Abstract
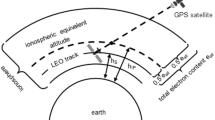
The correction of higher-order ionospheric (HOI) delays remaining in the dual-frequency ionosphere-free combined observations is suggested after the confirmation of its impact on precise Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data processing. However, in the precise orbit determination (POD) for generating ultra-rapid orbits, the higher-order corrections are not always considered most likely because a RT ionospheric model needed for calculating the higher-order corrections is hardly available or the HOI impact is believed rather small compared to the accuracy of the predicted orbit. With the increasing requirement on the positioning performances from various applications, providing more accurate and reliable ultra-rapid orbits becomes an essential task of the real-time GNSS precise positioning services. In this contribution, the temporal–spatial characteristics of HOI effects on GNSS observables are investigated thoroughly using data collected from International GNSS Service (IGS) global ground stations and fluctuations of the higher-order delays up to several centimeters are detected during periods of high ionospheric activity. Hereafter, we evaluate the HOI effects on the multi-GNSS POD based on a network with globally distributed IGS stations. Results show that owing to the applied HOI corrections, the agreement of overlapping orbits can be improved significantly for all satellites and especially in radial direction. The three-dimensional RMS values of the overlapping differences are reduced from 1.6, 2.0, 4.6 and 1.7 to 1.0, 1.1, 3.4, and 1.5 cm for GPS, GALILEO, BDS, and GLONASS, respectively. Furthermore, the orbit improvement is also confirmed by the satellite laser ranging (SLR) observations over a 2-month time period where the STD of SLR residuals is reduced by HOI corrections from 6.4 to 5.3 cm for the BDS-IGSO satellites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassiri S, Hajj GA (1993) Higher-order ionospheric effects on the global positioning systems observables and means of modeling them. Manuscr Geod 18:280–289
Beutler G, Brockmann E, Gurtner W, Hugentobler U, Mervart L, Rothacher M, Verdun A (1994) Extended orbit modeling techniques at the CODE processing center of the international GPS service for geodynamics(IGS): theory and initial results. Manuscr geod 19:367–386
Brunner FK, Gu M (1991) An improved model for the dual frequency ionospheric corrections of GPS observations. Manuscr geod 16:205–214
Chen X, Lu C, Guo B, Guo F, Ge M, Li X, Schuh H (2018) GPS/GLONASS combined Precise Point Positioning with the modeling of highly stable receiver clock in the application of monitoring active seismic deformation. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JB015060
Dach R, Schaer S, Hugentobler U (2006) Combined multi-system GNSS analysis for time and frequency transfer. In: Proceedings of the European frequency and time forum, pp 530–537
Davies K (1990) Ionospheric radio. Peter Peregrinus Ltd, London
Fritsche M, Dietrich R, Knöfel C, Rülke A, Vey S, Rothacher M, Steigenberger P (2005) Impact of higher-order ionospheric terms on GPS estimates. Geophys Res Lett 32:L23311. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL024342
Ge M, Gendt G, Rothacher M, Shi C, Liu J (2008) Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in Precise Point Positioning with daily observations. J Geodesy 82(7):389–399
Gustafsson G, Papitashvili NE, Papitashvili VO (1992) A revised corrected geomagnetic system for epochs 1985 and 1990. J Atmos Terr Phys Great Br 54(11/12):1609–1631
Hapgood MA (1992) Space physics coordinate transformations: a user guide. Planet Space Sci Great Br 40(5):711–717
Hartmann GK, Leitinger R (1984) Range errors due to ionospheric and tropospheric effects for signal frequencies above 100 MHz. Bull Géod 58:109–136
Hawarey M, Hobiger T, Schuh H (2005) Effect of the 2nd order ionospheric terms on VLBI measurements. Geophys Res Lett 32:L11304. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL022729
Hernández-Pajares M, Juan JM, Sanz J, Orús R (2007) Second-order ionospheric term in GPS: implementation and impact on geodetic estimates. J Geophys Res 112(B08417):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JB004707
Hernández-Pajares M, Juan JM, Sanz J, Orus R, Garcia-Rigo A, Feltens J, Komjathy A, Schaer SC, Krankowski A (2009) The IGS VTEC maps: a reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J Geod 83:263–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-008-0266-1
Hernández-Pajares M, Roma-Dollase D, Krankowski A, García-Rigo A, Orús-Pérez R (2017) Methodology and consistency of slant and vertical assessments for ionospheric electron content models. J Geodesy 91:1405–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1032-z
Hoque MM, Jakowski N (2007) Higher order ionospheric effects in precise GNSS positioning. J Geodesy 81(4):259–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-006-0106-0
Hoque MM, Jakowski N (2010) Higher order ionospheric propagation effects on GPS radio occultation signals. Adv Space Res 46(2):162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2010.02.013
Jackson JD (1962) Classical electrodynamics. Wiley, Hoboken
Kedar S, Hajj A, Wilson BD, Heflin MB (2003) The effect of the second order GPS ionospheric correction on receiver positions. Geophys Res Lett 30(16):1829. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017639
Kouba J (2005) A possible detection of the 26 December 2004 great Sumatra-Andaman islands earthquake with solution products of the International GNSS Service. Stud Geophys Geod 49:463–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-005-0022-4
