Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis
To verify the intra- and inter-rater reliability of urethral mobility measurement evaluated by ultrasound (US).
Methods
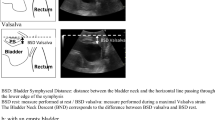
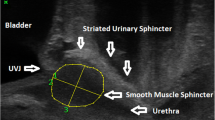
This is a reliability study realized according to Consensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) recommendations. Twenty-one nulliparous women (25.5 ± 3.3 SD years) were volunteers. Two examiners (E1 and E2) performed the measurement of urethral mobility at rest and Valsalva on the same day. Three measurements were recorded for each moment and the mean of them were used for analysis. To perform the analysis, bladder mobility was calculated using the following equation: \( UM=\sqrt{{\left( Vy- Ry\right)}^2+{\left( Vx- Rx\right)}^2} \), where “x” is the vertical distance, “y” is the horizontal distance from the dorsocaudal margin of the pubic symphysis, “V” is the Valsalva maneuver, and “R” means rest. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was calculated considering: ICC ≥ 0.75, excellent; 0.40 ≤ ICC <0.75, satisfactory; ICC < 0.40, poor, with a significance level of 5% and 95% confidence interval.
Results
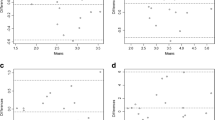
The intra-rater reliabilities of E1 and E2 were considered excellent between the two evaluations, with ICC 0.98 (p < 0.0001) for the E1 and 0.84 (p < 0.0001) for E2. The inter-rater reliability was considered excellent (ICC = 0.83).
Conclusions
Both intra- and inter-rater reliabilities of urethral mobility measurement were considered to have excellent agreement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeLancey JOL. Structural support of the urethra as it relates to stress urinary incontinence: the hammock hypothesis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;170:1713–23.
Schaer GN, Koechli OR, Schuessler B, Haller U. Perineal ultrasound for evaluating the bladder neck in urinary stress incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 1995;85:220–4.
Granados Loarca EA, Alcahe VR, de Leon López H, Echeverria Reyes J. The usefulness of perineal ultrasound in urinary incontinence in women. Arch Esp Urol. 1999;52:778–82.
Naranjo-Ortiz C, Shek KL, Martin AJ, Dietz HP. What is normal bladder neck anatomy? Int Urogynecol J. 2016;27:945–50.
Di Pietto L, et al. Perineal ultrasound in the study of urethral mobility: proposal of a normal physiological range. Int Urogynecol J. 2008;19:1405–9.
Jamard E, et al. Utility of 2D-ultrasound in pelvic floor muscle contraction and bladder neck mobility assessment in women with urinary incontinence. J Gynecol Obstet Human Reprod. 2019;49:101629.
World Health Organization, WHO. Manual of diagnostic ultrasound, vol. 1. 2nd ed. Geneva: WHO; 2011.
Dietz HP. Ultrasound imaging of the pelvic floor. Part I: two-dimensional aspects. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2004;23:80–92.
Brækken IH, et al. Test-retest and intra-observer repeatability of two-, three- and four-dimensional perineal ultrasound of pelvic floor muscle anatomy and function. Int Urogynecol J. 2008;19:227–35.
Pereira VS, Hirakawa HS, Oliveira AB, Driusso P. Relationship among vaginal palpation, vaginal squeeze pressure, electromyographic and ultrasonographic variables of female pelvic floor muscles. Braz J Phys Ther. 2014;18:428–34.
Shek KL, Dietz HP. The urethral motion profile: a novel method to evaluate urethral support and mobility. Aust New Zeal J Obstet Gynaecol. 2008;48:337–42.
Bisi MC, et al. Ultrassonografia articular: confiabilidade interobservadores em artrite reumatoide. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2014;54:250–4.
Ouchi M, Kitta T, Suzuki S, Shinohara N, Kato K. Evaluating pelvic floor muscle contractility using two-dimensional transperineal ultrasonography in patients with pelvic organ prolapse. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019;38:1363–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23987.
Bonett DG. Sample size requirements for estimating intraclass correlations with desired precision. Stat Med. 2002;21:1331–5.
Padilha JF, da Silva JB, Seidel EJ, Driusso P. Intra- and inter-rater reliability of post-void residual bladder volume with ultrasound. Int Urogynecol J. 2019:1–7.
Talasz H, Kofler M, Lechleitner M. Misconception of the Valsalva maneuver. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22:1197–8.
Junginger B, Baessler K, Sapsford R, Hodges PW. Effect of abdominal and pelvic floor tasks on muscle activity, abdominal pressure and bladder neck. Int Urogynecol J. 2010;21:69–77.
Bø K, Berghmans B, Morkved S, Van Kampen M. Evidence-based physical therapy for the pelvic floor. London: Churchill Livingstone; 2015.
Hulley SB, Cummings SR, Brower WS, Grady DG, Newman TB. Designing clinical research: an epidemiologic approach. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
Martin Bland J, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;327:307–10.
Pizzoferrato AC, et al. Perineal ultrasound for the measurement of urethral mobility: a study of inter- and intra-observer reliability. Int Urogynecol J. 2019;30:1551–7.
Salvatore S, et al. Inter-observer reliability of three different methods of measuring urethrovesical mobility. Int Urogynecol J. 2008;19:1513–7.
Dickie K, Shek K, Dietz H. The relationship between urethral mobility and parity. BJOG An Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2010;117:1220–4.
Bø K. Pelvic floor muscle training is effective in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence, but how does it work? Int Urogynecol J. 2004;15:76–84.
Funding
This study was financed in part by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – (CAPES)-Finance Code 001 and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), project no. 2018/26718-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AJS Sousa: Project development, data collection, manuscript writing/editing, other (approval of the submitted version).
JF Padilha: Project development, data collection, manuscript writing/editing, other (approval of the submitted version).
JB Silva: Data collection, manuscript writing/editing, other (approval of the submitted version).
HS Hirakawa: Project development, other (approval of the submitted version).
EJ Seidel: Data analysis, manuscript writing/editing, other (approval of the submitted version).
P Driusso: Project development, manuscript writing/editing, other (approval of the submitted version).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of Federal University of São Carlos (CAAE: 17429019.3.0000.5504).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos Sousa, A.J., Padilha, J.F., da Silva, J.B. et al. Intra- and inter-rater reliability of urethral mobility measurement by ultrasound in women: a cross-section study. Int Urogynecol J 32, 119–125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-020-04381-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-020-04381-7