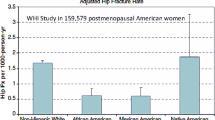
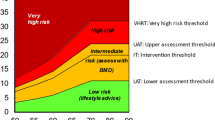
Abstract
Patients with celiac disease (CD) have low bone mineral density. Evidence of increased fracture risk in these patients is conflicting, and the indication for bone mineral density screening of all adult CD patients is debated. Our aim was to review current published data on fractures in CD. Cross-sectional cohort studies and one case study were identified by searching Medline and Embase. Although the identified studies are heterogeneous and difficult to compare, the overall findings indicate a positive association between CD and risk of fracture. Adult patients with CD should be considered for bone densitometry in order to estimate fracture risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dube C, Rostom A, Sy R, Cranney A, Saloojee N, Garritty C, Sampson M, Zhang L, Yazdi F, Mamaladze V, Pan I, Macneil J, Mack D, Patel D, Moher D (2005) The prevalence of celiac disease in average-risk and at-risk Western European populations: a systematic review. Gastroenterology 128(4 Suppl 1):S57–S67
Lohi S, Mustalahti K, Kaukinen K, Laurila K, Collin P, Rissanen H, Lohi O, Bravi E, Gasparin M, Reunanen A, Maki M (2007) Increasing prevalence of coeliac disease over time. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26(9):1217–1225. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03502
Catassi C, Kryszak D, Bhatti B, Sturgeon C, Helzlsouer K, Clipp SL, Gelfond D, Puppa E, Sferruzza A, Fasano A (2010) Natural history of celiac disease autoimmunity in a USA cohort followed since 1974. Ann Med 42(7):530–538. doi:10.3109/07853890.2010.514285
Rubio-Tapia A, Kyle RA, Kaplan EL, Johnson DR, Page W, Erdtmann F, Brantner TL, Kim WR, Phelps TK, Lahr BD, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ 3rd, Murray JA (2009) Increased prevalence and mortality in undiagnosed celiac disease. Gastroenterology 137(1):88–93. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.03.059
Ciacci C, Cirillo M, Sollazzo R, Savino G, Sabbatini F, Mazzacca G (1995) Gender and clinical presentation in adult celiac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 30(11):1077–1081
West J, Logan RF, Smith CJ, Hubbard RB, Card TR (2004) Malignancy and mortality in people with coeliac disease: population based cohort study. BMJ 329(7468):716–719. doi:10.1136/bmj.38169.486701.7C
Smedby KE, Akerman M, Hildebrand H, Glimelius B, Ekbom A, Askling J (2005) Malignant lymphomas in coeliac disease: evidence of increased risks for lymphoma types other than enteropathy-type T cell lymphoma. Gut 54(1):54–59. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.032094
Askling J, Linet M, Gridley G, Halstensen TS, Ekstrom K, Ekbom A (2002) Cancer incidence in a population-based cohort of individuals hospitalized with celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis. Gastroenterology 123(5):1428–1435
Corrao G, Corazza GR, Bagnardi V, Brusco G, Ciacci C, Cottone M, Sategna Guidetti C, Usai P, Cesari P, Pelli MA, Loperfido S, Volta U, Calabro A, Certo M (2001) Mortality in patients with coeliac disease and their relatives: a cohort study. Lancet 358(9279):356–361
Green PH, Cellier C (2007) Celiac disease. N Engl J Med 357(17):1731–1743
Scanlon SA, Murray JA (2011) Update on celiac disease - etiology, differential diagnosis, drug targets, and management advances. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 4:297–311. doi:10.2147/ceg.s8315
Kanis JA (2002) Diagnosis of osteoporosis and assessment of fracture risk. Lancet 359(9321):1929–1936. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08761-5
Hillier TA, Stone KL, Bauer DC, Rizzo JH, Pedula KL, Cauley JA, Ensrud KE, Hochberg MC, Cummings SR (2007) Evaluating the value of repeat bone mineral density measurement and prediction of fractures in older women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. Arch Intern Med 167(2):155–160. doi:10.1001/archinte.167.2.155
Oyen J, Brudvik C, Gjesdal CG, Tell GS, Lie SA, Hove LM (2011) Osteoporosis as a risk factor for distal radial fractures: a case-control study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93(4):348–356. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.00303
