Abstract.
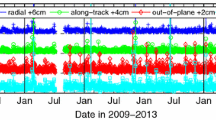
A prerequisite for the success of future gravity missions like the European Gravity field and steady-state Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) is a precise orbit determination (POD). A detailed simulation study has been carried out to assess the achievable orbit accuracy based on satellite-to-satellite tracking (SST) by the US global positioning system (GPS) and in conjunction the implications for gravity field determination. An orbit accuracy at the few centimeter level seems possible, sufficient to support the GOCE gravity mission and in particular its gravity gradiometer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 January 2000 / Accepted: 4 July 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Visser, P., van den IJssel, J. GPS-based precise orbit determination of the very low Earth-orbiting gravity mission GOCE. Journal of Geodesy 74, 590–602 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900000119
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900000119