Abstract:
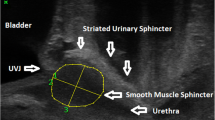
To determine whether differences in functional urodynamic parameters can be explained by changes in urethral anatomy, 39 patients underwent intraurethral ultrasonography to obtain a 360° view of the urethra. The point of maximal rhabdosphincter thickness was identified in all patients. The thickness, circumference and area of the urethral smooth and skeletal muscle layers were calculated. Data from patient histories and urodynamic evaluations were compared with this anatomical survey. The urodynamic diagnoses were as follows: 10 patients were normal, 24 had genuine stress incontinence and 5 had intrinsic sphincter deficiency. These patients had decreasing rhabdosphincter thicknesses of 3.91, 3.35 and 2.70 mm (P= 0.048). A weak linear relationship was found between maximal urethral closure pressure and rhabdosphincter (r= 0.40, P= 0.013) and longitudinal smooth muscle (r= 0.35, P = 0.027) thickness. It was concluded that a loss of urethral resistance as measured by maximal urethral closure pressure is associated with changes in urethral anatomy identified by intraurethral ultrasonography.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heit, M. Intraurethral Ultrasonography: Correlation of Urethral Anatomy with Functional Urodynamic Parameters in Stress Incontinent Women . Int Urogynecol J 11, 204–211 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001920070027
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001920070027