Abstract
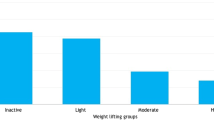
The objective of this study was to evaluate both baseline pelvic support and incontinence in relation to physical activity in nulliparous college women. Participants were examined using the pelvic organ prolapse and quantification system (POP-Q) and completed a questionnaire. Women with stage 0 prolapse and any other stage were compared. Potential risk factors and levels of physcial activity were analyzed using the chi-square test. We evaluated 144 women. Fifty percent had stage 0 support and 50% had stage I or II. Nineteen percent of participants reported incontinence. No risk factors for prolapse were identified, however running was associated with incontinence. Forty-six percent of physically active nulliparous college students had stage I pelvic support without identifiable risk factors. Stage I and II prolapse represent normal support.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- POPQ:
-
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index
References
Lopiano DA (2000) The athletic woman. Clin Sports Med 19:163–73
Nygaard IE, Thompson FL, Svengalis BS, Albright JP (1994) Urinary incontinence in elite nulliparous athletes. Obstet Gynecol 84:183–187
Thyssen HH, Clevin L, Olesen S, Lose G (2002) Urinary incontinence in elite female athletes and dancers. Int Urogynecol Journal 13:15–17
Nygaard IE (1997) Does prolonged high-impact activity contribute to later urinary incontinence? A retrospective cohort study of female Olympians. Obstet Gynecol 90:718–722
Nygaard IE, DeLancey JO, Arnsdorf L, Murphy E (1990) Exercise and incontinence. Obstet Gynecol 75: 848–851
DeLancy JO, Nygaard IE (1991) Exercise-associated urinary incontinence. JAMA 265:514
Bump RC, Mattiasson A, Bo K, Brubaker LP, DeLancy JO, Klarskov P, et al (1996) The Standardization of terminology of female pelvic organ prolapse and pelvic floor dysfunction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:10–17
Hall AF, Theofrastous JP, Cundiff GW, Harris RL, Hamilton LF, Swift SE et al (1996) Interobserver and intraobserver reliability of the proposed International Continence Society, Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, and American Urogynecologic Society pelvic organ prolapse classification system. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:1467–1471
Swift SE (2000) The distribution of pelvic organ support in a population of female subjects seen for routine gynecologic health care. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183:277–285
O’Boyle AL, Woodman PJ, O’Boyle JD, Davis GD, Swift SE (2002) Pelvic organ support in nulliparous pregnant and nonpregnant women: A case control study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 187:99–102
Bo K, Stien R, Kulseng-Hanssen S, Kristofferson M (1994) Clinical and Urodynamic assessment of nulliparous young women with and without stress incontinence symptoms: A case-control study. Obstet Gynecol 84:1028–1032
Acknowledgements
Disclaimers: The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private ones of the authors, and are not to be construed as official or reflecting the views of the Department of Defense or the United States Military Academy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, W.I., Yavorek, T.A. Pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence in nulliparous women at the United States Military Academy. Int Urogynecol J 17, 208–210 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-005-1366-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-005-1366-6