Abstract
Summary
Mortality and remaining bedridden following the hip fracture surgery are not rare. We tried to measure the levels of inflammatory markers tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) following the hip fracture surgery and compare their levels with controls. We aimed to show a relationship between the levels of these markers and post-operative mortality and walking capability.
Introduction
Osteoporosis is a condition, causing the hip fractures in the elderly. Hip fractures have a high rate of overall mortality up to 30% following the incident. Cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α are suggested to play a role in bone resorption and, thus, in the etiology of osteoporosis.
Methods
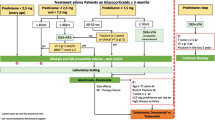
Plasma levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were measured pre-operatively and on the first and second days after the surgery in 40 Turkish hip fracture patients. The levels of these cytokines were compared with 40 Turkish age-matched healthy controls. The levels of these cytokines were compared between the deceased and surviving patients, as well as the existence of walking capability following the surgery.
Results
Significantly higher IL-6 levels were shown on the first and second days after the surgery (p = 0.005; p = 0.01, respectively). The overall death rate of our study group within the 2-year follow-up time was found to be 35%. No statistical significance was found in the means of 2-year follow-up mortality between the patients. Presence of walking capability did not differ between the patients, as well.
Conclusion
We demonstrated an association between IL-6 levels and hip fracture in our study group following the surgery. We also suggest that TNF-α and IL-6 levels are not related to the occurrence of death and walking capability after the surgery. However, these findings need further functional and clinical confirmation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandez MA, Griffin XL, Costa ML (2015) Management of hip fracture. Br Med Bull 115(1):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldv036
Kanis JA, Oden A, Johnell O, De Laet C, Jonsson B, Oglesby AK (2003) The components of excess mortality after hip fracture. Bone 32(5):468–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/S8756-3282(03)00061-9
Barbour KE, Lui LY, Ensrud KE, Hillier TA, LeBlanc ES, Ing SW, Hochberg MC, Cauley JA, Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF) Research Group (2014) Inflammatory markers and risk of hip fracture in older white women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res : Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 29(9):2057–2064. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2245
Zupan J, PristovŠek N, Mencej-Bedrač S, Komadina R, Preželj J, Marc J (2012) Interleukin-1α gene variants influence bone mineral density and the risk of osteoporotic hip fractures in elderly Slovenian people. Clin Chem Lab Med 50(8):1379–1385. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2011-0589
Barbour KE, Boudreau R, Danielson ME, Youk AO, Wactawski-Wende J, Greep NC, LaCroix AZ, Jackson RD, Wallace RB, Bauer DC, Allison MA, Cauley JA (2012) Inflammatory markers and the risk of hip fracture: the women’s health initiative. J Bone Miner Res 27(5):1167–1176. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1559
Salimi S, Shardell M, Miller R, Gruber-Baldini AL, Orwig D, Fedarko N, Hochberg MC, Guralnik JM, Magaziner J (2018) Soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 1, bone resorption, and bone mineral density in the year following hip fractures: the Baltimore hip studies. J Bone Miner Res 33:1649–1656. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3457
Ing SW, Orchard TS, Lu B, LaMonte MJ, Barbour KE, Cauley JA, Jackson RD (2015) TNF receptors predict hip fracture risk in the WHI study and fatty acid intake does not modify this association. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(9):3380–3387. https://doi.org/10.1210/JC.2015-1662
Miller RR, Cappola AR, Shardell MD, Hawkes WG, Yu-Yahiro JA, Hebel JR, Magaziner J (2006) Persistent changes in interleukin-6 and lower extremity function following hip fracture. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61:1053–1058. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/61.10.1053
Kawai VK, Grijalva CG, Arbogast PG, Curtis JR, Solomon DH, Delzell E, Chen L, Ouellet-Hellstrom R, Herrinton L, Liu L, Mitchell EF Jr, Stein CM, Griffin MR (2013) Initiation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) antagonists and risk of fractures in patients with selected rheumatic and autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Care Res 65(7):1085–1094. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21937
