Abstract
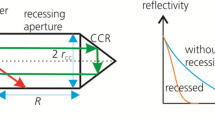
Specific features of spherical retroreflector arrays for high-precision laser ranging are considered, and errors in distance measurements are analyzed. A version of a glass retroreflector satellite with a submillimeter “target error” is proposed. Its cube-corner reflectors are located in recessions to reduce the effective angular aperture, and their faces have a dielectric interference coating.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altamimi Z, Rebischung P, Métivier L, Collilieux X (2016) ITRF2014: a new release of the international terrestrial reference frame modeling non-linear station motions. J Geophys Res 121(8):6109–6131
Arnold DA (1978) Optical and infrared transfer function of the LAGEOS retroreflector array. Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Cambridge
Arnold D (1979) Methods of calculating retroreflector-array transfer functions. Smithsonian astrophysical observatory special report, p 382
Bach H, Neuroth N (1998) The properties of optical glass. Springer, Berlin, p 414
Bloßfeld M, Kehm A, Rudenko S, Angermann D (2018) The role of laser ranging for the global geodetic observing system GGOS. In: 21st international workshop on laser ranging, Canberra, Australia
Crabtree K, Chipman R (2010) Polarization conversion cube-corner retroreflector. Appl Opt 49(30):5882–5890
Degnan JJ (1993) Millimeter accuracy satellite laser ranging: a review. Contrib Space Geod Geodyn Technol AGU Geodyn Ser 25:133–162
Dennis MR, O’Holleran K, Padgett MJ (2009) Singular optics: optical vortices and polarization singularities. Prog Opt 53:293–363
Oleyink I (2018) Russia space programs and exploration handbook, vol 1. International Business Publications, Inc., Washington, p 304
Otsubo T, Sherwood RA, Appleby GM, Neubert R (2015) Center-of-mass corrections for sub-cm-precision laser-ranging targets: Starlette, Stella and LARES. J Geod 89:303–312
Rozas D, Law C, Swartzlander G (1997) Propagation dynamics of optical vortices. J Opt Soc Am B 14(11):3054–3065
Sadovnikov MA, Sokolov AL (2009) Spatial polarization structure of radiation formed by a retroreflector with nonmetalized faces. Opt Spectrosc 107(2):201–206
Sokolov AL (2013) Formation of polarization-symmetrical beams using cube-corner reflectors. J Opt Soc Am A 30(7):1350–1357
Sokolov AL (2017) Optical vortices with axisymmetric polarization structure. Opt Eng 56(1):014109-1–014109-8
Sokolov AL, Murashkin VV (2011) Diffraction polarization-optical elements with the radial symmetry. Opt Spectrosc 111(6):900–907
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sokolov, A.L., Akentyev, A.S., Vasiliev, V.P. et al. Version of a glass retroreflector satellite with a submillimeter “target error”. J Geod 93, 2429–2435 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01260-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01260-y