Abstract
Summary
This study investigated the effect of the N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-associated SNPs on bone mineral density (BMD) and found plenty of m6A-SNPs that were associated with BMD. This study increases our understanding on the regulation patterns of SNP and may provide new clues for further detection of functional mechanism underlying the associations between SNPs and osteoporosis.
Introduction
m6A plays critical roles in many fundamental biological processes and a variety of diseases. The m6A-associated SNPs may be potential functional variants for BMD. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the genome-wide m6A-SNPs on BMD.
Methods
We examined the association of m6A-SNPs with femoral neck (FN) and lumbar spine (LS) BMD in 32,961 individuals and quantitative heel ultrasounds (eBMD) in 142,487 individuals. Furthermore, we performed expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) analyses for the m6A-SNPs using whole genome data of about 10.5 million SNPs and 21,323 mRNAs from 43 Chinese individuals, as well as public available data. Differential expression analyses were also performed to support the identified genes.
Results
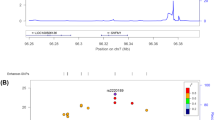
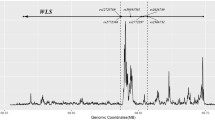
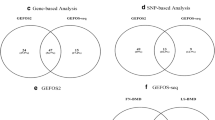
We found 138, 125, and 993 m6A-SNPs which were associated with FN-BMD, LS-BMD, and eBMD (P < 0.05), respectively. The associations of rs11614913 (P = 8.92 × 10−10) in MIR196A2 and rs1110720 (P = 2.05 × 10−10) in ESPL1 with LS-BMD reached the genome-wide significance level. In addition, a total of 24 m6A-SNPs were significantly associated with eBMD (P < 5.0 × 10−8). Further eQTL analyses showed that 47 of these BMD-associated m6A-SNPs were associated with expressions of the 46 corresponding local genes. Moreover, the expressions of 26 of these genes were associated with BMD.
Conclusion
The present study represents the first effort of investigating the associations and the mechanisms underlying the link between m6A-SNPs and BMD. The results suggested that m6A-SNP may play important roles in the pathology of osteoporosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanis JA, Borgstrom F, De Laet C, Johansson H, Johnell O, Jonsson B, Oden A, Zethraeus N, Pfleger B, Khaltaev N (2005) Assessment of fracture risk. Osteoporos Int 16(6):581–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-004-1780-5
Arden NK, Baker J, Hogg C, Baan K, Spector TD (1996) The heritability of bone mineral density, ultrasound of the calcaneus and hip axis length: a study of postmenopausal twins. J Bone Miner Res 11(4):530–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.5650110414
Howard GM, Nguyen TV, Harris M, Kelly PJ, Eisman JA (1998) Genetic and environmental contributions to the association between quantitative ultrasound and bone mineral density measurements: a twin study. J Bone Miner Res 13(8):1318–1327. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.8.1318
Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OM, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, Minster RL, Moayyeri A, Vandenput L, Willner D, Xiao SM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Zheng HF, Alonso N, Eriksson J, Kammerer CM, Kaptoge SK, Leo PJ, Thorleifsson G, Wilson SG, Wilson JF, Aalto V, Alen M, Aragaki AK, Aspelund T, Center JR, Dailiana Z, Duggan DJ, Garcia M, Garcia-Giralt N, Giroux S, Hallmans G, Hocking LJ, Husted LB, Jameson KA, Khusainova R, Kim GS, Kooperberg C, Koromila T, Kruk M, Laaksonen M, Lacroix AZ, Lee SH, Leung PC, Lewis JR, Masi L, Mencej-Bedrac S, Nguyen TV, Nogues X, Patel MS, Prezelj J, Rose LM, Scollen S, Siggeirsdottir K, Smith AV, Svensson O, Trompet S, Trummer O, van Schoor NM, Woo J, Zhu K, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Buckley BM, Cheng S, Christiansen C, Cooper C, Dedoussis G, Ford I, Frost M, Goltzman D, Gonzalez-Macias J, Kahonen M, Karlsson M, Khusnutdinova E, Koh JM, Kollia P, Langdahl BL, Leslie WD, Lips P, Ljunggren O, Lorenc RS, Marc J, Mellstrom D, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Olmos JM, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Reid DM, Riancho JA, Ridker PM, Rousseau F, Slagboom PE, Tang NL, Urreizti R, Van Hul