Baëhl S, Garneau H, Le Page A, Lorrain D, Viens I, Svotelis A, Lord JM, Phillips A, Cabana F, Larbi A, Dupuis G, Fülöp T (2015) Altered neutrophil functions in elderly patients during a 6-month follow-up period after a hip fracture. Exp Gerontol, Vol. 65, 01.05.2015; 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2015.03.009
Ginaldi L, De Martinis M, Ciccarelli F, Saitta S, Imbesi S, Mannucci C, Gangemi S (2015) Increased levels of interleukin 31 (IL-31) in osteoporosis. BMC Immunol 16:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12865-015-0125-9
Shi H, Na Q, Zhang X, Jiang X (2017) Correlations between the levels of acute infection markers and serum albumin in elderly patients with hip fracture. Aging Clin Exp Res 29:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-016-0585-7
Stojanović D, Bůžková P, Mukamal KJ, Heckbert SR, Psaty BM, Fink HA, Cauley JA, Wallace E, Curtis LH, Hirsch C, Budoff M, Li D, Young R, Jalal D, Delaney JA (2018) Soluble inflammatory markers and risk of incident fractures in older adults: the cardiovascular health study. J Bone Miner Res 33:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3301
Cauley JA, Barbour KE, Harrison SL, Cloonan YK, Danielson ME, Ensrud KE, Fink HA, Orwoll ES, Boudreau R (2016) Inflammatory markers and the risk of hip and vertebral fractures in men: the osteoporotic fractures in men (MrOS). J Bone Miner Res : Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 31(12):2129–2138. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2905
Sun T, Wang X, Liu Z, Chen X, Zhang J (2011) Plasma concentrations of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and outcome prediction in elderly hip fracture patients. Injury 42(7):707–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2011.01.010
Giannoudis PV, Hildebrand F, Pape HC (2004) Inflammatory serum markers in patients with multiple trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86-B(3):313–323. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.86B3.15035
Morettini M, Palumbo MC, Sacchetti M, Castiglione F, Mazzà C (2017) A system model of the effects of exercise on plasma interleukin-6 dynamics in healthy individuals: role of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. PLoS One 12(7):e0181224. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181224
Tecchio C, Micheletti A, Cassatella MA (2014) Neutrophil-derived cytokines: facts beyond expression. Front Immunol 5:508. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00508
Todd J, Simpson P, Estis J, Torres V, Wub AH (2013) Reference range and short- and long-term biological variation of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17A and tissue necrosis factor-alpha using high sensitivity assays. Cytokine 64(3):660–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2013.09.018
Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L (2007) Increased mortality in patients with a hip fracture-effect of pre-morbid conditions and post-fracture complications. Osteoporos Int 18:1583–1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-007-0403-3
Miller RR, Shardell MD, Hicks GE, Cappola AR, Hawkes WG, Yu-Yahiro JA, Magaziner J (2008) Association between interleukin-6 and lower extremity function after hip fracture - the role of muscle mass and strength. J Am Geriatr Soc 56:1050–1056. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01708.x
Magaziner J, Chiles N, Orwig D (2015) Recovery after hip fracture: interventions and their timing to address deficits and desired outcomes – evidence from the Baltimore hip studies. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser 83:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1159/000382064
Beloosesky Y, Hendel D, Weiss A, Hershkovitz A, Grinblat J, Pirotsky A, Barak V (2007) Cytokines and C-reactive protein production in hip-fracture-operated elderly patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 62:420–426. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/62.4.420
Clementsen T, Krohn CD, Reikerås O (2006) Systemic and local cytokine patterns during total hip surgery. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 66(6):535–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365510600889635
Sedlár M, Kudrnová Z, Erhart D, Trca S, Kvasnicka J, Krska Z, Mazoch J, Malíková I, Zeman M, Linhart A (2010) Older age and type of surgery predict the early inflammatory response to hip trauma mediated by interleukin-6 (IL-6). Arch Gerontol Geriatr 51(1):e1–e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2009.06.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants. The study was approved by the local ethics committee and carried out in compliance with the Helsinki declaration.
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saribal, D., Hocaoglu-Emre, F.S., Erdogan, S. et al. Inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α in patients with hip fracture. Osteoporos Int 30, 1025–1031 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-04874-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-04874-2