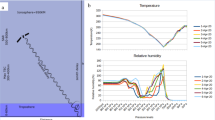
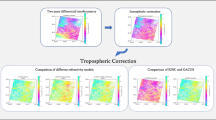
Abstract
Despite the many applications of time series interferometric synthetic aperture radar (TS-InSAR) techniques in geophysical problems, error analysis and assessment have been largely overlooked. Tropospheric propagation error is still the dominant error source of InSAR observations. However, the spatiotemporal variation of atmospheric effects is seldom considered in the present standard TS-InSAR techniques, such as persistent scatterer interferometry and small baseline subset interferometry. The failure to consider the stochastic properties of atmospheric effects not only affects the accuracy of the estimators, but also makes it difficult to assess the uncertainty of the final geophysical results. To address this issue, this paper proposes a network-based variance–covariance estimation method to model the spatiotemporal variation of tropospheric signals, and to estimate the temporal variance–covariance matrix of TS-InSAR observations. The constructed stochastic model is then incorporated into the TS-InSAR estimators both for parameters (e.g., deformation velocity, topography residual) estimation and uncertainty assessment. It is an incremental and positive improvement to the traditional weighted least squares methods to solve the multitemporal InSAR time series. The performance of the proposed method is validated by using both simulated and real datasets.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agram PS, Jolivet R, Riel B, Lin YN, Simons M, Hetland E, Doin MP, Lassere C (2013) New radar interferometric time series analysis toolbox released. Eos Trans AGU 94(7):69–76
Bamler R, Hartl P (1998) Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Probl 14:R1–R54
Bekaert DPS, Hooper A, Wright TJ (2015a) A spatially variable power law tropospheric correction technique for InSAR data. J Geophys Res 120(2):1345–1356. doi:10.1002/2014JB011558
Bekaert DPS, Walters RJ, Wright TJ, Hooper AJ, Parker DJ (2015) Statistical comparison of InSAR tropospheric correction techniques. Remote Sens Environ 170:40–47. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.035
Berardino P, Fornaro G, Lanari R, Sansosti E (2002) A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 40(11):2375–2383. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
Cao YM, Li ZW, Wei JC, Zhan WJ, Zhu JJ, Wang CC (2014) A novel method for determining the anisotropy of geophysical parameters: unit range variation increment (URVI). Appl Geophys 11(3):340–349. doi:10.1007/s11770-014-0448-y
Chaussard E, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E, Amelung F (2014) Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens Environ 140:94–106. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.038
Ding XL, Li ZW, Zhu JJ, Feng GC, Long JP (2008) Atmospheric effects on InSAR measurements and their mitigation. Sensors 8(9):5426–5448. doi:10.3390/s8095426
Doin MP, Lasserre C, Peltzer G, Cavalié O, Doubre C (2009) Corrections of stratified tropospheric delays in SAR interferometry: validation with global atmospheric models. J Appl Geophys 69(1):35–50
Emardson TR, Simons M, Webb FH (2003) Neutral atmospheric delay in interferometric synthetic aperture radar applications: statistical description and mitigation. J Geophys Res 108(B5):ETG4-1–ETG4-8. doi:10.1029/2002JB001781
Fattahi H, Amelung F (2015) InSAR bias and uncertainty due to the systematic and stochastic tropospheric delay. J Geophys Res 120(12):8758–8773. doi:10.1002/2015JB012419
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2001) Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39(1):8–20. doi:10.1109/36.898661
Ferretti A, Fumagalli A, Novali F, Prati C, Rocca F, Rucci A (2011) A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(9):3460–3470. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2011.2124465
Foster J, Kealy J, Cherubini T, Businger S, Lu Z, Murphy M (2013) The utility of atmospheric analyses for the mitigation of artifacts in InSAR. J Geophys Res 118(2):748–758. doi:10.1002/jgrb.50093
Gong WY, Meyer FJ, Liu SZ, Hanssen RF (2015) Temporal filtering of InSAR data using statistical parameters from NWP models. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(7):4033–4044. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2015.2389143
González PJ, Fernández J (2011) Error estimation in multitemporal InSAR deformation time series, with application to Lanzarote, Canary Islands. J Geophys Res 116:B10404–1–B10404–17. doi:10.1029/2011JB008412