Casella S, Zanini B, Lanzarotto F, Villanacci V, Ricci C, Lanzini A (2012) Celiac disease in elderly adults: clinical, serological, and histological characteristics and the effect of a gluten-free diet. J Am Geriatr Soc 60(6):1064–1069. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.03997.x
Meyer D, Stavropolous S, Diamond B, Shane E, Green PH (2001) Osteoporosis in a North American adult population with celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 96(1):112–119. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03507.x
Duerksen DR, Leslie WD (2010) Positive celiac disease serology and reduced bone mineral density in adult women. Can J Gastroenterol 24(2):103–107
Corazza GR, Di Sario A, Cecchetti L, Tarozzi C, Corrao G, Bernardi M, Gasbarrini G (1995) Bone mass and metabolism in patients with celiac disease. Gastroenterology 109(1):122–128
Bianchi ML, Bardella MT (2008) Bone in celiac disease. Osteoporos Int 19(12):1705–1716. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0624-0
Szymczak J, Bohdanowicz-Pawlak A, Waszczuk E, Jakubowska J (2012) Low bone mineral density in adult patients with coeliac disease. Endokrynol Pol 63(4):270–276
Wishart J, Horowitz M, Need A, Nordin BE (1990) Relationship between forearm and vertebral mineral density in postmenopausal women with primary hyperparathyroidism. Arch Intern Med 150(6):1329–1331
Selby PL, Davies M, Adams JE, Mawer EB (1999) Bone loss in celiac disease is related to secondary hyperparathyroidism. J Bone Miner Res 14(4):652–657. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.4.652
Garcia-Manzanares A, Tenias JM, Lucendo AJ (2012) Bone mineral density directly correlates with duodenal Marsh stage in newly diagnosed adult celiac patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 8–9(47):927–936. doi:10.3109/00365521.2012.688217
Rodrigo L (2006) Celiac disease. World J Gastroenterol 12(41):6585–6593
Sategna-Guidetti C, Grosso SB, Grosso S, Mengozzi G, Aimo G, Zaccaria T, Di Stefano M, Isaia GC (2000) The effects of 1-year gluten withdrawal on bone mass, bone metabolism and nutritional status in newly-diagnosed adult coeliac disease patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14(1):35–43
Kemppainen T, Kroger H, Janatuinen E, Arnala I, Lamberg-Allardt C, Karkkainen M, Kosma VM, Julkunen R, Jurvelin J, Alhava E, Uusitupa M (1999) Bone recovery after a gluten-free diet: a 5-year follow-up study. Bone 25(3):355–360
Bai JC, Gonzalez D, Mautalen C, Mazure R, Pedreira S, Vazquez H, Smecuol E, Siccardi A, Cataldi M, Niveloni S, Boerr LA, Maurino E (1997) Long-term effect of gluten restriction on bone mineral density of patients with coeliac disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 11(1):157–164
Goddard CJ, Gillett HR (2006) Complications of coeliac disease: are all patients at risk? Postgrad Med J 82(973):705–712. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2006.048876
Valdimarsson T, Lofman O, Toss G, Strom M (1996) Reversal of osteopenia with diet in adult coeliac disease. Gut 38(3):322–327
McFarlane XA, Bhalla AK, Reeves DE, Morgan LM, Robertson DA (1995) Osteoporosis in treated adult coeliac disease. Gut 36(5):710–714
Lucendo AJ, Garcia-Manzanares A (2013) Bone mineral density in adult coeliac disease: an updated review. Rev Esp Enferm Dig Organo Off Soc Esp Patol Dig 105(3):154–162
Leffler DA, Edwards-George J, Dennis M, Schuppan D, Cook F, Franko DL, Blom-Hoffman J, Kelly CP (2008) Factors that influence adherence to a gluten-free diet in adults with celiac disease. Dig Dis Sci 53(6):1573–1581. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-0055-3
Rastogi A, Bhadada SK, Bhansali A, Kochhar R, Santosh R (2012) Celiac disease: a missed cause of metabolic bone disease. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 16(5):780–785. doi:10.4103/2230-8210.100674
Kanis JA, Borgstrom F, De Laet C, Johansson H, Johnell O, Jonsson B, Oden A, Zethraeus N, Pfleger B, Khaltaev N (2005) Assessment of fracture risk. Osteoporos Int 16(6):581–589. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1780-5
