Abstract
Summary
This study examined the role of estrogen receptor (ER) beta during mouse femoral fracture healing by employing ER knockout (KO) mice. The fracture healing in KO mice was enhanced in the early stage of neovascularization and the middle stage of endochondral ossification.
Introduction
This study was conducted to examine the role of ER beta during fracture healing.
Methods
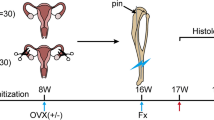
Female ERbeta knockout (KO) mice (18 weeks old) and age-matched female wild-type (WT) mice underwent open osteotomy on the right femur. They were sacrificed at 1, 2, 4 and 6 weeks post-fracture. The sera and callus samples were subjected to the following analyses: micro-computed tomography (CT)-based angiography, micro-CT evaluation, histological examination, histomorphometry examination, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, biochemical marker, and mechanical testing.
Results
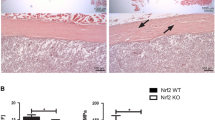
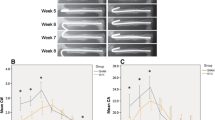
Micro-CT-based angiography showed that the total vessel volume at the fracture site was larger in the KO group than the WT group at 1 and 2 weeks post-fracture. Micro-CT analysis revealed that the callus volume was significantly higher in the KO group from week 2 to week 4 post-fracture when compared with the WT group consistent with the histological data. Analysis of biochemical markers indicated that circulating P1NP levels in the KO mice were significantly higher than in the WT mice from week 2 to week 4 and that temporal expression of circulating C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX) levels was also higher in the KO mice than in the WT mice. These results were consistent with quantitative real-time PCR analysis. The ultimate load, stiffness, and energy to failure were significantly higher in the KO mice than in the WT mice at week 4.
Conclusions
The fracture healing in KO mice was enhanced in the early stage of neovascularization and the middle stage of endochondral ossification, but not by the end of healing. Blockade of ERbeta can be considered as another therapeutic strategy for osteoporotic fracture and non-union fracture.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- KO:
-
Knockout
- Micro-CT:
-
Micro-computed tomography
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Ferguson C, Alpern E, Miclau T, Helms JA (1999) Does adult fracture repair recapitulate embryonic skeletal formation? Mech Dev 87:57–66
Einhorn TA (1998) The cell and molecular biology of fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res S7–S21
Gerstenfeld LC, Cho TJ, Kon T, Aizawa T, Tsay A, Fitch J, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA (2003) Impaired fracture healing in the absence of TNF-alpha signaling: the role of TNF-alpha in endochondral cartilage resorption. J Bone Miner Res 18:1584–1592
Einhorn TA (2005) The science of fracture healing. J Orthop Trauma 19:S4–S6
Turner RT, Riggs BL, Spelsberg TC (1994) Skeletal effects of estrogen. Endocr Rev 15:275–300
Beil FT, Barvencik F, Gebauer M, Seitz S, Rueger JM, Ignatius A, Pogoda P, Schinke T, Amling M (2010) Effects of estrogen on fracture healing in mice. J Trauma 69:1259–1265
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1996) Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5925–5930
Green S, Walter P, Greene G, Krust A, Goffin C, Jensen E, Scrace G, Waterfield M, Chambon P (1986) Cloning of the human oestrogen receptor cDNA. J Steroid Biochem 24:77–83
Chagin AS, Lindberg MK, Andersson N, Moverare S, Gustafsson JA, Savendahl L, Ohlsson C (2004) Estrogen receptor-beta inhibits skeletal growth and has the capacity to mediate growth plate fusion in female mice. J Bone Miner Res 19:72–77
Ke HZ (2005) In vivo characterization of skeletal phenotype of genetically modified mice. J Bone Miner Metab 23(Suppl):84–89
Ke HZ, Brown TA, Qi H, Crawford DT, Simmons HA, Petersen DN, Allen MR, McNeish JD, Thompson DD (2002) The role of estrogen receptor-beta, in the early age-related bone gain and later age-related bone loss in female mice. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2:479–488
Lindberg MK, Alatalo SL, Halleen JM, Mohan S, Gustafsson JA, Ohlsson C (2001) Estrogen receptor specificity in the regulation of the skeleton in female mice. J Endocrinol 171:229–236
Windahl SH, Vidal O, Andersson G, Gustafsson JA, Ohlsson C (1999) Increased cortical bone mineral content but unchanged trabecular bone mineral density in female ERbeta(−/−) mice. J Clin Invest 104:895–901
