Abstract
Summary
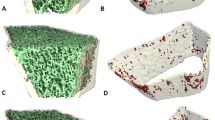
Radius and tibia bone microarchitecture, analyzed through a high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography, were significantly impaired in female patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis compared with healthy controls. Acroosteolysis, quality of life-grip strength, hand disability, and disease duration were significantly associated with this bone deterioration.
Introduction
The effect of diffuse systemic sclerosis (dSSc) on the bone is not completely understood. The objective of this study was to analyze the volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), microarchitecture, and biomechanical parameters at the distal radius and tibia using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT, XtremeCT) in female patients with dSSc and identify clinical and laboratory variables associated with these parameters.
Methods
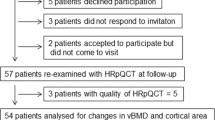
Thirty-eight women with dSSc and 76 healthy controls were submitted to HR-pQCT at the distal radius and tibia. Clinical and laboratory findings, bone mineral density(BMD), nailfold capillaroscopy (NC), total passive range of motion(ROM), and quality of life (health assessment questionnaire—HAQ) were associated with HR-pQCT (Scanco Medical AG, Brüttisellen, Switzerland) parameters. Multiple linear regression models adjusted for clinical and laboratory variables, ROM and HAQ, were performed.
Results
Density, microarchitecture, and biomechanical parameters at the distal radius and tibia were significantly impaired in dSSc patients compared with healthy controls (p < 0.001). Multiple linear regression models showed that lower trabecular density (Tb.vBMD) (radius R2 = 0.561, p = 0.002; and tibia R2 = 0.533, p = 0.005), and lower trabecular number (Tb.N) (tibia R2 = 0.533, p = 0.005) were significantly associated with acroosteolysis. Higher trabecular separation (Tb.Sp) was associated with disease duration and higher HAQ-grip strength (radius R2 = 0.489, p = 0.013), while cortical density (Ct.vBMD) was associated with ROM (radius R2 = 0.294, p = 0.002).
Conclusion
Bone microarchitecture in patients with dSSc, analyzed through HR-pQCT, showed impairment of trabecular and cortical bone at distal radius and tibia. Variables associated with hand involvement (acroosteolysis, quality of life-grip strength, and ROM) and disease duration may be considered prognostic factors of this bone impairment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avouac J, Guerini H, Wipff J, Assous N, Chevrot A, Kahan A, Allanore Y (2006) Radiological hand involvement in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1088–1092
Koutaissoff S, Vanthuyne M, Smith V, de Langhe E, Depresseux G, Westhovens R, de Keyser F, Malghem J, Houssiau FA (2011) Hand radiological damage in systemic sclerosis: comparison with a control group and clinical and functional correlations. Semin Arthritis Rheum 40:455–460
Arslan Tas D, Erken E, Sakalli H, Yucel AE (2012) Evaluating hand in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Int 32:3581–3586
Morardet L, Avouac J, Sammour M, Baron M, Kahan A, Feydy A, Allanore Y (2016) Late nailfold videocapillaroscopy patterns associated with hand calcinosis and acro-osteolysis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 68:366–373
Bálint Z, Farkas H, Farkas N et al (2014) A three-year follow-up study of the development of joint contractures in 131 patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(6 Suppl 86):S68–S74
Poole JL, Steen VD (1991) The use of the health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) to determine physical disability in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res 4:27–31
Medsger TA Jr, Bombardieri S, Czirjak L et al (2003) Assessment of disease severity and prognosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 21(3 Suppl 29):S42–S46
Omair MA, Pagnoux C, McDonald-Blumer H, Johnson SR (2013) Low bone density in systemic sclerosis: a systematic review. J Rheumatol 40:1881–1890
Fuller H, Fuller R, Pereira RMR (2015) High resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography for the assessment of morphological and mechanical bone parameters. Rev Bras Reumatol 55:352–362