Valdimarsson T, Toss G, Lofman O, Strom M (2000) Three years’ follow-up of bone density in adult coeliac disease: significance of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Scand J Gastroenterol 35(3):274–280
West J, Logan RF, Hill PG, Khaw KT (2007) The iceberg of celiac disease: what is below the waterline? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(1):59–62. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2006.10.020
Fouda MA, Khan AA, Sultan MS, Rios LP, McAssey K, Armstrong D (2012) Evaluation and management of skeletal health in celiac disease: position statement. Can J Gastroenterol 26(11):819–829
Turner J, Pellerin G, Mager D (2009) Prevalence of metabolic bone disease in children with celiac disease is independent of symptoms at diagnosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 49(5):589–593. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e31819ca18e
Delco F, El-Serag HB, Sonnenberg A (1999) Celiac sprue among US military veterans: associated disorders and clinical manifestations. Dig Dis Sci 44(5):966–972
Zittermann A (2003) Vitamin D in preventive medicine: are we ignoring the evidence? Br J Nutr 89(5):552–572. doi:10.1079/bjn2003837
Lerner A, Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Pacht A, Ben-Ami Shor D, Lopez HM, Sanchez-Castanon M, Shoenfeld Y (2012) The clinical significance of 25OH-vitamin D status in celiac disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 42(3):322–330. doi:10.1007/s12016-010-8237-8
Fornari MC, Pedreira S, Niveloni S, Gonzalez D, Diez RA, Vazquez H, Mazure R, Sugai E, Smecuol E, Boerr L, Maurino E, Bai JC (1998) Pre- and post-treatment serum levels of cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, and IL-1 receptor antagonist in celiac disease. Are they related to the associated osteopenia? Am J Gastroenterol 93(3):413–418. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00413.x
Jameson S (2000) Coeliac disease, insulin-like growth factor, bone mineral density, and zinc. Scand J Gastroenterol 35(8):894–896
Devine A, Rosen C, Mohan S, Baylink D, Prince RL (1998) Effects of zinc and other nutritional factors on insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr 68(1):200–206
Farthing MJ, Rees LH, Dawson AM (1983) Male gonadal function in coeliac disease: III. Pituitary regulation. Clin Endocrinol 19(6):661–671
Sher KS, Jayanthi V, Probert CS, Stewart CR, Mayberry JF (1994) Infertility, obstetric and gynaecological problems in coeliac sprue. Dig Dis (Basel, Switzerland) 12(3):186–190
Graat-Verboom L, Smeenk FW, van den Borne BE, Spruit MA, Donkers-van Rossum AB, Aarts RP, Wouters EF (2012) Risk factors for osteoporosis in Caucasian patients with moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a case control study. Bone 50(6):1234–1239. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.02.638
Ludvigsson JF, Rubio-Tapia A, Chowdhary V, Murray JA, Simard JF (2012) Increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in 29,000 patients with biopsy-verified celiac disease. J Rheumatol 39(10):1964–1970. doi:10.3899/jrheum.120493
Baptista ML, Koda YK, Mitsunori R, Nisihara, Ioshii SO (2005) Prevalence of celiac disease in Brazilian children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 41(5):621–624
Shaoul R, Lerner A (2007) Associated autoantibodies in celiac disease. Autoimmun Rev 6(8):559–565. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2007.02.006
Garcia-Manzanares A, Lucendo AJ (2011) Nutritional and dietary aspects of celiac disease. Nutr Clin Pract Off Publ Am Soc Parenter Enter Nutr 26(2):163–173. doi:10.1177/0884533611399773
Taranta A, Fortunati D, Longo M, Rucci N, Iacomino E, Aliberti F, Facciuto E, Migliaccio S, Bardella MT, Dubini A, Borghi MO, Saraifoger S, Teti A, Bianchi ML (2004) Imbalance of osteoclastogenesis-regulating factors in patients with celiac disease. J Bone Miner Res 19(7):1112–1121. doi:10.1359/jbmr.040319
Moreno ML, Crusius JB, Chernavsky A, Sugai E, Sambuelli A, Vazquez H, Maurino E, Pena AS, Bai JC (2005) The IL-1 gene family and bone involvement in celiac disease. Immunogenetics 57(8):618–620. doi:10.1007/s00251-005-0033-x