Kouba J (2009) A guide to using international GNSS service (IGS) products. http://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov/igscb/resource/pubs/UsingIGSProductsVer21.pdf. Accessed May 2009
Li X, Chen X, Ge M, Schuh H (2018) Improving multi-GNSS ultra-rapid orbit determination for real-time precise point positioning. J Geod. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1138-y
Liu J, Ge M (2003) PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ J Nat Sci 8(603–609):9. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02899825
Marini JW, Murray CW (1973) Correction of laser range tracking data for atmospheric refraction at elevations above 10 degrees. NASA Tech, Rep. X-591-73-351
Marques HA, Monico JFG, Aquino M (2011) RINEX_HO: second- and third-order ionospheric corrections for RINEX observation files. GPS Solut 15(3):305–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0220-1
Montenbruck O, Schmid R, Mercier F, Steigenberger P, Noll C, Fatkulin R, Kogure S, Ganeshan AS (2015a) GNSS satellite geometry and attitude models. Adv Space Res 56(6):1015–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2015.06.019
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Hugerntobler U (2015b) Enhanced solar radiation pressure modeling for Galileo satellites. J Geod 89:283–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0774-0
Montenbruck O, Steigenberger P, Prange L, Deng Z, Zhao Q, Perosanz F, Romero I, Noll C, Stürze A, Weber G, Schmid R, MacLeod K, Schaer S (2017) The multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS)—achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv Space Res 59:1671–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.01.011
Odijk D (2002) Fast precise GPS positioning in the presence of ionospheric delays. Phd dissertation, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences, Delft University of Technology, Delft
Pan L, Zhang X, Li X, Li X, Lu C, Liu J, Wang Q (2017) Satellite availability and point positioning accuracy evaluation on a global scale for integration of GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and Galileo. Adv Space Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.07.029
Papas CH (1965) Theory of electromagnetic wave propagation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Pearlman M, Degnan J, Bosworth J (2002) The international laser ranging service. Adv Space Res 30(2):125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00277-6
Petrie EJ, King MA, Moore P, Lavallée DA (2010) Higher-order ionospheric effects on the GPS reference frame and velocities. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 115:B03417. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB006677
PIM (2001) Parameterized ionospheric model 1.7: user guide. Computational Physics Inc, Springfield
Pireaux S, Defraigne P, Wauters L, Bergeot N, Baire Q, Bruyninx C (2010) Higher-order ionospheric effects in GPS time and frequency transfer. GPS Solut 14:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-009-0152-1
Saastamoinen J (1973) Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction—part II. Refraction corrections in satellite geodesy. Bull Géod 47(1):13–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522083
Schaer S, Beutler G, Rothacher M, Brockmann E, Wiger A, Wild U (1999) The impact of the atmosphere and other systematic errors on permanent GPS networks. In: President of IAG symposium on positioning, Birmingham, 19–24 July, p 406
Shi C, Zhao Q, Geng J, Lou Y, Ge M, Liu J (2008) Recent development of PANDA software in GNSS data processing. In: Proceedings of SPIE 7285, international conference on earth observation data processing and analysis (ICEODPA), 72851S, 29 Dec 2008. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.816261
Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Montenbruck O, Hauschild A (2011) Precise orbit determination of GIOVE-B based on the CONGO network. J Geod 85:357–365
Thébault E, Finlay CC, Beggan CD, Alken P, Aubert J, Barrois O et al (2015) International geomagnetic reference field: the 12th generation. Earth Planets Space 67(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0228-9
Wang H, Wang C, Wang JX, Dang YM, Bai GX, Wang QX (2014) Global characteristics of the second-order ionospheric delay error using inversion of electron density profiles from COSMIC occultation data. Sci China Phys Mech Astron 57(2):365–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5376-y
Zhao Q, Liu J, Ge M, Shi C, Du RL (2005) Precise orbits determination of GPS and CHAMP satellite with PANDA software. J Geod Geodyn 2:113–116
Zumberge J, Heflin M, Jefferson D, Watkins M, Webb F (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res 102(B3):5005–5017. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB03860
Acknowledgements
Xinghan Chen and Maorong Ge conceived and designed the experiments and analyzed data. Haroldo Antonio Marques and Harald Schuh provided advice on HOI corrections. Xinghan Chen performed the experiments and wrote this paper. The paper was modified by Maorong Ge, Haroldo Antonio Marques, and Harald Schuh. Thanks go to the IGS for providing multi-GNSS data and products. Our study is financially supported by the China Scholarship Council (CSC, File No. 201606270206) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 41404006, 41704010, and 41774030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Ge, M., Marques, H.A. et al. Evaluating the impact of higher-order ionospheric corrections on multi-GNSS ultra-rapid orbit determination. J Geod 93, 1347–1365 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01249-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01249-7