Abstract
Summary
We performed a systematic review of the literature to assess the association between sleep apnea and bone metabolism diseases including osteoporosis in adult population. Results from clinical trials suggest that the association between sleep apnea and low bone mass in adults is possible.
Introduction
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on the potential association between sleep apnea and low bone mass in adults.
Methods
Electronic searches of five databases were performed. The inclusion criteria consisted of studies in humans that assessed potential associations between sleep apnea and bone metabolic diseases in an adult population. For diagnosis of sleep apnea overnight polysomnography, home polygraphy, or validated records from healthcare databases were considered. Reduced bone density, osteoporosis, serum/urinary levels for markers of bone formation and resorption, or risk of fractures caused without history of trauma were considered indicators of low bone mass. A random-effects model meta-analysis was applied when possible.
Results
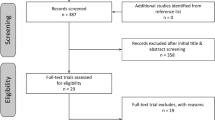
Of the 963 relevant references, 12 studies met our inclusion criteria and were assessed to be of medium to low bias. Nine out of 12 studies reported an association between sleep apnea and low bone mass (increased bone resorption markers, reduced bone density, and higher risk of osteoporosis). Two studies did not report a significant association, whereas one study reported an increase of bone density in sleep apnea patients compared to non-sleep apnea patients. Meta-analysis of 2 studies (n = 112,258 patients) showed that sleep apnea was a significant risk factor for osteoporosis (odds ratio (OR), 1.92; 95%CI, 1.24 to 2.97; I2 = 66%); females only had an OR of 2.56 (95% CI, 1.96 to 3.34; I2 = 0%) while the OR in males was 2.03 (95% CI, 1.24 to 3.35; I2 = 38%).
Conclusions
An association between sleep apnea and low bone mass in adults is plausible, but supporting evidence has a risk of bias and is inconsistent.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Looker AC, Orwoll ES, Johnston CC Jr, Lindsay RL, Wahner HW, Dunn WL, Calvo MS, Harris TB, Heyse SP (1997) Prevalence of low femoral bone density in older U.S. adults from NHANES III. J Bone Miner Res 12:1761–1768
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Peppard PE, Nieto FJ, Hla KM (2009) Burden of sleep apnea: rationale, design, and major findings of the Wisconsin sleep cohort study. WMJ 108:246–249
Tarasiuk A, Reuveni H (2013) The economic impact of obstructive sleep apnea. Curr Opin Pulm Med 19:639–644
Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A (2007) Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res 22:465–475
Swanson CM, Shea SA, Stone KL, Cauley JA, Rosen CJ, Redline S, Karsenty G, Orwoll ES (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic bone disease: insights into the relationship between bone and sleep. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research 30:199–211
Center JR (2013) Chapter 35—outcomes following osteoporotic fractures. In: Cauley RMFWDLA (ed) Osteoporosis, Fourth edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 841–852
Wright NC, Looker AC, Saag KG, Curtis JR, Delzell ES, Randall S, Dawson-Hughes B (2014) The recent prevalence of osteoporosis and low bone mass in the United States based on bone mineral density at the femoral neck or lumbar spine. J Bone Miner Res 29:2520–2526
Kario K (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and hypertension: ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension 32:428–432
Vijayan VK (2012) Morbidities associated with obstructive sleep apnea. Expert Rev Respir Med 6:557–566
Luyster FS, Strollo PJ, Zee PC, Walsh JK, on behalf of the Boards of Directors of the American Academy of Sleep M, the Sleep Research S (2012) Sleep: a health imperative. Sleep 35:727–734
Leger D, Bayon V, Laaban JP, Philip P (2012) Impact of sleep apnea on economics. Sleep Med Rev 16:455–462
Douglas N (2012) Chapter 265. Sleep apnea. In: LDFAKDHSJJL J (ed) Sleep apnea. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, pp 2186–2194
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Grp P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–W264
Wells GS, B; O’Connell, D; Peterson, J; Welch, V; Losos, M; Tugwell, P (2015) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute
Higgins JPT, Green S, Cochrane Collaboration (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester, England; Hoboken, NJ
