Abstract
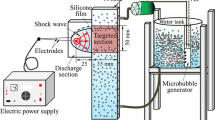
This paper reports the summary of experiments performed to successive generate small-scale underwater shock waves by means of shock-induced collapse of microbubbles confined in a narrow gap. The project is motivated to develop a method for efficient inactivation of marine bacteria contained in ship ballast water by high impulsive pressure loading. The shock wave–air bubbles interaction was visualized by shadowgraph; the images were recorded by ImaCon200, and simultaneous pressure measurements were performed by using an optical fiber pressure transducer with higher temporal resolution. Attaching small air bubbles on a single nylon fiber and placing it in a confined space, we demonstrated sequential generation of impulsive high pressures at the successive collapses of small bubbles at incident and reflected shock loadings. The values of the very short impulsive pressures that occurred repeatedly for a relatively long term are found high enough to inactivate marine bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Maritime Organization: Science of Ship and the Sea. http://www.imo.org/home.asp
International Convention for the Control and Management of Ship’s Ballast Water and Sediments, and Technical Innovations of Ballast Water Pasteurization Instruments. NTS Publishers (2008) (in Japanese)
Abe A., Mimura H., Ikeda T., Katakura R.: Shock compression of marine bacterial cells enclosed in aluminum container. JIME 40(2), 260–265 (2005)
Abe A., Kawasaki H.: Study on shock wave propagation under saltwater sealed in aluminum containers. Trans. JSME Ser. B 72(722), 2418–2424 (2006)
Abe A., Mimura H., Ishida H., Yoshida K.: The effect of shock pressures on the inactivation of a marine Vibrio sp. Shock Waves 17(1–2), 143–151 (2007)
Mimura H., Abe A., Yoshida K., Ishida H.: Changes in the number of colony-forming marine Vibrio sp. cells after exposure to shock pressures in the presence of sodium ascorbate. Bull. Soc. Sea Water Sci. Jpn. 61(2), 132–133 (2007)
Mimura, H., Abe, A., Ishida, H.: In: Kurladze, G.V. (ed.) Environmental Microbiology Research Trends, pp. 191–212 (2007)
Takahashi M., Chiba K., Li P.: Free-radical generation from collapsing microbubbles in the absence of a dynamic stimulus. J. Phys. Chem. B 111(6), 1343–1347 (2007)
Takahashi M., Chiba K., Li P.: Formation of hydroxyl radicals by collapsing ozone microbubbles under strongly acidic conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 111(39), 11443–11446 (2007)
Wolfrum B., Kurz T., Mettin R., Lauterborn W.: Shock wave induced interaction of microbubbles and boundaries. Phys. Fluids 15(10), 2916–2922 (2003)
Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A.: Shock-induced collapse of bubbles in liquid. In: Hannemann, K., Seiler, F. (eds.) Proceedings of 26th ISSW, vol. 2, pp. 931–936 (2007)
Hu X.Y., Khoo B.C., Adams N.A., Huang F.L.: A conservative interface method for compressible flows. J. Comp. Phys. 219, 553–578 (2006)
Takayama, K.: Holographic interferometric observation of shock wave propagation in two-pahse media. In: Groenig, H. (ed.) Proceedings of 16th Interernational Symposium on Shock Tube and Waves, Aachen, pp. 51–62 (1987)
Cole R.H.: Underwater Explosions. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1948)
Kedrinskii V.: Hydrodynamics of Explosion: experiments and models, pp. 153–221. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V.K. Kedrinskii.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, A., Ohtani, K. & Takayama, K. Overpressure generation and repetition of collapsing microbubbles induced by shock wave reflection in a narrow gap. Shock Waves 21, 331–339 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-011-0315-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-011-0315-1