Abstract
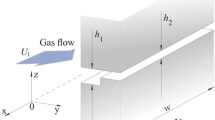
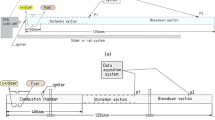
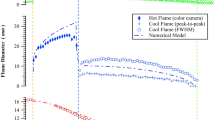
A rotating detonation propagating at nearly Chapman–Jouguet velocity is numerically stabilized on a two-dimensional simple chemistry flow model. Under purely axial injection of a combustible mixture from the head end of a toroidal section of coaxial cylinders, the rotating detonation is proven to give no average angular momentum at any cross section, giving an axial flow. The detonation wavelet connected with an oblique shock wave ensuing to the downstream has a feature of unconfined detonation, causing a deficit in its propagation velocity. Due to Kelvin–Helmholtz instability existing on the interface of an injected combustible, unburnt gas pockets are formed to enter the junction between the detonation and oblique shock waves, generating strong explosions propagating to both directions. Calculated specific impulse is as high as 4,700 s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholls, J.A., Wilkinson, H.R., Morrison, R.B.: Intermediate detonation as a thrust-producing mechanism. Jet Propuls. 27 (1957)
Voitsekhovskii, B.V.: Stationary detonation. Doklady USSR Acad. Sci. 129 (1959)
Voitsekhovskii, B.V., Mitrofanov, V.V., Topchiyan, M.E.: Structure of the detonation front in gases. Siberian Branch USSR Acad. Sci. Publ., Novosibirsk (1963)
Bykowski F.A., Mitrofanov V.V., Vedernikov E.F.: Continuous detonation combustion of fuel–air mixtures, Combustion. Explos. Shock Waves 33, 344–353 (1997). doi:10.1007/BF02671875
Bykovskii F.A., Zhdan S.A., Verdernikov E.F.: Continuous spin detonation in ducted annular combustors. In: Roy, G., Frolov, S.(eds) Application of Detonation to Propulsion, pp. 174–179. Torus press, Moscow (2004)
Wolanski P., Kindracki J., Fujiwara T.: An experimental study of small rotating detonation engine. In: Roy, G, Frolov, S, Sinibaldi, J.(eds) Pulsed and Continuous Detonations, pp. 332–338. Torus press, Moscow (2006)
Zhdan S.A., Bykovskii F.A., Vedernikov E.F.: Mathematical modeling of a rotating detonation wave in a hydrogen-oxygen mixture, Combustion. Explos. Shock Waves 43, 449–459 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10573-007-0061-y
Dabora E.K., Nicholls J.A., Morrison R.B.: Tenth Symposium on Combustion, pp. 817. Combustion Institute, Pittsburgh (1965)
Fujiwara T., Tsuge S.: Quasi-onedimensional analysis of gaseous free detonations. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 33, 237–241 (1972). doi:10.1143/JPSJ.33.237
Tsuge S., Fujiwara T.: On the propagation velocity of a detonation-shock combined wave. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 54, 157–164 (1974). doi:10.1002/zamm.19740540305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Zhang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hishida, M., Fujiwara, T. & Wolanski, P. Fundamentals of rotating detonations. Shock Waves 19, 1–10 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-008-0178-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-008-0178-2
Keywords
- Rotating detonation
- Unconfined detonation
- Detonation wavelet
- Kelvin–Helmholtz instability
- Unburnt pocket
- Standing detonation