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH (1997) Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med 127:820–826
Sterne JA, Egger M (2001) Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol 54:1046–1055
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Tomiyama H, Okazaki R, Inoue D, Ochiai H, Shiina K, Takata Y, Hashimoto H, Yamashina A (2008) Link between obstructive sleep apnea and increased bone resorption in men. Osteoporos Int 19:1185–1192
Mariani S, Fiore D, Varone L, Basciani S, Persichetti A, Watanabe M, Saponara M, Spera G, Moretti C, Gnessi L (2012) Obstructive sleep apnea and bone mineral density in obese patients. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy 5:395–401
Sforza E, Thomas T, Barthelemy JC, Collet P, Roche F (2013) Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with preserved bone mineral density in healthy elderly subjects. Sleep 36:1509–1515
Uzkeser H, Yildirim K, Aktan B, Karatay S, Kaynar H, Araz O, Kilic K (2013) Bone mineral density in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 17:339–342
Yuceege M, Dulgeroglu DE, Firat H, Yalcindag A (2015) Can sleep apnea be a secondary cause of osteoporosis in young people? Sleep and Biological Rhythms 13:189–194
Wang TY, Lo YL, Chou PC, Chung FT, Lin SM, Lin TY, Lin HC, Wang CH, Yu CT, Kuo HP (2015) Associated bone mineral density and obstructive sleep apnea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J COPD 10:231–237
Aslan SH, Se Y, Kıyıcı A, Sarı O (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome may be a risk factor for the development of osteoporosis in men at an early age? The Turkish Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 61:216–222
Terzi R, Yilmaz Z (2016) Bone mineral density and changes in bone metabolism in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Bone Miner Metab 4:475–481
Hamada S, Ikezoe K, Hirai T, Oguma T, Tanizawa K, Inouchi M, Handa T, Oga T, Mishima M, Chin K (2016) Evaluation of bone mineral density by computed tomography in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Sleep Med 1:25–34
Liguori C, Mercuri NB, Izzi F et al (2016) Obstructive sleep apnoea as a risk factor for osteopenia and osteoporosis in the male population. Eur Respir J 47:987–990
Chen YL, Weng SF, Shen YC, Chou CW, Yang CY, Wang JJ, Tien KJ (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea and risk of osteoporosis: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:2441–2447
Yen CM, Kuo CL, Lin MC, Lee CF, Lin KY, Lin CL, Chang SN, Sung FC, Kao CH (2014) Sleep disorders increase the risk of osteoporosis: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Sleep Med 15:1339–1344
Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (2008) Analysing data and undertaking m-analyses. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of Interventions. Wiley, Ltd, pp 243–296
Burch J, Rice S, Yang HQ, Neilson A, Stirk L, Francis R, Holloway P, Selby P, Craig D (2014) Systematic review of the use of bone turnover markers for monitoring the response to osteoporosis treatment: the secondary prevention of fractures, and primary prevention of fractures in high-risk groups. Health Technol Asses 18:1-+
Peacock M (2010) Calcium metabolism in health and disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5(Suppl 1):S23–S30
Almendros I, Wang Y, Gozal D (2014) The polymorphic and contradictory aspects of intermittent hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L129–L140
Narkiewicz K, Somers VK (1997) The sympathetic nervous system and obstructive sleep apnea: implications for hypertension. J Hypertens 15:1613–1619
Elefteriou F, Ahn JD, Takeda S et al (2005) Leptin regulation of bone resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and CART. Nature 434:514–520
Kondo H, Takeuchi S, Togari A (2013) Beta-adrenergic signaling stimulates osteoclastogenesis via reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304:E507–E515
Luyster FS, Strollo PJ, Zee PC, Walsh JK, Sleep BDAA (2012) Sleep: a health imperative. Sleep 35:727–734
Liu J, Huang F, He HW (2013) Melatonin effects on hard tissues: bone and tooth. Int J Mol Sci 14:10063–10074
Cardinali DP, Ladizesky MG, Boggio V, Cutrera RA, Mautalen C (2003) Melatonin effects on bone: experimental facts and clinical perspectives. J Pineal Res 34:81–87
Kheirandish-Gozal L, Peris E, Gozal D (2014) Vitamin D levels and obstructive sleep apnea in children. Sleep Med 15:459–463
