Abstract
Introduction
Kyphoplasty has been shown to restore vertebral height and sagittal alignment. Proponents of vertebroplasty have recently demonstrated that many vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) are mobile and positional correction can lead to clinically significant height restoration. The current investigation tested the hypothesis that positional maneuvers do not achieve the same degree of vertebral height correction as kyphoplasty balloon tamps for the reduction of low-energy VCFs.
Methods
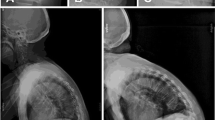
Twenty-five consecutive patients with a total of 43 osteoporotic VCFs were entered into a prospective analysis. Each patient was sequentially evaluated for postural and balloon vertebral fracture reduction. Preoperative standing and lateral radiographs of the fractured vertebrae were compared with prone cross-table lateral radiographs with the patient in a hyper-extension position and on pelvic and sternal rolls. Following positional manipulation, patients underwent a unilateral balloon kyphoplasty. Postoperative standing radiographs were evaluated for the percentage of height restoration related to positioning and balloon kyphoplasty.
Results
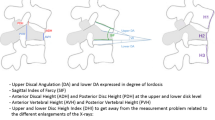
In the middle portion of the vertebrae, the percentage available for restoration restored with extension positioning was 10.4% (median 11.1%) and after balloon kyphoplasty was 57.0% (median 62.2%). This difference was statistically significant (p<0.001). Thus, kyphoplasty provided an additional 46.6% of the height available for restoration from the positioning alone. With operative positioning, 51.2% of VCFs had >10% restoration of the central portion of the vertebral body, whereas 90.7% of fractures improved at least 10% following balloon kyphoplasty (p<0.002).
Conclusion
Although this study supports the concept that many VCFs can be moved with positioning, balloon kyphoplasty enhanced the height reduction >4.5-fold over the positioning maneuver alone and accounted for over 80% of the ultimate reduction. If height restoration is the goal, kyphoplasty is clearly superior in most cases to the positioning maneuver alone.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riggs BL, Melton LJ 3rd (1986) Involutional osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 314(26):1676–1686
Riggs BL, Melton LJ 3rd (1995) The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: Insights afforded by epidemiology. Bone 17(5 Suppl):505S–511S
Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK (2001) Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Osteoporosis Int 12(6):429–437
Lyles KW, Gold DT, Shipp KM, Pieper CF, Martinez S, Mulhausen PL (1993) Association of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with impaired functional status. Am J Med 94(6):595–601
Crandall D, Slaughter D, Hankins PJ, Moore C, Jerman J (2004) Acute versus chronic vertebral compression fractures treated with kyphoplasty: early results. Spine J 4(4):418–424
Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, DeNardo AJ, Lawler GJ, Negin GA, Remley KB, Boutin SM, Dunnagan SA (2003) Vertebral compression fractures: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty—retrospective report of 245 cases. Radiology 226(2):366–372
Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H (2001) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. Am J Neuroradiol 22(2):371–381
Mathis JM, Ortiz AO, Zoarski GH (2004) Vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty: a comparison and contrast. Am J Neuroradiol 25(5):840–845
Phillips FM, Ho E, Campbell-Hupp M, McNally T, Todd Wetzel F, Gupta P (2003) Early radiographic and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28(19):2260–2267
Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, Bell G (2001) Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine 26(14):1631–1638
Lieberman I, Reinhardt MK (2003) Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteolytic vertebral collapse. Clin Orthop 415(Suppl):S176–S186
Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, McCann RM (2000) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine 25(8):923–928
Belmont PJ Jr, Plly DW Jr, Cunningham BW, Klemme WR (2001) The effects of hook pattern and kyphotic angulation on mechanical strength and apical rod strain in a long-segment posterior construct using a synthetic model. Spine 26(6):627–635
White AA 3rd, Panjabi MM, Thomas CL (1977) The clinical biomechanics of kyphotic deformities. Clin Orthop 128:8–17
Ledlie JT, Renfro M (2003) Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain, and activity levels. J Neurosurg 98(1 Suppl):36–42
Dudeney S, Lieberman IH, Reinhardt MK, Hussein M (2002) Kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteolytic vertebral compression fractures as a result of multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 20(9):2382–2387
Rhyne A 3rd, Banit D, Laxer E, Odum S, Nussman D (2004) Kyphoplasty: report of eighty-two thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18(5):294–299
McKiernan F, Jensen R, Faciszewski T (2003) The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res 18(1):24–29
Faciszewski T, McKiernan F (2002) Calling all vertebral fractures classification of vertebral compression fractures: a consensus for comparison of treatment and outcome. J Bone Miner Res 17(2):185–191
McKiernan F, Faciszewski T, Jensen R (2003) Reporting height restoration in vertebral compression fractures. Spine 28(22):2517–2521
Tohmeh AG, Mathis JM, Fenton DC, Levine AM, Belkoff SM (1999) Biomechanical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular vertebroplasty for the management of osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine 24(17):1772–1776
Steinmann J, Tingey CT, Cruz G, Dai Q (2005) Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty. Spine 30(2):201–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shindle, M.K., Gardner, M.J., Koob, J. et al. Vertebral height restoration in osteoporotic compression fractures: kyphoplasty balloon tamp is superior to postural correction alone. Osteoporos Int 17, 1815–1819 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-006-0195-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-006-0195-x