Bardella MT, Bianchi ML, Teti A (2005) Chronic inflammatory intestinal diseases and bone loss. Gut 54(10):1508
Wischmeyer PE (2006) Glutamine: role in gut protection in critical illness. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 9(5):607–612. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000241672.09676.03
Koh JM, Khang YH, Jung CH, Bae S, Kim DJ, Chung YE, Kim GS (2005) Higher circulating hsCRP levels are associated with lower bone mineral density in healthy pre- and postmenopausal women: evidence for a link between systemic inflammation and osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 16(10):1263–1271. doi:10.1007/s00198-005-1840-5
Cauley JA, Danielson ME, Boudreau RM, Forrest KY, Zmuda JM, Pahor M, Tylavsky FA, Cummings SR, Harris TB, Newman AB (2007) Inflammatory markers and incident fracture risk in older men and women: the Health Aging and Body Composition Study. J Bone Miner Res 22(7):1088–1095. doi:10.1359/jbmr.070409
Olmos M, Antelo M, Vazquez H, Smecuol E, Maurino E, Bai JC (2008) Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies on the prevalence of fractures in coeliac disease. Dig Liver Dis 40(1):46–53. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2007.09.006
Vasquez H, Mazure R, Gonzalez D, Flores D, Pedreira S, Niveloni S, Smecuol E, Maurino E, Bai JC (2000) Risk of fractures in celiac disease patients: a cross-sectional, case-control study. Am J Gastroenterol 95(1):183–189. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.01682.x
Fickling WE, McFarlane XA, Bhalla AK, Robertson DA (2001) The clinical impact of metabolic bone disease in coeliac disease. Postgrad Med J 77(903):33–36
Thomason K, West J, Logan RF, Coupland C, Holmes GK (2003) Fracture experience of patients with coeliac disease: a population based survey. Gut 52(4):518–522
Moreno ML, Vazquez H, Mazure R, Smecuol E, Niveloni S, Pedreira S, Sugai E, Maurino E, Gomez JC, Bai JC (2004) Stratification of bone fracture risk in patients with celiac disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2(2):127–134
Davie MW, Gaywood I, George E, Jones PW, Masud T, Price T, Summers GD (2005) Excess non-spine fractures in women over 50 years with celiac disease: a cross-sectional, questionnaire-based study. Osteoporos Int 16(9):1150–1155. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1822-z
Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L (2002) Fracture risk in patients with celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis: a nationwide follow-up study of 16,416 patients in Denmark. Am J Epidemiol 156(1):1–10
West J, Logan RF, Card TR, Smith C, Hubbard R (2003) Fracture risk in people with celiac disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 125(2):429–436
Jafri MR, Nordstrom CW, Murray JA, Van Dyke CT, Dierkhising RA, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ 3rd (2008) Long-term fracture risk in patients with celiac disease: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Dig Dis Sci 53(4):964–971. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9976-0
Ludvigsson JF, Michaelsson K, Ekbom A, Montgomery SM (2007) Coeliac disease and the risk of fractures - a general population-based cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 25(3):273–285. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03203.x
Sanchez MI, Mohaidle A, Baistrocchi A, Matoso D, Vazquez H, Gonzalez A, Mazure R, Maffei E, Ferrari G, Smecuol E, Crivelli A, de Paula JA, Gomez JC, Pedreira S, Maurino E, Bai JC (2011) Risk of fracture in celiac disease: gender, dietary compliance, or both? World J Gastroenterol 17(25):3035–3042. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i25.3035
Vilppula A, Kaukinen K, Luostarinen L, Krekela I, Patrikainen H, Valve R, Luostarinen M, Laurila K, Maki M, Collin P (2011) Clinical benefit of gluten-free diet in screen-detected older celiac disease patients. BMC Gastroenterol 11:136. doi:10.1186/1471-230x-11-136
Larussa T, Suraci E, Nazionale I, Abenavoli L, Imeneo M, Luzza F (2012) Bone mineralization in celiac disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2012:198025. doi:10.1155/2012/198025
