Abstract
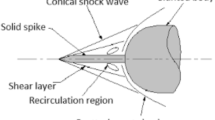
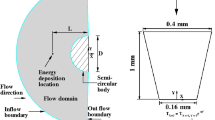
Energy deposition is a robust technique for various high-speed flow control applications including drag reduction. A numerical study of energy deposition is performed for perfect gas flow approaching a blunt cylinder at Mach 3. The energy deposition is simulated by a high-temperature filament injected instantaneously in front of the cylinder. The effect of important dimensionless parameters is studied to characterize the drag modification. The results indicate a saturation effect on maximum drag reduction at higher magnitudes of energy deposition. The computations reveal that the discharge location of the filament does not significantly impact the drag. A phenomenological examination of the interaction is performed. The effectiveness and efficiency of the filament on drag reduction are investigated. A one-dimensional analytical approach is studied to describe the numerical results.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knight, D., Kolesnichenko, U.: High speed flow control using microwave and laser discharge. In: Lecture Series Notes, von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics, Brussels, Belgium, February (2011)
Knight, D., Kuchinskiy, V., Kuranov, A., Sheikin, E.: Aerodynamic flow control at high speed using energy deposition. In: Fourth Workshop on Magneto-Plasma Aerodynamics for Aersopace Applications. Institute for High Temperatures, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, April, 9–11 (2002)
Bletzinger, P., Ganguly, B., Van Wie, D., Garscadden, A.: Plasmas in high speed aerodynamics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 38, R33–R57 (2005)
Kolesnichenko, Y., Brovkin, V., Azarova, O., Grudnitsky, V., Lashkov, V., Mashek, I.: Microwave energy release regimes for drag reduction in supersonic flow. In: AIAA Paper 2002-0353, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2002)
Kim, J.-H., Matsuda, A., Sakai, T., Sasoh, A.: Wave drag reduction with acting spike induced by laser-pulse energy depositions. AIAA J. 49(9), 2076–2078 (2011)
Fomin, V., Tretyakov, P., Taran, J.-P.: Flow control using various plasma and aerodynamic approaches (Short review). Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 8, 411–421 (2004)
Knight, D.: Survey of aerodynamic drag reduction at high speed by energy deposition. J. Propuls. Power 24(6), 1153–1167 (2008)
Ogino, Y., Ohnishi, N., Taguchi, S., Sawada, K.: Baroclinic vortex influence on wave drag reduction induced by pulse energy deposition. Phys. Fluids 21(066102), 1–11 (2009)
Kim, J.-H., Matsuda, A., Sasoh, A.: Interactions among baroclinically-generated vortex rings in building up an acting spike to a bow shock layer. Phys. Fluids 23(2), 021703-1–021703-4 (2011)
Golbabaei-Asl, M., Knight, D.: Interaction of high temperature filament with blunt cylinder at Mach 3. In: AIAA Paper 2012-1026, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, (2012)
Adelgren, R., Yan, H., Elliott, G., Knight, D., Beutner, T., Zheltovodov, A.: Control of Edney IV interaction by pulsed laser energy deposition. AIAA J. 43(2), 256–269 (2005)
Sasoh, A., Ohtani, T., Mori, K.: Pressure effect in a shock-wave–plasma interaction induced by a focused laser pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. Am. Phys. Soc. PRL 97, 205004 (2006)
Fornet, B., Dufour, G., Rogier, F.: Interaction of plasma and incoming flow at Mach 3. Procedia Comput. Sci. 1(1), 617–626 (2010)
Kandala, R., Candler, G.: Numerical studies of laser-induced energy deposition for supersonic flow control. AIAA J. 42(11), 2266–2275 (2004)
Rogier, F., Dufour, G., Fornet, B.: Numerical Modelling of Supersonic Flow Actuated by Laser-induced Plasma. In: AVT190 Meeting, NATO RTO AVT Panel Business Meeting, Edinburgh, UK, October (2011)
Schulein, E., Zheltovodov, A., Pimonov, E., Loginov, M.: Experimental and numerical modeling of the bow shock interaction with pulse-heated air bubbles. Int. J. Aerosp. Innov. 2, 165–187 (2010)
Exton, R., Balla, R., Shirinzadeh, B., Brauckmann, G., Herring, G., Kelliher, W., Fugitt, J., Lazard, C., Khodataev, K.: On-board projection of a microwave plasma upstream of a Mach 6 bow shock. Phys. Plasma 8(11), 5013–5017 (2001)
Lashkov, V., Mashek, I., Anisimov, Y., Ivanov, V., Kolesnichenko, Y., Azarova, A.: Gas dynamic effects around the body under energy deposition in supersonic flow. In: AIAA Paper 2007-1231, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2007)
Knight, D., Kolesnichenko, Y., Brovkin, V., Khmara, D., Lashkov, V., Mashek, I.: Interaction of microwave-generated plasma with a hemisphere cylinder at Mach 2.1. AIAA J. 47(12), 2996–3010 (2009)
Bodrov, S., Kulagin, D., Malkov, Y., Murzanev, A., Smirnov, A., Stepanov, A.: Initiation and channelling of a microwave discharge by a plasma filament created in atmospheric air by an intense femtosecond laser pulse. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45, 045202 (2012)