W, Viikari J, Zarrabeitia MT, Aulchenko YS, Castano-Betancourt M, Grundberg E, Herrera L, Ingvarsson T, Johannsdottir H, Kwan T, Li R, Luben R, Medina-Gomez C, Palsson ST, Reppe S, Rotter JI, Sigurdsson G, van Meurs JB, Verlaan D, Williams FM, Wood AR, Zhou Y, Gautvik KM, Pastinen T, Raychaudhuri S, Cauley JA, Chasman DI, Clark GR, Cummings SR, Danoy P, Dennison EM, Eastell R, Eisman JA, Gudnason V, Hofman A, Jackson RD, Jones G, Jukema JW, Khaw KT, Lehtimaki T, Liu Y, Lorentzon M, McCloskey E, Mitchell BD, Nandakumar K, Nicholson GC, Oostra BA, Peacock M, Pols HA, Prince RL, Raitakari O, Reid IR, Robbins J, Sambrook PN, Sham PC, Shuldiner AR, Tylavsky FA, van Duijn CM, Wareham NJ, Cupples LA, Econs MJ, Evans DM, Harris TB, Kung AW, Psaty BM, Reeve J, Spector TD, Streeten EA, Zillikens MC, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ohlsson C, Karasik D, Richards JB, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ralston SH, Ioannidis JP, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F (2012) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nat Genet 44(5):491–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2249
Kemp JP, Morris JA, Medina-Gomez C, Forgetta V, Warrington NM, Youlten SE, Zheng J, Gregson CL, Grundberg E, Trajanoska K, Logan JG, Pollard AS, Sparkes PC, Ghirardello EJ, Allen R, Leitch VD, Butterfield NC, Komla-Ebri D, Adoum AT, Curry KF, White JK, Kussy F, Greenlaw KM, Xu C, Harvey NC, Cooper C, Adams DJ, Greenwood CMT, Maurano MT, Kaptoge S, Rivadeneira F, Tobias JH, Croucher PI, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Bassett JHD, Williams GR, Richards JB, Evans DM (2017) Identification of 153 new loci associated with heel bone mineral density and functional involvement of GPC6 in osteoporosis. Nat Genet 49(10):1468–1475. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3949
Zheng HF, Forgetta V, Hsu YH, Estrada K, Rosello-Diez A, Leo PJ, Dahia CL, Park-Min KH, Tobias JH, Kooperberg C, Kleinman A, Styrkarsdottir U, Liu CT, Uggla C, Evans DS, Nielson CM, Walter K, Pettersson-Kymmer U, McCarthy S, Eriksson J, Kwan T, Jhamai M, Trajanoska K, Memari Y, Min J, Huang J, Danecek P, Wilmot B, Li R, Chou WC, Mokry LE, Moayyeri A, Claussnitzer M, Cheng CH, Cheung W, Medina-Gomez C, Ge B, Chen SH, Choi K, Oei L, Fraser J, Kraaij R, Hibbs MA, Gregson CL, Paquette D, Hofman A, Wibom C, Tranah GJ, Marshall M, Gardiner BB, Cremin K, Auer P, Hsu L, Ring S, Tung JY, Thorleifsson G, Enneman AW, van Schoor NM, de Groot LC, van der Velde N, Melin B, Kemp JP, Christiansen C, Sayers A, Zhou Y, Calderari S, van Rooij J, Carlson C, Peters U, Berlivet S, Dostie J, Uitterlinden AG, Williams SR, Farber C, Grinberg D, LaCroix AZ, Haessler J, Chasman DI, Giulianini F, Rose LM, Ridker PM, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV, Center JR, Nogues X, Garcia-Giralt N, Launer LL, Gudnason V, Mellstrom D, Vandenput L, Amin N, van Duijn CM, Karlsson MK, Ljunggren O, Svensson O, Hallmans G, Rousseau F, Giroux S, Bussiere J, Arp PP, Koromani F, Prince RL, Lewis JR, Langdahl BL, Hermann AP, Jensen JE, Kaptoge S, Khaw KT, Reeve J, Formosa MM, Xuereb-Anastasi A, Akesson K, McGuigan FE, Garg G, Olmos JM, Zarrabeitia MT, Riancho JA, Ralston SH, Alonso N, Jiang X, Goltzman D, Pastinen T, Grundberg E, Gauguier D, Orwoll ES, Karasik D, Davey-Smith G, Smith AV, Siggeirsdottir K, Harris TB, Zillikens MC, van Meurs JB, Thorsteinsdottir U, Maurano MT, Timpson NJ, Soranzo N, Durbin R, Wilson SG, Ntzani EE, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Hinds DA, Spector T, Cupples LA, Ohlsson C, Greenwood CM, Jackson RD, Rowe DW, Loomis CA, Evans DM, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Joyner AL, Duncan EL, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F, Richards JB (2015) Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture. Nature 526(7571):112–117. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14878
Mao F, Xiao L, Li X, Liang J, Teng H, Cai W, Sun ZS (2016) RBP-Var: a database of functional variants involved in regulation mediated by RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D154–D163. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1308
