Abstract
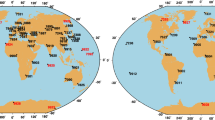
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) and the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) worked closely together in the early years of the space program to deploy satellite laser ranging (SLR) systems at overseas sites to enhance global coverage to support specific missions. The data were routinely made available for use by the science community for programs in geodesy, gravity field, atmospheric physics, and ultimately for oceanography and geodynamics. SAO and CNES organized campaigns for international participation and loaned each other equipment to enhance the network. SAO and CNES provided technical expertise and advice to a number of other groups as they planned and deployed SLR systems. In this paper, we will discuss the history and the role of the two institutions in the building of the international SLR network.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlier F, Lefebvre M (2001) A new look at planet earth: satellite geodesy and geosciences. In: Bleeker J, Geiss J, Huber M (eds) The century of space sciences. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Pays-Bas, pp 1623–1651
Courde C, Torre JM, Samain E, Martinot-Lagarde G, Aimar M, Albanese D, Chabé J, Exertier P, Feraudy D, Fienga A, Mariey H, Metris G, Viot H, Viswanathan V (2017) Lunar Laser ranging in infrared at the Grasse laser station. Astron Astrophys 602:A90
Exertier P, Bonnefond P, Nicolas J, Barlier F (2001) Contributions of satellite laser ranging to past and future radar altimetry missions. Surv Geophys Spec Issue Evolv Geodesy 22(5–6):491–507
Exertier P, Belli A, Lemoine JM (2017) Time biases in laser ranging observations: a concerning issue of space geodesy. Adv Sp Res 60:948–968
Flick JA, Stomp N (2002) Sciences de la Terre au Luxembourg, Réminiscences, Musée National d’Histoire Naturelle, Luxembourg. ISNB 2-919877-00-8
Gaposchkin EM (1966) Orbit determination. In: Lundquist C, Veis G (eds) Geodetic parameters for a 1966 Smithsonian Institution Standard Earth. Smithsonian Astrophys Obs Spec Rep 200(I). Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Cambridge MA, pp 77–183
Gaposchkin EM, Smith DM et al (1973) Smithsonian Standard Earth (III). Smithsonian Astrophys Obs Spec Rep 353. Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Cambridge MA
Henriksen SW (1977) National geodetic satellite program, a report compiled and edited for NASA by the American Geophysical Union, NASA SP-365
Kaula WM (1970) The terrestrial environment: solid earth and ocean physics. Report of a study at Williamstown, Massachusetts, sponsored by NASA-Electronics Research Center and MIT Measurement Systems Laboratory
Lehr CG, Pearlman MR, Scott JL, Wohn J (1970) Laser satellite ranging. In: Proceedings of symposium on laser applications in the geosciences, Douglas Advanced Research Laboratories, McDonald Douglas Corp., pp 111–130
Luck JMcK, Greene BA (1985) Report from Orroral. In: Proceedings of the international conference on earth rotation and the terrestrial reference frame (reports on the MERIT-COTES campaign on earth rotation and reference systems, IAU/IAG/IUGG, Part II), Columbus, Ohio, 31 July–2 August 1985, vol 1, pp 257–273
Mao D, McGarry J, Torrence M, Neu-mann G, Mazarico E, Barker M, Sun X, Rowlands D, Golder J, Zagwodzki T, Cavanaugh J, Zuber M, Smith D (2011) Laser ranging experiment on lunar reconnaissance orbiter: Timing determination and orbit constraints. In: Proceedings of the 17th international workshop on laser ranging, Bad Kötzting, Germany, pp 16–20
Nicolas J, Pierron F, Kasser M, Exertier P, Bonnefond P, Barlier F, Haase J (2000) French transportable laser ranging station: scientific objectives, technical features, and performance. Appl Opt Lasers Photonics Environ Opt 39(3):402–410
Pearlman MR, Lanham NW, Wohn J, Thorp JM, Imbier E, Young FD (1978) The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory satellite ranging hardware. In: Proceedings of the third international workshop on laser ranging instrumentation, Lagonissi, Greece, 23–27 May 1978 (available on the ILRS website)
Pearlman MR, Lanham N, Wohn J, Thorp J (1981) Current status and upgrading of the SAO laser ranging systems. In: Proceedings of the third international workshop on laser ranging instrumentation, Austin, TX, 12–16 October 1981 (available on the ILRS Website)
Plotkin HH, Johnson TS, Spadin P, Moye J (1965) Reflection of ruby laser radiation from explorer 22. Proc IEEE 53:301–302
Samain E, Exertier P, Courde C, Fridelance P, Guillemot Ph, Laas-Bourez M, Torre J-M (2015) Time transfer by laser link: a complete analysis of the error budget. Metrologia 52:423–432
Smith DE, Lerch FJ, Marsh JG, Wagner CA, Kolenkiewicz R, Khan MA (1976) Contributions to the national geodetic satellite program by goddard space flight. J Geophys Res Solid Earth Planets 81(5):1006–1026
Space Oceanography, Navigation and Geodynamics (1978) SONG workshop. Schloss Elmau, Germany, 16–21 January 1978, ESA-SP-137
Wang X, Bonnefond P, Exertier P et al (2015) Laser ranging data analysis for a colocation campaign of French Transportable Laser Ranging System (FTLRS) in Tahiti. J Geodesy 89(1):1–11
Acknowledgements
Michael Pearlman acknowledges the support of NASA Grant 80NSSC18K0220. Gérard Brachet, Michel Lefebvre, François Barlier, and Pierre Exertier acknowledge the support of CNES, INSU/CNRS, Université de Nice/Sophia Antipolis/Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur/GEOAZUR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pearlman, M., Brachet, G., Lefebvre, M. et al. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) and the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES): contributions to the international laser ranging network. J Geod 93, 869–875 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1209-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1209-0