale F, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Gauna AT (2013) Negative correlation between bone mineral density and TSH receptor antibodies in long-term euthyroid postmenopausal women with treated Graves’ disease. Thyroid Res 6(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6614-6-11
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff of the Eighth Core Lab in the Department of Medical Research of the National Taiwan University Hospital for technical support during the study. The authors also thank Professor Tien-Shang Huang for the support funding.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Liver Disease Prevention and Treatment Research Foundation, Taiwan, National Taiwan University Hospital (grant number: 107-S3859), National Taiwan University and Wong-Yuan Endocrine Fund in Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consents were signed by all participants prior to the study, and ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of NTUH (protocol number 201105045RC, 201107013RC, and 201411013RINB).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CH., Chang, CK., Shih, CW. et al. Serum fibroblast growth factor 23 and mineral metabolism in patients with euthyroid Graves’ diseases: a case-control study. Osteoporos Int 30, 2289–2297 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-05116-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-05116-1