Gheita TA, Fawzy SM, Nour El-Din AM, Gomaa HE (2012) Asymptomatic celiac sprue in juvenile rheumatic diseases children. Int J Rheum Dis 15(2):220–226. doi:10.1111/j.1756-185X.2011.01681.x
Rodrigo L, Hernandez-Lahoz C, Fuentes D, Alvarez N, Lopez-Vazquez A, Gonzalez S (2011) Prevalence of celiac disease in multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurol 11:31. doi:10.1186/1471-2377-11-31
Bai D, Brar P, Holleran S, Ramakrishnan R, Green PH (2005) Effect of gender on the manifestations of celiac disease: evidence for greater malabsorption in men. Scand J Gastroenterol 40(2):183–187. doi:10.1080/00365520510011498
Hasserius R, Karlsson MK, Nilsson BE, Redlund-Johnell I, Johnell O (2002) Non-participants differ from participants as regards risk factors for vertebral deformities: a source of misinterpretation in the European Vertebral Osteoporosis Study. Acta Orthop Scand 73(4):451–454. doi:10.1080/00016470216326
Felsenberg D, Silman AJ, Lunt M, Armbrecht G, Ismail AA, Finn JD, Cockerill WC, Banzer D, Benevolenskaya LI, Bhalla A, Bruges Armas J, Cannata JB, Cooper C, Dequeker J, Eastell R, Felsch B, Gowin W, Havelka S, Hoszowski K, Jajic I, Janott J, Johnell O, Kanis JA, Kragl G, Lopes Vaz A, Lorenc R, Lyritis G, Masaryk P, Matthis C, Miazgowski T, Parisi G, Pols HA, Poor G, Raspe HH, Reid DM, Reisinger W, Schedit-Nave C, Stepan JJ, Todd CJ, Weber K, Woolf AD, Yershova OB, Reeve J, O'Neill TW (2002) Incidence of vertebral fracture in Europe: results from the European Prospective Osteoporosis Study (EPOS). J Bone Miner Res 17(4):716–724. doi:10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.4.716
Melton LJ 3rd, Lane AW, Cooper C, Eastell R, O'Fallon WM, Riggs BL (1993) Prevalence and incidence of vertebral deformities. Osteoporos Int 3(3):113–119
Riggs BL, Melton LJ 3rd (1995) The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: insights afforded by epidemiology. Bone 17(5 Suppl):505S–511S
Middleton ET, Steel SA (2008) Routine versus targeted vertebral fracture assessment for the detection of vertebral fractures. Osteoporos Int 19(8):1167–1173. doi:10.1007/s00198-007-0548-0
Stobaugh DJ, Deepak P, Ehrenpreis ED (2013) Increased risk of osteoporosis-related fractures in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Osteoporos Int 24(4):1169–1175. doi:10.1007/s00198-012-2141-4
Yen CM, Muo CH, Lin MC, Chang SN, Chang YJ, Kao CH (2014) A nationwide population cohort study: irritable bowel syndrome is a risk factor of osteoporosis. Eur J Intern Med 25(1):87–91. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2013.10.009
Vilppula A, Kaukinen K, Luostarinen L, Krekela I, Patrikainen H, Valve R, Maki M, Collin P (2009) Increasing prevalence and high incidence of celiac disease in elderly people: a population-based study. BMC Gastroenterol 9:49. doi:10.1186/1471-230x-9-49
Murray JA, Van Dyke C, Plevak MF, Dierkhising RA, Zinsmeister AR, Melton LJ 3rd (2003) Trends in the identification and clinical features of celiac disease in a North American community, 1950–2001. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 1(1):19–27. doi:10.1053/jcgh.2003.50004
Lurie Y, Landau DA, Pfeffer J, Oren R (2008) Celiac disease diagnosed in the elderly. J Clin Gastroenterol 42(1):59–61. doi:10.1097/01.mcg.0000247995.12087.7b
Dennison EM, Compston JE, Flahive J, Siris ES, Gehlbach SH, Adachi JD, Boonen S, Chapurlat R, Diez-Perez A, Anderson FA Jr, Hooven FH, LaCroix AZ, Lindsay R, Netelenbos JC, Pfeilschifter J, Rossini M, Roux C, Saag KG, Sambrook P, Silverman S, Watts NB, Greenspan SL, Premaor M, Cooper C, Investigators G (2012) Effect of co-morbidities on fracture risk: findings from the Global Longitudinal Study of Osteoporosis in Women (GLOW). Bone 50(6):1288–1293. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.02.639
Rios LP, Khan A, Sultan M, McAssey K, Fouda MA, Armstrong D (2013) Approach to diagnosing celiac disease in patients with low bone mineral density or fragility fractures: multidisciplinary task force report. Can Fam Phys Med Fam Can 59(10):1055–1061, e1441–1058
