Abstract
Summary
Premenopausal women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a higher prevalence of low bone mineral density and vertebral fractures. Multiple genetic loci for osteoporotic fracture were identified in recent genome-wide association studies. This study provides a novel data demonstrating that receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) polymorphisms likely plays an important role in the bone remodeling process in SLE premenopausal women.
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to evaluate single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the RANKL, RANK, and OPG genes in premenopausal SLE patients and their association with sRANKL and OPG serum levels, vertebral fractures, and bone mineral density (BMD).
Methods
A total of 211 premenopausal SLE patients (American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria) and 154 healthy controls were enrolled. SNPs of RANKL 290A>G (rs2277438), OPG 1181G>C (rs2073618), 245T>G (rs3134069), 163A>G (rs3102735), and RANK A>G (rs3018362) were obtained by real-time PCR. sRANKL/OPG serum levels were determined by ELISA. BMD and vertebral fractures were evaluated by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Results
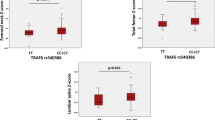
SLE patients and controls had similar frequencies of the RANKL 290 G allele (p = 0.94), OPG 1181 C allele (p = 0.85), OPG 245 G allele (p = 0.85), OPG 163 G allele (p = 0.78), and RANK G allele (p = 0.87). Further analysis of the SLE patients revealed that the frequency of the RANKL 290 G allele was lower in patients with fractures than that in patients without fractures (28.1 vs 46.9 %, p = 0.01). In addition, the frequency of the OPG 245 G allele was higher in patients with low BMD than that in patients with normal BMD (31.4 vs 18.1 %, p = 0.04). No association of OPG 1181 G>C, OPG 163 A>G, and RANK A>G SNPs with BMD/fractures was found. Additionally, no association was observed between RANKL/OPG/RANK SNPs and sRANKL/OPG serum levels.
Conclusions
Our study provides novel data demonstrating that RANKL/OPG genetic variations appear to play a role in bone remodeling, particularly in its major complication, fracture, in premenopausal patients with SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee C, Ramsey-Goldman R (2005) Osteoporosis in systemic lupus erythematosus mechanisms. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 31:363–385
Sinigaglia L, Varenna M, Girasole G, Bianchi G (2006) Epidemiology of osteoporosis in in Rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 32:631–658
Pereira RM, Carvalho JF, Canalis E (2010) Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in rheumatic diseases. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 65:1197–1205
Regio P, Bonfá E, Takayama L, Pereira R (2008) The influence of lean mass in trabecular and cortical bone in juvenile onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 17:787–792
Sinigaglia L, Varenna M, Binelli L, Zucchi F, Ghiringhelli D, Fantini F (2000) Bone mass in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:S27–S34
Bultink IEM, Lems WF, Kostense PJ, Dijkmans BAC, Voskuyl AE (2005) Prevalence of and risk factors for low bone mineral density and vertebral fractures in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis & Rheumatism 54:2044–2050
Arko B, Prezelj J, Komel R, Kocijancic A, Hudler P, Marc J (2002) Sequence variations in the osteoprotegerin gene promoter in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4080–4084
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR, Burgess T et al (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93:165–176
Mencej-Bedrac S, Prezelj J, Marc J (2011) TNFRSF11B gene polymorphisms 1181G>C and 245T>G as well as haplotype CT influence bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Maturitas 69:263–267
Bezerra MC, Carvalho JF, Prokopowitsch AS, Pereira RM (2005) RANK, RANKL and osteoprotegerin in arthritic bone loss. Braz J Med Biol Res 38:161–170
Lane NE (2006) Therapy Insight: osteoporosis and osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2:562–569
Bhalla AK (2010) Management of osteoporosis in a pre-menopausal woman. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 24:313–327
Tan W, Wu H, Zhao J, Derber LA, Lee DM, Shadick NA et al (2010) A functional RANKL polymorphism associated with younger age at onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:2864–2875
Styrkarsdottir U, Halldorsson BV, Gretarsdottir S, Gudbjartsson DF, Walters GB, Ingvarsson T et al (2008) Multiple genetic loci for bone mineral density and fractures. N Engl J Med 358:2355–2365
Langdahl BL, Carstens M, Stenkjaer L, Eriksen EF (2002) Polymorphisms in the osteoprotegerin gene are associated with osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 17:1245–1255