Lai CC, Wang SH, Chen WS, Liu CJ, Chen TJ, Lee PC, Chang YS (2015) Increased risk of osteoporotic fractures in patients with systemic sclerosis: a nationwide population-based study. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1347–1352
Avouac J, Koumakis E, Toth E, Meunier M, Maury E, Kahan A, Cormier C, Allanore Y (2012) Increased risk of osteoporosis and fracture in women with systemic sclerosis: a comparative study with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 64:1871–1878
Frediani B, Baldi F, Falsetti P, Acciai C, Filippou G, Spreafico A, Siagri C, Chellini F, Capperucci C, Filipponi P, Galeazzi M, Marcolongo R (2004) Clinical determinants of bone mass and bone ultrasonometry in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 22:313–318
Kilic G, Kilic E, Akgul O, Ozgocmen S (2016) Increased risk for bone loss in women with systemic sclerosis: a comparative study with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis 19:405–411
Arnson Y, Amital H, Agmon-Levin N, Alon D, Sánchez-Castañón M, López-Hoyos M, Matucci-Cerinic M, Szücs G, Shapira Y, Szekanecz Z, Shoenfeld Y (2011) Serum 25-OH vitamin D concentrations are linked with various clinical aspects in patients with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective cohort study and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev 10:490–494
Sampaio-Barros MM, Takayama L, Sampaio-Barros PD, Bonfá E, Pereira RM (2016) Low vitamin D serum levels in diffuse systemic sclerosis: a correlation with worst quality of life and severe capillaroscopic findings. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed 56:337–344
Zhu TY, Griffith JF, Qin L, Hung VWY, Fong TN, Kwok AW, Leung PC, Li EK, Tam LS (2012) Bone density and microarchitecture: relationship between hand, peripheral, and axial skeletal sites assessed by HR-pQCT and DXA in rheumatoid arthritis. Calcif Tissue Int 91:343–355
Kocijan R, Finzel S, Englbrecht M, Engelke K, Rech J, Schett G (2014) Decreased quantity and quality of the periarticular and nonperiarticular bone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional HR-pQCT study. J Bone Miner Res 29:1005–1014
Marot M, Valéry A, Esteve E, Bens G, Müller A, Rist S, Toumi H, Lespessailles E (2015) Prevalence and predictive factors of osteoporosis in systemic sclerosis patients: a case-control study. Oncotarget 6:14865–14873
Mok CC, Chan PT, Chan KL, Ma KM (2013) Prevalence and risk factors of low bone mineral density in Chinese patients with systemic sclerosis: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52:296–303
LeRoy EC, Black C, Fleischmajer R, Jablonska S, Krieg T, Medsger TA Jr, Rowell N, Wollheim F (1988) Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 15:202–205
Steen VD, Medsger TA Jr (2000) Severe organ involvement in systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 43:2437–2444
Furst DE, Clements PJ, Steen VD, Medsger TA Jr, Masi AT, D'Angelo WA, Lachenbruch PA, Grau RG, Seibold JR (1998) The modified Rodnan skin score is an accurate reflection of skin biopsy thickness in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 25:84–88
Medsger TA Jr, Stillman AJ, Steen VD et al (1999) A disease severity scale for systemic sclerosis: development and testing. J Rheumatol 26:2159–2167
Mugii N, Hasegawa M, Matsushita T, Kondo M, Orito H, Yanaba K, Komura K, Hayakawa I, Hamaguchi Y, Ikuta M, Tachino K, Fujimoto M, Takehara K, Sato S (2006) The efficacy of self-administered stretching for finger joint motion in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 33:1586–1592
Ferraz MB, Oliveira LM, Araujo PM et al (1990) Crosscultural reliability of the physical ability dimension of the health assessment questionnaire. J Rheumatol 17:813–817
Cutolo M, Sulli A, Smith V (2013) How to perform and interpret capillaroscopy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 27:237–248
Vilayphiou N, Boutroy S, Sornay-Rendu E, van Rietbergen B, Chapurlat R (2016) Age-related changes in bone strength from HR-pQCT derived microarchitectural parameters with an emphasis on the role of cortical porosity. Bone 83:233–240
Alvarenga JC, Fuller H, Pasoto SG, Pereira RMR (2017) Age-related reference curves of volumetric bone density, structure, and biomechanical parameters adjusted for weight and height in a population of healthy women: an HR-pQCT study. Osteoporos Int 28:1335–1346