Drummond FJ, Annis P, O'Sullivan K, Wynne F, Daly M, Shanahan F, Quane KA, Molloy MG (2003) Screening for asymptomatic celiac disease among patients referred for bone densitometry measurement. Bone 33(6):970–974
Gonzalez D, Sugai E, Gomez JC, Oliveri MB, Gomez Acotto C, Vega E, Bagur A, Mazure R, Maurino E, Bai JC, Mautalen C (2002) Is it necessary to screen for celiac disease in postmenopausal osteoporotic women? Calcif Tissue Int 71(2):141–144. doi:10.1007/s00223-001-1027-9
Lindh E, Ljunghall S, Larsson K, Lavo B (1992) Screening for antibodies against gliadin in patients with osteoporosis. J Intern Med 231(4):403–406
Mather KJ, Meddings JB, Beck PL, Scott RB, Hanley DA (2001) Prevalence of IgA-antiendomysial antibody in asymptomatic low bone mineral density. Am J Gastroenterol 96(1):120–125. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03461.x
Nuti R, Martini G, Valenti R, Giovani S, Salvadori S, Avanzati A (2001) Prevalence of undiagnosed coeliac syndrome in osteoporotic women. J Intern Med 250(4):361–366
Sanders DS, Patel D, Khan FB, Westbrook RH, Webber CV, Milford-Ward A, McCloskey EV (2005) Case-finding for adult celiac disease in patients with reduced bone mineral density. Dig Dis Sci 50(3):587–592
Stenson WF, Newberry R, Lorenz R, Baldus C, Civitelli R (2005) Increased prevalence of celiac disease and need for routine screening among patients with osteoporosis. Arch Intern Med 165(4):393–399. doi:10.1001/archinte.165.4.393
Karakan T, Ozyemisci-Taskiran O, Gunendi Z, Atalay F, Tuncer C (2007) Prevalence of IgA-antiendomysial antibody in a patient cohort with idiopathic low bone mineral density. World J Gastroenterol 13(21):2978–2982
Armagan O, Uz T, Tascioglu F, Colak O, Oner C, Akgun Y (2005) Serological screening for celiac disease in premenopausal women with idiopathic osteoporosis. Clin Rheumatol 24(3):239–243. doi:10.1007/s10067-004-1011-7
Kavuncu V, Dundar U, Ciftci IH, Evcik D, Yigit I (2009) Is there any requirement for celiac disease screening routinely in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis? Rheumatol Int 29(7):841–845. doi:10.1007/s00296-008-0797-z
Scott EM, Gaywood I, Scott BB (2000) Guidelines for osteoporosis in coeliac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut 46(Suppl 1):i1–i8
Muhammad R, Ahmed AM, Limdi J (2012) The predictive accuracy of pre-BMD FRAX scoring in identifying the need for treating osteoporosis in patients with coeliac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 107(Suppl):S1–S880
Rubio-Tapia A, Hill ID, Kelly CP, Calderwood AH, Murray JA (2013) ACG clinical guidelines: diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 108(5):656–676. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.79, quiz 677
Bai JC, Fried M, Corazza GR, Schuppan D, Farthing M, Catassi C, Greco L, Cohen H, Ciacci C, Eliakim R, Fasano A, Gonzalez A, Krabshuis JH, LeMair A (2013) World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guidelines on Celiac Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 47(2):121–126. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e31827a6f83
McCloskey E, Kanis JA (2012) FRAX updates 2012. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24(5):554–560. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e328356d2f5
Watts NB (2011) The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX®): applications in clinical practice. J Women’s Health (2002) 20(4):525–531. doi:10.1089/jwh.2010.2294
Derbyshire E, Dhar A (2012) Can a 10 year fracture risk score (FRAX) be used to avoid dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans in patients with coeliac disease? Gut 61:A248. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302514c.153
Acknowledgments
We thank Sigrun M. Hjelle and Karl Ove Hufthammer for the editorial and statistical assistance.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hjelle, A.M., Apalset, E., Mielnik, P. et al. Celiac disease and risk of fracture in adults—a review. Osteoporos Int 25, 1667–1676 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2683-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2683-8