Abstract
Summary
This study provides novel evidence that sex determining region Y (SRY)-box (SOX6) and runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) play essential roles in the communication of chondrocyte and osteoblast. Our findings open a new avenue to the limited understanding of the coordination effect between chondrogenesis and osteogenesis.
Introduction
Sox6 and Runx2 are two new susceptibility genes for osteoporosis identified by genome-wide association studies, but the functions of these genes in osteogenesis remain unclear. Both genes are essential transcription factors in chondrogenesis, which reminds us that SOX6 and RUNX2 might be involved in the coordination of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the functions of SOX6 and RUNX2 in the coupling regulation of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis.
Methods
We established a chondrogenic differentiation model of ATDC5 cell and profiled the expression of SOX6 and RUNX2 during chondroblast differentiation. We co-cultured osteoblast cells with ATDC5 cells in different differentiation stages and examined the proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and differentiation of osteoblast cells. SOX6 or RUNX2 was knocked down using specific siRNA and the effect was examined.
Results
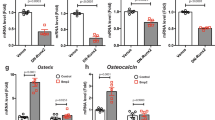
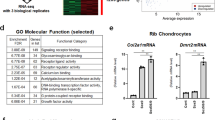
During chondrogenic differentiation, SOX6 and RUNX2 expressed sequentially in the proliferating and hypertrophic stages. Proliferative ATDC5 cells stimulated the multiplication of osteoblasts and promoted more osteoblasts to enter S-phase. Hypertrophic ATDC5 cells enhanced the differentiation of osteoblasts. Yet, the apoptosis of osteoblasts was neither affected by proliferating nor hypertrophic ATDC5 cells. Knockdown of SOX6 in proliferating ATDC5 cells significantly repressed the stimulation of osteoblast multiplication, whereas depletion of RUNX2 in hypertrophic ATDC5 cells retarded the expression of osteoblastic markers.
Conclusions
Our study first reveals that SOX6 and RUNX2 play important roles in the chondrogenesis–osteogenesis coordination. This finding enriches the limited understanding about this coordination and unravels the novel function of SOX6 and RUNX2 in the endochondral ossification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y (2009) Skeletal morphogenesis during embryonic development. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 19:197–218
Long F, Ornitz DM (2013) Development of the endochondral skeleton. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a008334
Colnot C (2005) Cellular and molecular interactions regulating skeletogenesis. J Cell Biochem 95:688–697
Hojo H, Ohba S, Yano F, Chung UI (2010) Coordination of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis by hypertrophic chondrocytes in endochondral bone development. J Bone Miner Metab 28:489–502
Liu Z, Xu J, Colvin JS, Ornitz DM (2002) Coordination of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis by fibroblast growth factor 18. Genes Dev 16:859–869
Wang W, Lian N, Li L, Moss HE, Perrien DS, Elefteriou F, Yang X (2009) Atf4 regulates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation during endochondral ossification by activating Ihh transcription. Development 136:4143–4153
Wang W, Lian N, Ma Y, Li L, Gallant RC, Elefteriou F, Yang X (2012) Chondrocytic Atf4 regulates osteoblast differentiation and function via Ihh. Development 139:601–611
Chung UI, Lanske B, Lee K, Li E, Kronenberg H (1998) The parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor coordinates endochondral bone development by directly controlling chondrocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13030–13035
Schipani E, Lanske B, Hunzelman J, Luz A, Kovacs CS, Lee K, Pirro A, Kronenberg HM, Juppner H (1997) Targeted expression of constitutively active receptors for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide delays endochondral bone formation and rescues mice that lack parathyroid hormone-related peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:13689–13694
Chung UI, Schipani E, McMahon AP, Kronenberg HM (2001) Indian hedgehog couples chondrogenesis to osteogenesis in endochondral bone development. J Clin Invest 107:295–304
Griffin M, Hindocha S, Khan WS (2012) Chondrogenic differentiation of adult MSCs. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 7:260–265
Lefebvre V, Smits P (2005) Transcriptional control of chondrocyte fate and differentiation. Birth Defects Res C Embryol Today 75:200–212
Ikeda T, Kawaguchi H, Kamekura S, Ogata N, Mori Y, Nakamura K, Ikegawa S, Chung UI (2005) Distinct roles of Sox5, Sox6, and Sox9 in different stages of chondrogenic differentiation. J Bone Miner Metab 23:337–340
Solomon LA, Berube NG, Beier F (2008) Transcriptional regulators of chondrocyte hypertrophy. Birth Defects Res C Embryol Today 84:123–130
Hsu YH, Zillikens MC, Wilson SG, Farber CR, Demissie S, Soranzo N, Bianchi EN, Grundberg E, Liang L, Richards JB, Estrada K, Zhou Y, van Nas A, Moffatt MF, Zhai G, Hofman A, van Meurs JB, Pols HA, Price RI, Nilsson O, Pastinen T, Cupples LA, Lusis AJ, Schadt EE, Ferrari S, Uitterlinden AG, Rivadeneira F, Spector TD, Karasik D, Kiel DP (2010) An integration of genome-wide association study and gene expression profiling to prioritize the discovery of novel susceptibility loci for osteoporosis-related traits. PLoS Genet 6:e1000977
