Abstract
Summary
Bone mineral density (BMD) of offspring was significantly associated with their parents’ BMD. Parental BMD Z-score ≤−1 was a significant predictor for BMD Z-score ≤−1 in their offspring. Peak bone mass acquisition during early adulthood is more substantially influenced by genetic factors rather than lifestyle or environmental factors.
Introduction
A person’s BMD is affected by both genetic and environmental factors. Family history of osteoporosis or fragility fracture is a well-known risk factor for low bone mass or fracture. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the familial association of BMD between parents and offspring in Korean population.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study based on the data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) conducted from 2008 to 2011. A total of 5947 subjects (3135 parents and 2812 offspring) were included.
Results
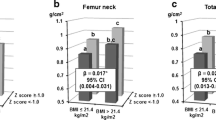
In age-adjusted partial correlation analyses, all BMD values acquired from the lumbar spine, femur neck, total hip, and whole body showed significant associations between parents and offspring. Among these associations, whole-body BMD showed the strongest relationship between offspring and parents. The narrow-sense heritability of BMD ranged from 0.203 to 0.542 in male offspring and from 0.396 to 0.689 in female offspring. Multiple linear regression analyses showed that offspring’s BMD was independently associated with BMD of both parents after adjusting for covariates. Lifestyle or environmental factors including dietary calcium intake, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level, regular exercise, current smoking, and alcohol intake showed only moderate or no associations with BMD. In multiple logistic regression analyses in offspring aged 19–25 years, the son’s risk of having BMD Z-score ≤−1 was associated with both parents’ BMD Z-score ≤−1, while the daughter’s risk was only associated with maternal BMD Z-score ≤−1.
Conclusions
Our findings confirm the strong familial association of BMD between parents and offspring in Korean population and suggest that peak bone mass acquisition during early adulthood is more substantially influenced by genetic factors rather than lifestyle or environmental factors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper C (1997) The crippling consequences of fractures and their impact on quality of life. Am J Med 103:12S–17S
Kado DM, Browner WS, Palermo L, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, Cummings SR (1999) Vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Arch Intern Med 159:1215–1220
Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ 3rd (1992) Hip fractures in the elderly: a world-wide projection. Osteoporos Int 2:285–289
Lee J, Lee S, Jang S, Ryu OH (2013) Age-related changes in the prevalence of osteoporosis according to gender and skeletal site: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 28:180–191
Lee YK, Yoon BH, Koo KH (2013) Epidemiology of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures in South Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 28:90–93
Kelly PJ, Eisman JA, Sambrook PN (1990) Interaction of genetic and environmental influences on peak bone density. Osteoporos Int 1:56–60
Bonjour JP, Theintz G, Buchs B, Slosman D, Rizzoli R (1991) Critical years and stages of puberty for spinal and femoral bone mass accumulation during adolescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 73:555–563
Sigurdsson G, Halldorsson BV, Styrkarsdottir U, Kristjansson K, Stefansson K (2008) Impact of genetics on low bone mass in adults. J Bone Miner Res 23:1584–1590
Deng HW, Chen WM, Conway T, Zhou Y, Davies KM, Stegman MR, Deng H, Recker RR (2000) Determination of bone mineral density of the hip and spine in human pedigrees by genetic and life-style factors. Genet Epidemiol 19:160–177
Mitchell BD, Kammerer CM, Schneider JL, Perez R, Bauer RL (2003) Genetic and environmental determinants of bone mineral density in Mexican Americans: results from the San Antonio Family Osteoporosis Study. Bone 33:839–846