Bozkurt NC, Cakal E, Sahin M, Ozkaya EC, Firat H, Delibasi T (2012) The relation of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin-D levels with severity of obstructive sleep apnea and glucose metabolism abnormalities. Endocrine 41:518–525
Malavolta N, Pratelli L, Frigato M, Mule R, Mascia ML, Gnudi S (2005) The relationship of vitamin D status to bone mineral density in an Italian population of postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 16:1691–1697
Cauley JA, Parimi N, Ensrud KE et al (2010) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and the risk of hip and nonspine fractures in older men. J Bone Miner Res 25:545–553
Calvin AD, Albuquerque FN, Lopez-Jimenez F, Somers VK (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea, inflammation, and the metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 7:271–278
Arnett TR, Gibbons DC, Utting JC, Orriss IR, Hoebertz A, Rosendaal M, Meghji S (2003) Hypoxia is a major stimulator of osteoclast formation and bone resorption. J Cell Physiol 196:2–8
Guner I, Uzun DD, Yaman MO et al (2013) The effect of chronic long-term intermittent hypobaric hypoxia on bone mineral density in rats: role of nitric oxide. Biol Trace Elem Res 154:262–267
Santamaria JD, Prior JC, Fleetham JA (1988) Reversible reproductive dysfunction in men with obstructive sleep apnoea. Clin Endocrinol 28:461–470
Attal P, Chanson P (2010) Endocrine aspects of obstructive sleep apnea. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 95:483–495
Chakhtoura M, Nasrallah M, Chami H (2015) Bone loss in obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: a review of literature. Journal of clinical sleep medicine : JCSM : official publication of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine 11:575–580
St-Onge MP, O’Keeffe M, Roberts AL, RoyChoudhury A, Laferrere B (2012) Short sleep duration, glucose dysregulation and hormonal regulation of appetite in men and women. Sleep 35:1503–1510
Moseley KF (2012) Type 2 diabetes and bone fractures. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 19:128–135
Strohl KP, Saunders NA, Feldman NT, Hallett M (1978) Obstructive sleep apnea in family members. N Engl J Med 299:969–973
Friberg D, Gazelius B, Hokfelt T, Nordlander B (1997) Abnormal afferent nerve endings in the soft palatal mucosa of sleep apnoics and habitual snorers. Regul Pept 71:29–36
Song L, Liang X, Zhou Y (2014) Estrogen-mimicking isoflavone genistein prevents bone loss in a rat model of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:1687–1694
Torres M, Montserrat JM, Pavia J, Dalmases M, Ros D, Fernandez Y, Barbe F, Navajas D, Farre R (2013) Chronic intermittent hypoxia preserves bone density in a mouse model of sleep apnea. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 189:646–648
Carreras A, Almendros I, Acerbi I, Montserrat JM, Navajas D, Farre R (2009) Obstructive apneas induce early release of mesenchymal stem cells into circulating blood. Sleep 32:117–119
Oishi S, Shimizu Y, Hosomichi J et al (2016) Intermittent hypoxia induces disturbances in craniofacial growth and defects in craniofacial morphology. Arch Oral Biol 61:115–124
Heaney RP, Abrams S, Dawson-Hughes B, Looker A, Marcus R, Matkovic V, Weaver C (2000) Peak bone mass. Osteoporos Int 11:985–1009
Woolf AD, Akesson K (2003) Preventing fractures in elderly people. BMJ 327:89–95
Nordstrom A, Karlsson C, Nyquist F, Olsson T, Nordstrom P, Karlsson M (2005) Bone loss and fracture risk after reduced physical activity. J Bone Miner Res 20:202–207
Sforza E, Saint Martin M, Thomas T, Collet P, Garet M, Barthelemy JC, Roche F (2016) Risk factors of osteoporosis in healthy elderly with unrecognized obstructive sleep apnea: role of physical activity. Sleep Med 22:25–32
Cummings SR, Bates D, Black DM (2002) Clinical use of bone densitometry: scientific review. JAMA 288:1889–1897
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the operating grant from the Alberta Innovates—Health Solutions (AIHS, Grant RES0027174) and a studentship to Hazem Eimar and Humam Saltaji from the AIHS. We also thank Liza Chan for her excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 139 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eimar, H., Saltaji, H., Ghorashi, S. et al. Association between sleep apnea and low bone mass in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 28, 1835–1852 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-3912-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-3912-8