Rivadeneira F, Styrkarsdottir U, Estrada K, Halldorsson BV, Hsu YH, Richards JB, Zillikens MC, Kavvoura FK, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Cupples LA, Deloukas P, Demissie S, Grundberg E, Hofman A, Kong A, Karasik D, van Meurs JB, Oostra B, Pastinen T, Pols HA, Sigurdsson G, Soranzo N, Thorleifsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Williams FM, Wilson SG, Zhou Y, Ralston SH, van Duijn CM, Spector T, Kiel DP, Stefansson K, Ioannidis JP, Uitterlinden AG (2009) Twenty bone-mineral-density loci identified by large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 41:1199–1206
Styrkarsdottir U, Halldorsson BV, Gudbjartsson DF, Tang NL, Koh JM, Xiao SM, Kwok TC, Kim GS, Chan JC, Cherny S, Lee SH, Kwok A, Ho S, Gretarsdottir S, Kostic JP, Palsson ST, Sigurdsson G, Sham PC, Kim BJ, Kung AW, Kim SY, Woo J, Leung PC, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2010) European bone mineral density loci are also associated with BMD in East-Asian populations. PLoS ONE 5:e13217
Yang TL, Guo Y, Liu YJ, Shen H, Liu YZ, Lei SF, Li J, Tian Q, Deng HW (2012) Genetic variants in the SOX6 gene are associated with bone mineral density in both Caucasian and Chinese populations. Osteoporos Int 23:781–787
Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OM, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, Minster RL, Moayyeri A, Vandenput L, Willner D, Xiao SM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Zheng HF, Alonso N, Eriksson J, Kammerer CM, Kaptoge SK, Leo PJ, Thorleifsson G, Wilson SG, Wilson JF, Aalto V, Alen M, Aragaki AK, Aspelund T, Center JR, Dailiana Z, Duggan DJ, Garcia M, Garcia-Giralt N, Giroux S, Hallmans G, Hocking LJ, Husted LB, Jameson KA, Khusainova R, Kim GS, Kooperberg C, Koromila T, Kruk M, Laaksonen M, Lacroix AZ, Lee SH, Leung PC, Lewis JR, Masi L, Mencej-Bedrac S, Nguyen TV, Nogues X, Patel MS, Prezelj J, Rose LM, Scollen S, Siggeirsdottir K, Smith AV, Svensson O, Trompet S, Trummer O, van Schoor NM, Woo J, Zhu K, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Buckley BM, Cheng S, Christiansen C, Cooper C, Dedoussis G, Ford I, Frost M, Goltzman D, Gonzalez-Macias J, Kahonen M, Karlsson M, Khusnutdinova E, Koh JM, Kollia P, Langdahl BL, Leslie WD, Lips P, Ljunggren O, Lorenc RS, Marc J, Mellstrom D, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Olmos JM, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Reid DM, Riancho JA, Ridker PM, Rousseau F, Slagboom PE, Tang NL, Urreizti R, Van Hul W, Viikari J, Zarrabeitia MT, Aulchenko YS, Castano-Betancourt M, Grundberg E, Herrera L, Ingvarsson T, Johannsdottir H, Kwan T, Li R, Luben R, Medina-Gomez C, Palsson ST, Reppe S, Rotter JI, Sigurdsson G, van Meurs JB, Verlaan D, Williams FM, Wood AR, Zhou Y, Gautvik KM, Pastinen T, Raychaudhuri S, Cauley JA, Chasman DI, Clark GR, Cummings SR, Danoy P, Dennison EM, Eastell R, Eisman JA, Gudnason V, Hofman A, Jackson RD, Jones G, Jukema JW, Khaw KT, Lehtimaki T, Liu Y, Lorentzon M, McCloskey E, Mitchell BD, Nandakumar K, Nicholson GC, Oostra BA, Peacock M, Pols HA, Prince RL, Raitakari O, Reid IR, Robbins J, Sambrook PN, Sham PC, Shuldiner AR, Tylavsky FA, van Duijn CM, Wareham NJ, Cupples LA, Econs MJ, Evans DM, Harris TB, Kung AW, Psaty BM, Reeve J, Spector TD, Streeten EA, Zillikens MC, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ohlsson C, Karasik D, Richards JB, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ralston SH, Ioannidis JP, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F (2012) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nat Genet 44:491–501
Hoemann CD, Lafantaisie-Favreau CH, Lascau-Coman V, Chen G, Guzman-Morales J (2012) The cartilage-bone interface. J Knee Surg 25:85–97
Hagiwara N (2011) Sox6, jack of all trades: a versatile regulatory protein in vertebrate development. Dev Dyn 240:1311–1321
Takarada T, Hinoi E, Nakazato R, Ochi H, Xu C, Tsuchikane A, Takeda S, Karsenty G, Abe T, Kiyonari H, Yoneda Y (2013) An analysis of skeletal development in osteoblast-specific and chondrocyte-specific runt-related transcription factor-2 (Runx2) knockout mice. J Bone Miner Res 28:2064–2069
Yamashita S, Andoh M, Ueno-Kudoh H, Sato T, Miyaki S, Asahara H (2009) Sox9 directly promotes Bapx1 gene expression to repress Runx2 in chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res 315:2231–2240
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471188, 31371278, 81300716), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20120201120089), Scientific Research Fund of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Health (2012D59), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 198 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, TL., Li, X. et al. Functional analyses reveal the essential role of SOX6 and RUNX2 in the communication of chondrocyte and osteoblast. Osteoporos Int 26, 553–561 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2882-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2882-3