Piedra M, García-Unzueta MT, Berja A, Paule B, Lavin BA, Valero C, Riancho JA, Amado JÁ (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphism of the OPG/RANKL system genes in primary hyperparathyroidism and their relatioship with bone mineral density. BMC Med Genet 20:168
Nguyen TV, Eisman JA (2013) Genetic profiling and individualized assessment of fracture risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9:153–161
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640
Gladman DD, Goldsmith CH, Urowitz MB, Bacon P, Fortin P, Ginzler E et al (2000) The Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology (SLICC/ACR) Damage Index for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus International Comparison. J Rheumatol 27:373–376
Lewiecki EM, Gordon CM, Baim S, Leonard MB, Bishop NJ, Bianchi ML et al (2008) International Society for Clinical Densitometry 2007 Adult and Pediatric Official Positions. Bone 43:1115–1121
Obrant KJ, Bengnér U, Johnell O, Nilsson BE, Sernbo I (1989) Increasing age-adjusted risk of fragility fractures: a sign of increasing osteoporosis in successive generations? Calcif Tissue Int 44:157–167
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Domiciano DS, Figueiredo CP, Lopes JB, Kuroishi ME, Takayama L, Caparbo VF et al (2013) Vertebral fracture assessment by dual X-ray absorptiometry: a valid tool to detect vertebral fractures in community-dwelling older adults in a population-based survey. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 65:809–815
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC (2006) Essential medical statistics, 2nd edn. Blackwell Science, Massachusetts, USA, p 502
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (2000) Applied logistic regression, 2ath edn. Wiley, New York, p 320
Yeap SS, Fauzi AR, Kong NC, Halim AG, Soehardy Z, Rahimah S et al (2009) Influences on bone mineral density in Malaysian premenopausal systemic lupus erythematosus patients on corticosteroids. Lupus 18:178–181
Grossman JM, Gordon R, Ranganath VK, Deal C, Caplan L, Chen W et al (2010) American College of Rheumatology 2010 recommendations for the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Arthr Care Res (Hoboken) 62:1515–1526
Chugh PK (2013) Management of women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Maturitas 75:207–214
Lopes JB, Fung LK, Cha CC, Gabriel GM, Takayama L, Figueiredo CP, Pereira RM (2012) The impact of asymptomatic vertebral fractures on quality of life in older community-dwelling women: the São Paulo Ageing & Health Study. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67:1401–1406
Miyagawa H, Yamai M, Sakaguchi D, Kiyohara C, Tsukamoto H, Kimoto Y et al (2008) Association of polymorphisms in complement component C3 gene with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 47:158–164
Kim JG, Kim JH, Kim JY, Ku SY, Jee BC, Suh CS, Kim SH, Choi YM (2007) Association between osteoprotegerin (OPG), receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK), and RANK ligand (RANKL) gene polymorphisms and circulating OPG, soluble RANKL levels, and bone mineral density in Korean postmenopausal women. Menopause 14(5):913–918
Rhee EJ, Yun EJ, Oh KW, Park SE, Park CY, Lee WY, Park SW, Kim SW, Baek KH, Kang MI (2010) The relationship between receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL) gene polymorphism and aortic calcification in Korean women. Endocr J 57(6):541–549
Kearns AE, Khosla S, Kostenuik PJ (2008) Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease. Endocr Rev 29:155–192
Hawa G, Brinskelle-Schmal N, Glatz K, Maitzen S, Woloszczuk W (2003) Immunoassay for soluble RANKL (receptor activator of NF-B ligand) in serum. Clin Lab 49:461–463
Ueland T, Bollerslev J, Wilson SG, Dick IM, Islam FM, Mullin BH et al (2007) No associations between OPG gene polymorphisms or serum levels and measures of osteoporosis in elderly Australian women. Bone 40:175–181
Jørgensen HL, Kusk P, Madsen B, Fenger M, Lauritzen JB (2004) Serum osteoprotegerin (OPG) and the A163G polymorphism in the OPG promoter region are related to peripheral measures of bone mass and fracture odds ratios. J Bone Miner Metab 22:132–138
Acknowledgments
We thank Jackeline C Alvarenga and Liliam Takayama for technical support and Dr Rogerio Ruscitto for statistical analysis.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPQ #301805/2013-0 and #472754/2013-0 to RMRP and #301411/2009-3 to EB) and Federico Foundation (to RMRP and EB) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES to ACB).
Conflicts of interest
Alessandra C Bonfa, Luciana PC Seguro, Valeria F Caparbo, Eloisa Bonfa, and Rosa Maria Rodrigues Pereira declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonfá, A.C., Seguro, L.P.C., Caparbo, V. et al. RANKL and OPG gene polymorphisms: associations with vertebral fractures and bone mineral density in premenopausal systemic lupus erythematosus. Osteoporos Int 26, 1563–1571 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3029-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3029-x