Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis
The goal of this study was to characterize associations between caffeine consumption and severity of urinary incontinence (UI) in US women. We hypothesized that moderate and high caffeine intake would be associated with UI in US women when controlling for other factors associated with UI.
Methods
US women participated in the 2005–2006 and 2007–2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), a cross-sectional, nationally representative survey. Using the Incontinence Severity Index, UI was categorized as “any” and “moderate/severe”. Types of UI included stress, urge, mixed, and other. Food diaries were completed, and average water (grams/day), total dietary moisture (grams/day), and caffeine (milligrams/day) intake were calculated into quartiles. Stepwise logistic regression models were constructed adjusting for sociodemographics, chronic diseases, body mass index, self-rated health, depression, physical activity, alcohol use, dietary water and moisture intake, and reproductive factors.
Results
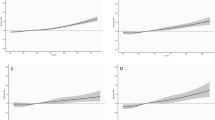
From the 4,309 nonpregnant women (aged ≥20 years) who had complete UI and dietary data, UI prevalence for any UI was 41.0 % and 16.5 % for moderate/severe UI, with stress UI the most common type (36.6 %). Women consumed a mean caffeine intake of 126.7 mg/day. After adjusting for multiple factors, caffeine intake in the highest quartile (≥204 mg/day) was associated with any UI [prevalence odds ratio (POR) 1.47, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.07–2.01], but not moderate/severe UI (POR 1.42, 95 % CI 0.98–2.07). Type of UI (stress, urgency, mixed) was not associated with caffeine intake.
Conclusions
Caffeine intake ≥204 mg/day was associated with any UI but not with moderate/severe UI in US women.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nygaard I, Barber MD, Burgio KL et al (2008) Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Prevalence of symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in US women. JAMA 300:1311
Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Thompson CL et al (2009) The prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in the USA, the UK and Sweden: results from the Epidemiology of LUTS (EpiLUTS) study. BJU Int 104:352
Hunskaar S, Burgio K, Diokno A et al (2003) Epidemiology and natural history of urinary incontinence in women. Urology 62:16
Tennstedt SL, Link CL, Steers WD et al (2008) Prevalence and risk factors for urine leakage in a racially and ethnically diverse population of adults. The Boston Area Community Health (BACH) Survey. Am J Epidemiol 167:390
Caffeine content for coffee, tea, soda and more. Mayo Clinic. Available at http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/caffeine/AN01211. Retrieved January 3, 2012
Nawrot P, Jordan S, Eastwood J et al (2003) Effects of caffeine on human health. Food Addit Contam 20:1
Arria AM, O’Brien MC (2011) The “high” risk of energy drinks. JAMA 305:600
Riesenhuber A, Boehm M, Posch M et al (2006) Diuretic potential of energy drinks. Amino Acids 31:81
Creighton SM, Stanton SL (1990) Caffeine: does it affect your bladder? Br J Urol 66:613
Maughan RJ, Griffin J (2003) Caffeine ingestion and fluid balance: a review. Hum Nutr Diet 16:411
Arya LA, Myers DL, Jackson ND (2000) Dietary caffeine intake and the risk for detrusor instability: a case-control study. Obstet Gynecol 96:85
Tomlinson BU, Dougherty MC, Pendergast JF et al (1999) Dietary caffeine, fluid intake and urinary incontinence in older rural women. Int Urogynecol J 10:22
Bortolotti A, Bernardini B, Colli E et al (2000) Prevalence and risk factors for urinary incontinence in Italy. Eur Urol 37:30
Bradley CS, Kennedy CM, Nygaard IE (2005) Pelvic floor symptoms and lifestyle factors in older women. J Women’s Health 14:128
Hannestad YS, Rortveit G, Dalveit AK et al (2003) Are smoking and other lifestyle factors associated with female urinary incontinence? The Norweigian EPINCONT Study. BJOG 110:247
Tettamanti G, Altman D, Pedersen NL et al (2011) Effects of coffee and tea consumption on urinary incontinence in female twins. BJOG 118:806
Dallosso HM, McGrother CW, Matthews RJ et al (2003) The association of diet and other lifestyle factors with overactive bladder and stress incontinence: a longitudinal study in women. BJU Int 92:69
Jura YH, Townsend MK, Curhan G et al (2011) Caffeine intake, and the risk of stress, urgency and mixed urinary incontinence. J Urol 185:1775
Bryant CM, Dowell CJ, Fairbrother G (2002) Caffeine reduction education to improve urinary symptoms. Br J Nurs 11:560
Swithinbank L, Hashim H, Abrams P (2005) The effect of fluid intake on urinary symptoms in women. J Urol 174:187
Sandvik H, Seim A, Vanvik A et al (2000) A severity index for epidemiological surveys of female urinary incontinence: comparison with 48-hour pad-weighing tests. Neurourol Urodyn 19:137
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville Human Nutrition Research Center, Food Surveys Research Group (Beltsville, MD) and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics (Hyattsville, MD). What We Eat In America, NHANES 2005-2006. Available from: http://www.ars.usda.gov/Services/docs.htm?docid=18354. Retrieved January 3, 2012
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB (2001) The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 16:606
Barber MD, Walters MD, Bump RC (2005) Short forms of two condition-specific quality-of-life questionnaires for women with pelvic floor disorders (PFDI-20 and PFIQ-7). Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:103
National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Continuous NHANES Tutorial on Sampling Design, Website accessed on January 3,2012: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/tutorials/Nhanes/SurveyDesign/SampleDesign/intro.htm
Kant AK, Graubard BI, Atchison EA (2009) Intakes of water, moisture in foods and beverages, and total water in the adult US population – nutritional, meal pattern, and body weight correlates: National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1999-2006. Am J Clin Nutr 90:655
Kincade JE, Dougherty MC, Carlson JR et al (2007) Randomized clinical trial of efficacy of self-monitoring techniques to treat urinary incontinence in women. Neurourol Urodyn 26:507
Financial support or funding
Partially funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases 2 K24-DK068389 to HER and a Department of Veterans Affairs Career Development Award-2 to ADM.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gleason, J.L., Richter, H.E., Redden, D.T. et al. Caffeine and urinary incontinence in US women. Int Urogynecol J 24, 295–302 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-012-1829-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-012-1829-5