Abstract
Summary
This study evaluated racial differences in bone size and volumetric density at the spine and hip in pre- and postmenopausal Chinese American and White women. Compared with White women, Chinese American women have greater cortical volumetric bone density (vBMD) at the hip, congruent with the results at the peripheral skeleton.
Introduction
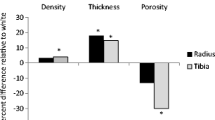
Chinese American women have lower rates of fracture than White women despite lower areal bone density. At the forearm and tibia, however, Chinese American women have higher cortical vBMD as well as greater trabecular and cortical thickness, but smaller bone area as measured by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) compared with White women. Since HR-pQCT data are obtained at peripheral sites, it is unclear whether these differences are relevant to the clinically important lumbar spine and hip. This study assesses racial differences in bone size and vBMD at the spine and hip in Chinese American and White women.
Methods
QCT of the spine and hip was measured to assess racial differences in bone size, structure, and vBMD in pre- (n = 83) and postmenopausal (n = 50) Chinese American and White women. Data were adjusted for weight, height, physical activity, total calcium intake, parathyroid hormone, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels.
Results
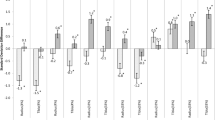
Among premenopausal women, lumbar spine trabecular vBMD was 5.8% greater in Chinese American versus White women (p = 0.01). At the hip, cortical vBMD was 3% greater at the femoral neck (p = 0.05) and 3.6% greater at the total hip (p = 0.01) in premenopausal Chinese American compared with White women. Among postmenopausal women, there was no difference in lumbar spine trabecular vBMD. Cortical vBMD was 4% greater at the total hip (p = 0.02) and tended to be greater at the femoral neck (p = 0.058) in Chinese American versus White women.
Conclusions
Consistent with earlier findings in the peripheral skeleton, cortical vBMD is greater at the hip in Chinese American versus White women.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett-Connor E, Siris ES, Wehren LE, Miller PD, Abbott TA, Berger ML, Santora AC, Sherwood LM (2005) Osteoporosis and fracture risk in women of different ethnic groups. J Bone Miner Res 20:185–194
Walker MD, Babbar R, Opotowsky AR et al (2006) A referent bone mineral density database for Chinese American women. Osteoporos Int 17:878–887
Woo J, Li M, Lau E (2001) Population bone mineral density measurements for Chinese women and men in Hong Kong. Osteoporos Int 12:289–295
Xiaoge D, Eryuan L, Xianping W, Zhiguang Z, Gan H, Zaijing J, Xiaoli P, Hongzhuan T, Hanwen W (2000) Bone mineral density differences at the femoral neck and Ward's triangle: a comparison study on the reference data between Chinese and Caucasian women. Calcif Tissue Int 67:195–198
Russell-Aulet M, Wang J, Thornton JC, Colt EW, Pierson RN Jr (1993) Bone mineral density and mass in a cross-sectional study of white and Asian women. J Bone Miner Res 8:575–582
Lauderdale DS, Jacobsen SJ, Furner SE, Levy PS, Brody JA, Goldberg J (1997) Hip fracture incidence among elderly Asian-American populations. Am J Epidemiol 146:502–509
Xu L, Lu A, Zhao X, Chen X, Cummings SR (1996) Very low rates of hip fracture in Beijing, People's Republic of China: the Beijing Osteoporosis Project. Am J Epidemiol 144:901–907
Lau EM, Chan HH, Woo J, Lin F, Black D, Nevitt M, Leung PC (1996) Normal ranges for vertebral height ratios and prevalence of vertebral fracture in Hong Kong Chinese: a comparison with American Caucasians. J Bone Miner Res 11:1364–1368
Walker MD, McMahon DJ, Udesky J, Liu G, Bilezikian JP (2009) Application of high-resolution skeletal imaging to measurements of volumetric BMD and skeletal microarchitecture in Chinese-American and white women: explanation of a paradox. J Bone Miner Res 24:1953–1959
Walker MD, Liu XS, Stein E et al (2011) Differences in bone microarchitecture between postmenopausal Chinese-American and white women. J Bone Miner Res 26(7):1392–1398
Wang XF, Wang Q, Ghasem-Zadeh A, Evans A, McLeod C, Iuliano-Burns S, Seeman E (2009) Differences in macro- and microarchitecture of the appendicular skeleton in young Chinese and white women. J Bone Miner Res 24:1946–1952