Hartman J, Lindberg K, Morani A, Inzunza J, Strom A, Gustafsson JA (2006) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits angiogenesis and growth of T47D breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res 66:11207–11213
Doyon AR, Ferries IK, Li J (2010) Glucocorticoid attenuates the anabolic effects of parathyroid hormone on fracture repair. Calcif Tissue Int 87:68–76
He YX, Zhang G, Pan XH, Liu Z, Zheng LZ, Chan CW, Lee KM, Cao YP, Li G, Wei L, Hung LK, Leung KS, Qin L (2011) Impaired bone healing pattern in mice with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis: a drill-hole defect model. Bone 48:1388–1400
Zhang G, Sheng H, He YX, Xie XH, Wang YX, Lee KM, Yeung KW, Li ZR, He W, Griffith JF, Leung KS, Qin L (2009) Continuous occurrence of both insufficient neovascularization and elevated vascular permeability in rabbit proximal femur during inadequate repair of steroid-associated osteonecrotic lesions. Arthritis Rheum 60:2966–2977
Duvall CL, Taylor WR, Weiss D, Wojtowicz AM, Guldberg RE (2007) Impaired angiogenesis, early callus formation, and late stage remodeling in fracture healing of osteopontin-deficient mice. J Bone Miner Res 22:286–297
Hao YJ, Zhang G, Wang YS, Qin L, Hung WY, Leung K, Pei FX (2007) Changes of microstructure and mineralized tissue in the middle and late phase of osteoporotic fracture healing in rats. Bone 41:631–638
Qin L, Hung L, Leung K, Guo X, Bumrerraj S, Katz L (2001) Staining intensity of individual osteons correlated with elastic properties and degrees of mineralization. J Bone Miner Metab 19:359–364
Songlin P, Ge Z, Yixin H, Xinluan W, Pingchung L, Kwoksui L, Ling Q (2009) Epimedium-derived flavonoids promote osteoblastogenesis and suppress adipogenesis in bone marrow stromal cells while exerting an anabolic effect on osteoporotic bone. Bone 45:534–544
Zhang G, Qin L, Hung WY, Shi YY, Leung PC, Yeung HY, Leung KS (2006) Flavonoids derived from herbal Epimedium brevicornum Maxim prevent OVX-induced osteoporosis in rats independent of its enhancement in intestinal calcium absorption. Bone 38:818–825
He YX, Zhang G, Pan XH, Liu Z, Zheng LZ, Chan CW, Lee KM, Cao YP, Li G, Wei L, Hung LK, Leung KS, Qin L (2011) Impaired bone healing pattern in mice with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis: A drill-hole defect model. Bone 48:1388–1400
Rauner M, Stupphann D, Haas M, Fert I, Glatigny S, Sipos W, Breban M, Pietschmann P (2009) The HLA-B27 transgenic rat, a model of spondyloarthritis, has decreased bone mineral density and increased RANKL to osteoprotegerin mRNA ratio. J Rheumatol 36:120–126
Jacobsen KA, Al-Aql ZS, Wan C, Fitch JL, Stapleton SN, Mason ZD, Cole RM, Gilbert SR, Clemens TL, Morgan EF, Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC (2008) Bone formation during distraction osteogenesis is dependent on both VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 signaling. J Bone Miner Res 23:596–609
Lim W, Park Y, Cho J, Park C, Park J, Park YK, Park H, Lee Y (2011) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits transcriptional activity of hypoxia inducible factor-1 through the downregulation of arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator. Breast Cancer Res 13:R32
Holstein JH, Menger MD, Scheuer C, Meier C, Culemann U, Wirbel RJ, Garcia P, Pohlemann T (2007) Erythropoietin (EPO): EPO-receptor signaling improves early endochondral ossification and mechanical strength in fracture healing. Life Sci 80:893–900
Colburn NT, Zaal KJ, Wang F, Tuan RS (2009) A role for gamma/delta T cells in a mouse model of fracture healing. Arthritis Rheum 60:1694–1703
Windahl SH, Hollberg K, Vidal O, Gustafsson JA, Ohlsson C, Andersson G (2001) Female estrogen receptor beta−/− mice are partially protected against age-related trabecular bone loss. J Bone Miner Res 16:1388–1398
Gruber R, Koch H, Doll BA, Tegtmeier F, Einhorn TA, Hollinger JO (2006) Fracture healing in the elderly patient. Exp Gerontol 41:1080–1093
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by AO Research Grant (S-08-74Z) and CUHK Direct Grant (2008.1.063). We also thank Mr. Wang Yu-Gang for his support in animal care.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, YX., Liu, Z., Pan, XH. et al. Deletion of estrogen receptor beta accelerates early stage of bone healing in a mouse osteotomy model. Osteoporos Int 23, 377–389 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1812-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1812-x