Abstract
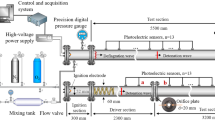
An experimental investigation was performed to establish the dependence of concentration limits of detonation re-initiation behind a multi-orifice plate on mixture composition and initial pressure for hydrogen–air mixtures. The experiments were carried out in detonation tubes of diameter 106 and 141 mm, separated by a multi-orifice plate into two sections. The tubes were equipped with pressure gauges and a semi-cylindrical smoked plate. It is shown that initial pressure has strong influence on the value of concentration limit, especially for lean hydrogen–air mixtures. On the basis of soot records it can be inferred that re-initiation occurs due to two different mechanisms that depend on the mixture sensitivity and properties of the multi-orifice plate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knystautas, R., Lee, J.H., Moen, I.O., Wagner H.G.: Direct initiation of spherical detonation by a hot turbulent jet. In: Proceedings of 17th Symposium (International) on Combustion. The Combustion Institute, pp 1235–1245, Pittsburg (1979)
Inada M., Lee J.H., Knystautas R.: Photographic study of direct initiation of detonation by a turbulent jet. Progr Astronaut Aeronaut 153, 253–269 (1993)
Chao, J., Lee J.H.S.: Detonation initiation at a turbulent interface. in: Proceedings of 2002 Spring Technical Meeting. The Combustion Institute Canadian Section, University of Windsor (2002)
Medvedev S.P., Khomik S.V., Olivier H., Polenov A.N., Bartenev A.M., Gelfand B.E.: Hydrogen detonation and fast deflagration triggered by a turbulent jet of combustion products. Shock Waves 14(3), 193–203 (2005)
Chao, J., Lee, J.H.S.: An investigation of the conditions for detonation initiation at a 1D turbulent mixing interface. In: Proceedings of 20 ICDERS on CD-ROM. Montreal (2005)
Medvedev S.P., Khomik S.V., Gelfand B.E.: Recovery and suppression of the detonation of hydrogen–air mixtures at an obstacle with orifices. Russ J Phys Chem B 3(6), 963–970 (2009)
Kaneshige, M., Shepherd, J.E.: Detonation database. Explosion Dynamics Laboratory Report FM97., California Institute of Technology. Pasadena (1997)
Gavrikov A.I., Efimenko A.A., Dorofeev S.B.: A model for detonation cell size prediction from chemical kinetics. Combust. Flame 120(1), 19–33 (2000)
Grondin J.-S., Lee J.H.S.: Experimental observation of the onset of detonation downstream of a perforated plate. Shock Waves 20(5), 381–386 (2010). doi:10.1007/s00193-010-0267-x
Khomik S.V., Medvedev S.P., Polenov A.N., Gelfand B.E.: Conditions of detonation initiating by focusing shock waves in a combustible gas mixture. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 43(6), 697–702 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10573-007-0094-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Dorofeev.
This paper is based on the work presented at the 22nd International Colloquium on the Dynamics of Explosion and Reactive Systems, Minsk, Belarus, 27–31 July 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khomik, S.V., Veyssiere, B., Medvedev, S.P. et al. Limits and mechanism of detonation re-initiation behind a multi-orifice plate. Shock Waves 22, 199–205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-012-0358-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-012-0358-y