Wu X, Hurst LD (2016) Determinants of the usage of splice-associated cis-motifs predict the distribution of human pathogenic SNPs. Mol Biol Evol 33(2):518–529. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msv251
Ramaswami G, Deng P, Zhang R, Anna Carbone M, Mackay TF, Li JB (2015) Genetic mapping uncovers cis-regulatory landscape of RNA editing. Nat Commun 6(8194):8194. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9194
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR (2014) The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(5):313–326. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3785
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, Ren B, Pan T, He C (2014) N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505(7481):117–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12730
Edupuganti RR, Geiger S, RGH L, Shi H, Hsu PJ, Lu Z, Wang SY, MPA B, Jansen P, Rossa M, Muller M, Stunnenberg HG, He C, Carell T, Vermeulen M (2017) N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) recruits and repels proteins to regulate mRNA homeostasis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24(10):870–878. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3462
Visvanathan A, Somasundaram K (2017) mRNA traffic control reviewed: N6-methyladenosine (m(6) A) takes the driver’s seat. BioEssays https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201700093, 40
Zheng Y, Nie P, Peng D, He Z, Liu M, Xie Y, Miao Y, Zuo Z, Ren J (2018) m6AVar: a database of functional variants involved in m6A modification. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D139–D145. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx895
Pickrell JK (2014) Joint analysis of functional genomic data and genome-wide association studies of 18 human traits. Am J Hum Genet 94(4):559–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.03.004
Zheng Y, Nie P, Peng D, He Z, Liu M, Xie Y, Miao Y, Zuo Z, Ren J (2017) m6AVar: a database of functional variants involved in m6A modification. Nucleic Acids Res. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx895
Mo XB, Wu LF, Zhu XW, Xia W, Wang L, He P, Bing PF, Lu X, Zhang YH, Deng FY, Lei SF (2017) Identification and evaluation of lncRNA and mRNA integrative modules in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Epigenomics 9(7):943–954. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2016-0178
Zhang L, Pei YF, Fu X, Lin Y, Wang YP, Deng HW (2014) FISH: fast and accurate diploid genotype imputation via segmental hidden Markov model. Bioinformatics 30(13):1876–1883. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu143
Shabalin AA (2012) Matrix eQTL: ultra fast eQTL analysis via large matrix operations. Bioinformatics 28(10):1353–1358. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts163
Ward LD, Kellis M (2012) HaploReg: a resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res 40(Database issue):D930–D934. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr917
Benisch P, Schilling T, Klein-Hitpass L, Frey SP, Seefried L, Raaijmakers N, Krug M, Regensburger M, Zeck S, Schinke T, Amling M, Ebert R, Jakob F (2012) The transcriptional profile of mesenchymal stem cell populations in primary osteoporosis is distinct and shows overexpression of osteogenic inhibitors. PLoS One 7(9):e45142. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045142
Lei SF, Wu S, Li LM, Deng FY, Xiao SM, Jiang C, Chen Y, Jiang H, Yang F, Tan LJ, Sun X, Zhu XZ, Liu MY, Liu YZ, Chen XD, Deng HW (2009) An in vivo genome wide gene expression study of circulating monocytes suggested GBP1, STAT1 and CXCL10 as novel risk genes for the differentiation of peak bone mass. Bone 44(5):1010–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2008.05.016
Liu YZ, Dvornyk V, Lu Y, Shen H, Lappe JM, Recker RR, Deng HW (2005) A novel pathophysiological mechanism for osteoporosis suggested by an in vivo gene expression study of circulating monocytes. J Biol Chem 280(32):29011–29016. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M501164200
Xiao P, Chen Y, Jiang H, Liu YZ, Pan F, Yang TL, Tang ZH, Larsen JA, Lappe JM, Recker RR, Deng HW (2008) In vivo genome-wide expression study on human circulating B cells suggests a novel ESR1 and MAPK3 network for postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 23(5):644–654. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.080105