Lee M, Czerwinski SA, Choh AC, Demerath EW, Sun SS, Chumlea WC, Towne B, Siervogel RM (2006) Unique and common genetic effects between bone mineral density and calcaneal quantitative ultrasound measures: the Fels Longitudinal Study. Osteoporos Int 17:865–871
Peacock M, Turner CH, Econs MJ, Foroud T (2002) Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev 23:303–326
Yang TL, Zhao LJ, Liu YJ, Liu JF, Recker RR, Deng HW (2006) Genetic and environmental correlations of bone mineral density at different skeletal sites in females and males. Calcif Tissue Int 78:212–217
Ng MY, Sham PC, Paterson AD, Chan V, Kung AW (2006) Effect of environmental factors and gender on the heritability of bone mineral density and bone size. Ann Hum Genet 70:428–438
Deng FY, Lei SF, Li MX, Jiang C, Dvornyk V, Deng HW (2006) Genetic determination and correlation of body mass index and bone mineral density at the spine and hip in Chinese Han ethnicity. Osteoporos Int 17:119–124
Liu PY, Qin YJ, Zhou Q, Recker RR, Deng HW (2004) Complex segregation analyses of bone mineral density in Chinese. Ann Hum Genet 68:154–164
Bonjour JP, Carrie AL, Ferrari S, Clavien H, Slosman D, Theintz G, Rizzoli R (1997) Calcium-enriched foods and bone mass growth in prepubertal girls: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Invest 99:1287–1294
Johnston CC Jr, Miller JZ, Slemenda CW, Reister TK, Hui S, Christian JC, Peacock M (1992) Calcium supplementation and increases in bone mineral density in children. N Engl J Med 327:82–87
Zhu K, Du X, Greenfield H, Zhang Q, Ma G, Hu X, Fraser DR (2004) Bone mass in Chinese premenarcheal girls: the roles of body composition, calcium intake and physical activity. Br J Nutr 92:985–993
Courteix D, Jaffre´ C, Lespessailles E, Benhamou L (2005) Cumulative effects of calcium supplementation and physical activity on bone accretion in premenarchal children: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial. Int J Sports Med 26:332–338
MacKelvie KJ, Khan KM, McKay HA (2002) Is there a critical period for bone response to weight-bearing exercise in children and adolescents? A systematic review. Br J Sports Med 36:250–257
Welten DC, Kemper HC, Post GB, Van Mechelen W, Twisk J, Lips P, Teule GJ (1994) Weight-bearing activity during youth is a more important factor for peak bone mass than calcium intake. J Bone Miner Res 9:1089–1096
Pollitzer WS, Anderson JJ (1989) Ethnic and genetic differences in bone mass: a review with a hereditary vs. environmental perspective. Am J Clin Nutr 50:1244–1259
Ohta H, Kuroda T, Onoe Y, Nakano C, Yoshikata R, Ishitani K, Hashimoto K, Kume M (2010) Familial correlation of bone mineral density, birth data and lifestyle factors among adolescent daughters, mothers and grandmothers. J Bone Miner Metab 28:690–695
Kuroda T, Onoe Y, Miyabara Y, Yoshikata R, Orito S, Ishitani K, Okano H, Ohta H (2009) Influence of maternal genetic and lifestyle factors on bone mineral density in adolescent daughters: a cohort study in 387 Japanese daughter-mother pairs. J Bone Miner Metab 27:379–385
Keller LF, Grant PR, Grant BR, Petren K (2001) Heritability of morphological traits in Darwin’s finches: misidentified paternity and maternal effects. Heredity (Edinb) 87(Pt 3):325–336
Ralston SH, Uitterlinden AG (2010) Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev 31:629–662
Richards JB, Zheng HF, Spector TD (2012) Genetics of osteoporosis from genome-wide association studies: advances and challenges. Nat Rev Genet 13:576–588
Rivadeneira F, Styrkársdottir U, Estrada K, Halldórsson BV, Hsu YH, Richards JB, Zillikens MC, Kavvoura FK, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Cupples LA, Deloukas P, Demissie S, Grundberg E, Hofman A, Kong A, Karasik D, van Meurs JB, Oostra B, Pastinen T, Pols HA, Sigurdsson G, Soranzo N, Thorleifsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Williams FM, Wilson SG, Zhou Y, Ralston SH, van Duijn CM, Spector T, Kiel DP, Stefansson K, Ioannidis JP, Uitterlinden AG, Genetic Factors for Osteoporosis (GEFOS) Consortium (2009) Twenty bone-mineral-density loci identified by large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Nature Genet 41:1199–1206
Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OM, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, Minster RL, Moayyeri A, Vandenput L, Willner D, Xiao SM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Zheng HF, Alonso N, Eriksson J, Kammerer CM, Kaptoge SK, Leo PJ, Thorleifsson G, Wilson SG, Wilson JF, Aalto V, Alen M, Aragaki AK, Aspelund T, Center JR, Dailiana Z, Duggan DJ, Garcia M, Garcia-Giralt N, Giroux S, Hallmans G, Hocking LJ, Husted LB, Jameson KA, Khusainova R, Kim GS, Kooperberg C, Koromila T, Kruk M, Laaksonen M, Lacroix AZ, Lee SH, Leung PC, Lewis JR, Masi L, Mencej-Bedrac S, Nguyen TV, Nogues X, Patel MS, Prezelj J, Rose LM, Scollen S, Siggeirsdottir K, Smith AV, Svensson O, Trompet S, Trummer O, van Schoor NM, Woo J, Zhu K, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Buckley BM, Cheng S, Christiansen C, Cooper C, Dedoussis G, Ford I, Frost M, Goltzman D, González-Macías J, Kähönen M, Karlsson M, Khusnutdinova E, Koh JM, Kollia P, Langdahl BL, Leslie WD, Lips P, Ljunggren Ö, Lorenc RS, Marc J, Mellström D, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Olmos JM, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Reid DM, Riancho JA, Ridker PM, Rousseau F, Slagboom PE, Tang NL, Urreizti R, Van Hul W, Viikari J, Zarrabeitia MT, Aulchenko YS, Castano-Betancourt M, Grundberg E, Herrera L, Ingvarsson T, Johannsdottir H, Kwan T, Li R, Luben R, Medina-Gómez C, Palsson ST, Reppe S, Rotter JI, Sigurdsson G, van Meurs JB, Verlaan D, Williams FM, Wood AR, Zhou Y, Gautvik KM, Pastinen T, Raychaudhuri S, Cauley JA, Chasman DI, Clark GR, Cummings SR, Danoy P, Dennison EM, Eastell R, Eisman JA, Gudnason V, Hofman A, Jackson RD, Jones G, Jukema JW, Khaw KT, Lehtimäki T, Liu Y, Lorentzon M, McCloskey E, Mitchell BD, Nandakumar K, Nicholson GC, Oostra BA, Peacock M, Pols HA, Prince RL, Raitakari O, Reid IR, Robbins J, Sambrook PN, Sham PC, Shuldiner AR, Tylavsky FA, van Duijn CM, Wareham NJ, Cupples LA, Econs MJ, Evans DM, Harris TB, Kung AW, Psaty BM, Reeve J, Spector TD, Streeten EA, Zillikens MC, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ohlsson C, Karasik D, Richards JB, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ralston SH, Ioannidis JP, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F (2012) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nature Genet 44:491–501
Perusse L, Leblanc C, Bouchard C (1988) Familial resemblance in lifestyle components: results from the Canada Fitness Survey. Can J Public Health 79:201–205
Gottlieb NH, Baker JA (1986) The relative influence of health beliefs, parental and peer behaviors and exercise program participation on smoking, alcohol use and physical activity. Soc Sci Med 22:915–927
Kim SH, Oh MK, Namgung R, Park MJ (2014) Prevalence of 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency in Korean adolescents: association with age, season and parental vitamin D status. Public Health Nutr 17:122–130
Danielson ME, Cauley JA, Baker CE, Newman AB, Dorman JS, Towers JD, Kuller LH (1999) Familial resemblance of bone mineral density (BMD) and calcaneal ultrasound attenuation: the BMD in mothers and daughters study. J Bone Miner Res 14:102–110
Michaelsson K, Melhus H, Ferm H, Ahlbom A, Pedersen NL (2005) Genetic liability to fractures in the elderly. Arch Intern Med 165:1825–1830.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2015R1C1A1A01054333) and by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2014R1A6A3A03056928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(DOCX 24 kb)
Table S2
(DOCX 21 kb)
Table S3
(DOCX 21 kb)
Supplemental Fig. 1
Selection of study data. KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. (PPTX 64 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H.S., Park, J.H., Kim, S.H. et al. Strong familial association of bone mineral density between parents and offspring: KNHANES 2008–2011. Osteoporos Int 28, 955–964 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3806-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3806-1