Liu XS, Walker MD, McMahon DJ, Udesky J, Liu G, Bilezikian JP, Guo XE (2011) Better skeletal microstructure confers greater mechanical advantages in Chinese-American women versus white women. J Bone Miner Res 26:1783–1792
Liu XS, Cohen A, Shane E et al (2010) Bone density, geometry, microstructure, and stiffness: relationships between peripheral and central skeletal sites assessed by DXA, HR-pQCT, and cQCT in premenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 25:2229–2238
Hertzler A, Frary R (1994) A dietary rapid assessment method (RAM). Top Clin Nutr 9:76–85
Baecke JA, Burema J, Frijters JE (1982) A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies. Am J Clin Nutr 36:936–942
Herrmann M, Harwood T, Gaston-Parry O, Kouzios D, Wong T, Lih A, Jimenez M, Janu M, Seibel MJ (2010) A new quantitative LC tandem mass spectrometry assay for serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D. Steroids 75:1106–1112
Cheng X, Li J, Lu Y, Keyak J, Lang T (2007) Proximal femoral density and geometry measurements by quantitative computed tomography: association with hip fracture. Bone 40:169–174
Lang T, LeBlanc A, Evans H, Lu Y, Genant H, Yu A (2004) Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine and hip in long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 19:1006–1012
Lang TF, Leblanc AD, Evans HJ, Lu Y (2006) Adaptation of the proximal femur to skeletal reloading after long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 21:1224–1230
Marshall LM, Lang TF, Lambert LC, Zmuda JM, Ensrud KE, Orwoll ES (2006) Dimensions and volumetric BMD of the proximal femur and their relation to age among older U.S. men. J Bone Miner Res 21:1197–1206
Duan Y, Wang XF, Evans A, Seeman E (2005) Structural and biomechanical basis of racial and sex differences in vertebral fragility in Chinese and Caucasians. Bone 36(6):987–998
Kin K, Lee JH, Kushida K, Sartoris DJ, Ohmura A, Clopton PL, Inoue T (1993) Bone density and body composition on the Pacific rim: a comparison between Japan-born and U.S.-born Japanese-American women. J Bone Miner Res 8:861–869
Lau EM, Suriwongpaisal P, Lee JK, De Das S, Festin MR, Saw SM, Khir A, Torralba T, Sham A, Sambrook P (2001) Risk factors for hip fracture in Asian men and women: the Asian osteoporosis study. J Bone Miner Res 16:572–580
Davis JW, Nevitt MC, Wasnich RD, Ross PD (1999) A cross-cultural comparison of neuromuscular performance, functional status, and falls between Japanese and white women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 54:M288–M292
Bouxsein ML, Szulc P, Munoz F, Thrall E, Sornay-Rendu E, Delmas PD (2007) Contribution of trochanteric soft tissues to fall force estimates, the factor of risk, and prediction of hip fracture risk. J Bone Miner Res 22:825–831
Majumder S, Roychowdhury A, Pal S (2008) Effects of trochanteric soft tissue thickness and hip impact velocity on hip fracture in sideways fall through 3D finite element simulations. J Biomech 41:2834–2842
Cummings SR, Cauley JA, Palermo L, Ross PD, Wasnich RD, Black D, Faulkner KG (1994) Racial differences in hip axis lengths might explain racial differences in rates of hip fracture. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Osteoporos Int 4:226–229
Faulkner KG, Cummings SR, Black D, Palermo L, Gluer CC, Genant HK (1993) Simple measurement of femoral geometry predicts hip fracture: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 8:1211–1217
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants K23 AR053507 and UL1 RR024156, a National Osteoporosis Foundation grant, and the Mary and David Hoar Fellowship Program of the New York Community Trust and the New York Academy of Medicine. We are grateful to Dr. Clyde Wu, whose direction and support were essential to the design and execution of this study.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walker, M.D., Saeed, I., McMahon, D.J. et al. Volumetric bone mineral density at the spine and hip in Chinese American and White women. Osteoporos Int 23, 2499–2506 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1855-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1855-z