Kheradpour P, Kellis M (2014) Systematic discovery and characterization of regulatory motifs in ENCODE TF binding experiments. Nucleic Acids Res 42(5):2976–2987. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1249
Visvanathan A, Somasundaram K (2018) mRNA traffic control reviewed: N6-methyladenosine (m(6) A) takes the driver’s seat. Bioessays 40 (1). https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201700093
Li LJ, Fan YG, Leng RX, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2018) Potential link between m(6)A modification and systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Immunol 93:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.11.009
Shastry BS (2009) SNPs: impact on gene function and phenotype. Methods Mol Biol 578:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-411-1_1
Hu Z, Chen J, Tian T, Zhou X, Gu H, Xu L, Zeng Y, Miao R, Jin G, Ma H, Chen Y, Shen H (2008) Genetic variants of miRNA sequences and non-small cell lung cancer survival. J Clin Invest 118(7):2600–2608. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI34934
Xu J, Hu Z, Xu Z, Gu H, Yi L, Cao H, Chen J, Tian T, Liang J, Lin Y, Qiu W, Ma H, Shen H, Chen Y (2009) Functional variant in microRNA-196a2 contributes to the susceptibility of congenital heart disease in a Chinese population. Hum Mutat 30(8):1231–1236. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.21044
Karabegovic I, Maas S, Medina-Gomez C, Zrimsek M, Reppe S, Gautvik KM, Uitterlinden AG, Rivadeneira F, Ghanbari M (2017) Genetic polymorphism of miR-196a-2 is associated with bone mineral density (BMD). Int J Mol Sci 18(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122529
Ahn TK, Kim JO, Kumar H, Choi H, Jo MJ, Sohn S, Ropper AE, Kim NK, Han IB (2018) Polymorphisms of miR-146a, miR-149, miR-196a2, and miR-499 are associated with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in Korean postmenopausal women. J Orthop Res 36(1):244–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23640
Da M, Feng Y, Xu J, Hu Y, Lin Y, Ni B, Qian B, Hu Z, Mo X (2014) Association of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases gene polymorphisms with the risk of congenital heart disease in the Chinese Han population. PLoS One 9(10):e110072. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110072
Bonomo JA, Guan M, Ng MC, Palmer ND, Hicks PJ, Keaton JM, Lea JP, Langefeld CD, Freedman BI, Bowden DW (2014) The ras responsive transcription factor RREB1 is a novel candidate gene for type 2 diabetes associated end-stage kidney disease. Hum Mol Genet 23(24):6441–6447. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu362
Keshari PK, Harbo HF, Myhr KM, Aarseth JH, Bos SD, Berge T (2016) Allelic imbalance of multiple sclerosis susceptibility genes IKZF3 and IQGAP1 in human peripheral blood. BMC Genet 17:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0367-4
Sham PC, Purcell SM (2014) Statistical power and significance testing in large-scale genetic studies. Nat Rev Genet 15(5):335–346. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3706
Mo XB, Lu X, Zhang YH, Zhang ZL, Deng FY, Lei SF (2015) Gene-based association analysis identified novel genes associated with bone mineral density. PLoS One 10(3):e0121811. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121811
Funding
The study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31401079, 81473046 and 81373010), the Startup Fund from Soochow University (Q413900313, Q413900412), Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014 M551649), and a Project of the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the ethical committee of Soochow University. The written informed consent was obtained from all of the participants.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table S1
(PDF 184 kb)
Supplementary Table S2
(PDF 213 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, X.B., Zhang, Y.H. & Lei, S.F. Genome-wide identification of m6A-associated SNPs as potential functional variants for bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int 29, 2029–2039 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-018-4573-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-018-4573-y