Hanssen RF (2001) Radar interferometry: data interpretation and error analysis. Kluwer, Alphen aan den Rijn
Hooper A (2008) A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys Res Lett 35(16):96–106. doi:10.1029/2008GL034654
Hooper A, Zebker HA, Segall P, Kampes B (2004) A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys Res Lett 31(23):611–615. doi:10.1029/2004GL021737
Hooper A, Bekaert D, Spaans K, Arıkan M (2012) Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics 514:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.10.013
Jolivet R, Grandin R, Lasserre C, Doin MP, Peltzer G (2011) Systematic InSAR tropospheric phase delay corrections from global meteorological reanalysis data. Geophys Res Lett 38:L17311. doi:10.1029/2011GL048757
Journel AG, Huijbregts CJ (1978) Mining geostatistics. Academic Press, London
Kampes B, Hanssen RF (2004) Ambiguity resolution for permanent scatterer interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(11):2446–2453. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2004.835222
Kinoshita Y, Furuya M, Hobiger T, Ichikawa R (2013) Are numerical weather model outputs helpful to reduce tropospheric delay signals in InSAR data? J Geodesy 87(3):267–277. doi:10.1007/s00190-012-0596-x
Knospe SHG, Jónsson S (2010) Covariance estimation for dInSAR surface deformation measurements in the presence of anisotropic atmospheric noise. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48(4):2057–2065. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2009.2033937
Lanari R, Mora O, Manunta M, Mallorqui J, Berardino P, Sansosti E (2004) A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 42(7):1377–1386. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2004.828196
Li ZW (2005) Modeling atmospheric effects on repeat-pass InSAR measurements. Ph.D. thesis, Hong Kong, Hong Kong Polytechnic University. http://hdl.handle.net/10397/2248
Li ZH, Muller JP, Cross P, Fielding EJ (2005) Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) atmospheric correction: GPS, Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS), and InSAR integration. J Geophys Res 110(B3):B03410–1. doi:10.1029/2004JB003446
Li ZW, Xu WB, Feng GC, Hu J, Wang CC, Ding XL, Zhu JJ (2012) Correcting atmospheric effects on InSAR with MERIS water vapour data and elevation-dependent interpolation model. Geophys J Int 189(2):898–910. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05432.x
Li ZW, Zhao R, Hu J, Wen LX, Feng GC, Zhang ZY, Wang QJ (2015) InSAR analysis of surface deformation over permafrost to estimate active layer thickness based on one-dimensional heat transfer model of soils. Sci Rep 5:15542. doi:10.1038/srep15542
Massonnet D, Rabaute T (1993) Radar interferometry: limits and potential. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 32(2):455–464. doi:10.1109/36.214922
Ng AHM, Ge LL, Li XJ, Zhang K (2012) Monitoring ground deformation in Beijing, China with persistent scatterer SAR interferometry. J Geodesy 86(6):375–392. doi:10.1007/s00190-011-0525-4
Rocca F (2007) Modeling interferogram stacks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45(10):3289–3299. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2007.902286
Williams S, Bock Y, Fang P (1998) Integrated satellite interferometry: tropospheric noise, GPS estimates and implications for interferometric synthetic aperture radar products. J Geophys Res 103(B11):27051–27067
Xu WB, Li ZW, Ding XL, Zhu JJ (2011) Interpolating atmospheric water vapor delay by incorporating terrain elevation information. J Geodesy 85(9):555–564. doi:10.1007/s00190-011-0456-0
Yang ZF, Li ZW, Zhu JJ, Yi HW, Hu J (2017) Deriving dynamic subsidence of coal mining areas using InSAR and logistic model. Remote Sens 9(2):125. doi:10.3390/rs9020125
Zebker HA, Rosen PA, Hensley S (1997) Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J Geophys Res 102:7547–7563. doi:10.1029/96JB03804
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41474007, 41404013) and the Doctoral Innovation Foundation of Central South University (2015zzts068), and the SAR images were provided by WInSAR and the European Space Agency (ESA) Cat-1 18234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Li, Z., Wei, J. et al. Stochastic modeling for time series InSAR: with emphasis on atmospheric effects. J Geod 92, 185–204 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1055-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-017-1055-5