Miles, R.: Plasma flow control, fundamentals, modeling, and applications. In: Lecture Series Notes, von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics, Brussels, Belgium, February (2011)
Brovkin, V., Afanas’ev, S., Khmara, D., Kolesnichenko, Y.: Experimental Investigation of Combined Laser-DC-MW Discharges. In: AIAA Paper 2006-1459, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2006)
Kolesnichenko, Y., Khmara, D., Brovkin, V., Afanas’ev, S.: Optimization of laser-pulse-controlled mw energy deposition. In: AIAA Paper 2007-1228, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2007)
Kolesnichenko, Y., Brovkin, V., Khmara, D.: Laser-MW energy deposition in air. In: EUCASS Paper, 2 edn. European Conference for Aerospace and Sciences, Brussels, Belgium, (2007)
Ionikh, Y., Chernysheva, N., Meshchanov, A., Yalin, A., Miles, R.: Direct evidence for thermal mechanism of plasma influence on shock wave propagation. Phys. Lett. A 259, 387–392 (1999)
Yan, H., Adelgren, R., Boguszko, M., Elliott, G., Knight, D.: Laser energy deposition in quiescent air. AIAA J. 11, 1988–1995 (2003)
Georgievsky, P., Levin, V.: Modification of regime of the flow over a sphere by means of local energy supply upstream. In: Proceedings Part 3, International Conference on the Methods of Aerophysical Research, Novosibirsk, Russia, September (1996)
Georgievsky, P., Levin, V.: Control of flow past bodies using localized energy addition to the supersonic oncoming flow. J. Fluid Mech. 38(5), 794–805 (2003)
Georgievsky, P., Levin, V.: Bow shock wave structures control by pulse-periodic energy input. In: AIAA Paper 2004-1019, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2004)
Kremeyer, K., Sebastian, K., Shu, C.: Computational study of shock mitigation and drag reduction by pulsed energy lines. AIAA J. 44(8), 1720–1731 (2006)
Girgis, I., Shneider, M., Macheret, S., Brown, G., Miles, R.: Steering moments creation in supersonic flow by off-axis plasma heat addition. J. Spacecr. Rocket 43(3), 607–613 (2006)
Azarova, O., Grudnitsky, V., Kolesnichenko, Y.: Some gas dynamic aspects of flow control by MW energy deposition. In: Sixth Workshop on Magneto-Plasma-Aerodynamics for Aerospace Applications, pp. 152–163. Institute for High Temperatures, Moscow, Russia (2005)
Azarova, O., Knight, D., Kolesnichenko, Y.: Instabilities, vortices and structures characteristics during interaction of microwave filaments with body in supersonic flow. In: AIAA Paper 2010-1004, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2010)
Azarova, O., Knight, D., Kolesnichenko, Y.: Characterization of flowfield types initiated by interaction of microwave filament with supersonic body. In: AIAA Paper 2011-1381, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2011)
Anderson, K., Knight, D.: Interaction of filaments with a blunt cylinder in supersonic flow. Shock Waves 21, 149–161 (2011)
Ardelyan, N., Bychkov, V., Malmuth, N.: Hot filaments for plasma aerodynamic applications. In: AIAA Paper 2007-1233, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2007)
Aerosoft: GASPex Version 5 Reference Guide. Aerosoft Inc., Blacksburg (2012)
ANSYS: ICEM CFD Version 13.0 Reference Guide. ANSYS Inc., Canonsburg (2011)
Yan, H., Adelgren, R., Boguszko, M., Elliott, G., Knight, D.: Laser energy deposition in quiescent air. In: AIAA Paper 2003-1051, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, January (2003)
Ganiev, Y., Gordeev, V., Krasilnikov, A., Lagutin, V., Otmennikov, V., Panasenko, A.: Theoretical and experimental study of the possibility of reducing aerodynamic drag by employing plasma injection. In: AIAA Paper A99–16474, International conference on the Methods of Aerophysical Research, January (1999)
Ganiev, Y., Gordeev, V., Krasilnikov, A., Lagutin, V., Otmennikov, V., Panasenko, A.: Aerodynamic drag reduction by plasma and hot-gas injection. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 14(1), 10–17 (2000)
Press, W., Flannery, B., Teukolsky, S., Vetterling, W.: Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge University Press, New York (1988)
Anderson, J.: Hypersonic and High Temperature Gas Dynamics. AIAA Education Series, New York (1989)
Choudhuri, P., Knight, D.: Two-dimensional unsteady leading-edge separation on a pitching airfoil. AIAA J. 32(4), 673–681 (1994)
Azarova, O.: Simulation of stochastic pulsating flows with instabilities using minimum-stencil difference schemes. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 49, 1397–1414 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under Grant F9550–10-1-0111 managed by Dr. John Schmisseur. The assistance of Dr. Jean Larour, Laboratory for Plasma Physics, France is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Sasoh.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golbabaei-Asl, M., Knight, D.D. Numerical characterization of high-temperature filament interaction with blunt cylinder at Mach 3. Shock Waves 24, 123–138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-013-0471-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-013-0471-6