Sampaio-Barros PD, Bortoluzzo AB, Marangoni RG et al (2012) Survival, causes of death, and prognostic factors in systemic sclerosis: analysis of 947 Brazilian patients. J Rheumatol 39:1971–1978
Maddali-Bongi S, Del Rosso A, Mikhaylova S et al (2014) Impact of hand and face disabilities on global disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(6 Suppl 86):S15–S20
Park JK, Fava A, Carrino J, del Grande F, Rosen A, Boin F (2016) Association of acroosteolysis with enhanced osteoclastogenesis and higher blood levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:201–209
Erre GL, Marongiu A, Fenu P, Faedda R, Masala A, Sanna M, Soro G, Tocco A, Piu D, Marotto D, Passiu G (2008) The "sclerodermic hand": a radiological and clinical study. Joint Bone Spine 75:426–431
La Montagna G, Sodano A, Capurro V et al (2005) The arthropathy of systemic sclerosis: a 12 month prospective clinical and imaging study. Skelet Radiol 34:35–41
Radic M, Martinovic Kaliterna D, Ljutic D (2006) The level of anti-topoisomerase I antibodies highly correlates with metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints flexion contractures in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24:407–412
La Montagna G, Vatti M, Valentini G et al (1991) Osteopenia in systemic sclerosis. Evidence of a participating role of earlier menopause. Clin Rheumatol 10:18–22
Sampaio-Barros PD, Costa-Paiva L, Filardi S, Sachetto Z, Samara AM, Marques-Neto JF (2005) Prognostic factors of low bone mineral density in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23:180–184
Souza RB, Borges CT, Takayama L et al (2006) Systemic sclerosis and bone loss: the role of the disease and body composition. Scand J Rheumatol 35:384–387
Yuen SY, Rochwerg B, Ouimet J, Pope JE (2008) Patients with scleroderma may have increased risk of osteoporosis. A comparison to rheumatoid arthritis and noninflammatory musculoskeletal conditions. J Rheumatol 35:1073–1078
Ibn Yacoub Y, Amine B, Laatiris A et al (2012) Bone density in Moroccan women with systemic scleroderma and its relationships with disease-related parameters and vitamin D status. Rheumatol Int 32:3143–3148
Kowal-Bielecka O, Fransen J, Avouac J, Becker M, Kulak A, Allanore Y, Distler O, Clements P, Cutolo M, Czirjak L, Damjanov N, del Galdo F, Denton CP, Distler JHW, Foeldvari I, Figelstone K, Frerix M, Furst DE, Guiducci S, Hunzelmann N, Khanna D, Matucci-Cerinic M, Herrick AL, van den Hoogen F, van Laar J, Riemekasten G, Silver R, Smith V, Sulli A, Tarner I, Tyndall A, Welling J, Wigley F, Valentini G, Walker UA, Zulian F, Müller-Ladner U, EUSTAR Coauthors (2017) Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 76:1327–1339
Poole JL, Santhanam DD, Latham AL (2013) Hand impairment and activity limitations in four chronic diseases. J Hand Ther 26:232–236
Sandqvist G, Hesselstrand R, Eberhardt K (2009) A longitudinal follow-up of hand involvement and activities of daily living in early systemic sclerosis. Scand J Rheumatol 38:304–310
Zhu TY, Griffith JF, Qin L, Hung VWY, Fong TN, Au SK, Tang XL, Kun EW, Kwok AW, Leung PC, LI EK, Tam LS (2015) Cortical thinning and progressive cortical porosity in female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus on long-term glucocorticoids: a 2-year case-control study. Osteoporos Int 26:1759–1771
Pistoia W, van Rietbergen B, Rüegsegger P (2003) Mechanical consequences of different scenarios for simulated bone atrophy and recovery in the distal radius. Bone 33:937–945
Financial support
Marília M. Sampaio-Barros is a recipient of a Post-Doctoral Research Grant from the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) / Ministério da Educação (MEC). Percival D. Sampaio-Barros and Rosa Maria R. Pereira were recipients of a research grant from Federico Foundation (Switzerland) and grant from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq # 472754/2013-0 to RMRP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sampaio-Barros, M., Alvarenga, J., Takayama, L. et al. Distal radius and tibia bone microarchitecture impairment in female patients with diffuse systemic sclerosis. Osteoporos Int 30, 1679–1691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-04965-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-04965-0