Abstract
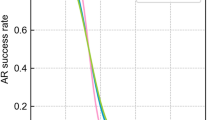
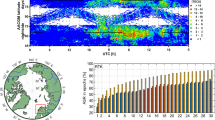
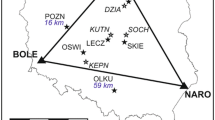
The network-based GPS technique provides a broad spectrum of corrections to support RTK (real-time kinematic) surveying and geodetic applications. The most important among them are the ionospheric corrections generated in the reference network. The accuracy of these corrections depends upon the ionospheric conditions and may not always be sufficient to support ambiguity resolution (AR), and hence accurate GPS positioning. This paper presents the analyses of the network-derived ionospheric correction accuracy under extremely varying – quiet and stormy – geomagnetic and ionospheric conditions. In addition, the influence of the correction accuracy on the instantaneous (single-epoch) and on-the-fly (OTF) AR in long-range RTK GPS positioning is investigated, and the results, based on post-processed GPS data, are provided. The network used here to generate the ionospheric corrections consists of three permanent stations selected from the Ohio Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS) network. The average separation between the reference stations was ∼200 km and the test baseline was 121 km long. The results show that, during the severe ionospheric storm, the correction accuracy deteriorates to the point when the instantaneous AR is no longer possible, and the OTF AR requires much more time to fix the integers. The analyses presented here also outline the importance of the correct selection of the stochastic constraints in the rover solution applied to the network-derived ionospheric corrections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartels J. (1957). The technique of scaling indices K and Q of geomagnetic activity. Ann Intern Geophys 4:215–226
Cannon ME., Lachapelle G., Alves P., Fortes LP., Townsend B. (2001). GPS RTK Positioning using a regional reference network: theory and results.In: Proceedings of the 5th GNSS international symposium, Seville, (CD-ROM) 8–11 May 2001
Colombo OL., Hernandez-Pajares M., Juan JM., Sanz J. (2000). Application of ionospheric tomography to real-time GPS carrier phase ambiguities resolution, at scales of 400–1000 km and with high geomagnetic activity. Geophys Res Lett 13(27):2009–2012
Grejner-Brzezinska DA, Kashani I, Wielgosz P (2004) On accuracy and reliability of instantaneous network RTK as a function of network geometry, station separation, and data processing strategy. GPS Solutions (in press)
Grejner-Brzezinska DA, Wielgosz P, Kashani I, Smith DA, Spencer PSJ, Robertson DS, Mader GL (2005) The analysis of the effects of different network-based ionosphere estimation models on the rover positioning accuracy. J GPS (in press)
Hunsucker RD., Hargreaves JK. (2002). The high-latitude ionosphere and its effects on radio propagation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 560
de Jonge PJ, Tiberius C (1996) The LAMBDA method for integer ambiguity estimation: implementation aspects. LGR-series 12, Delft Geodetic Computer Centre, pp 1–49
Kashani I., Grejner-Brzezinska DA., Wielgosz P. (2004). Towards instantaneous RTK GPS over 100 km distances.In: Proceedings of the ION 60th annual meeting, Dayton, OH, 7–9 June 2004, pp 679– 685
Kashani I, Wielgosz P, Grejner-Brzezinska DA (2005) The Impact of the ionospheric correction latency on long-baseline instantaneous kinematic GPS positioning. Surv Rev (in press)
Kim D, Langley RB (2000) GPS ambiguity resolution and validation: methodologies, trends and issues. In: Proceedings of the 7th GNSS workshop and international symposium on GPS/GNSS, Seoul, Korea, November 30–December 2, pp 213–221
Odijk D (2000) Weighting ionospheric corrections to improve fast GPS positioning over medium distances. In: Proceedings of the ION GPS 2000, Salt Lake City, UT, 19–22 September 2000, pp 1113–1123
Odijk D. (2001). Instantaneous GPS positioning under geomagnetic storm conditions. GPS Sol 2(5):29–42
Rizos C. (2002). Network RTK research and implementation: a geodetic perspective. J GPS 2(1):144–150
Teunissen PJG (1994) A new method for fast carrier phase ambiguity estimation.In: Proceedings of the IEEE PLANS’94, Las Vegas, NV, pp 562–573
Uotila UA. (1986). Notes on adjustment computation, Part I, Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying. The Ohio State University, Columbus, 168 p
Vollath U, Buecherl A, Landau H, Pagels C, Wagner B (2000) Multi-base RTK positioning using virtual reference stations. In: Proceedings of the ION GPS, Salt Lake City, UT, 19–22 September 2000, pp 123–131
Wang J., Stewart M., Tsakiri M. (1998). A discrimination test procedure for ambiguity resolution on-the-fly. J Geod 72:644–653
Wanninger L (1999) The performance of virtual reference stations in active geodetic GPS-networks under solar maximum conditions. In: Proceedings of the ION GPS’99, Nashville, TN, pp 1419–1427
Wanninger L (2004) Ionospheric Disturbance Indices for RTK and Network RTK Positioning. In: Proceedings of the ION GPS/GNSS 2004, Long Beach, CA, 21–24 september, pp 2849–2854
Wielgosz P., Baran LW., Shagimuratov II., Aleshnikova MV. (2004). Latitudinal variations of TEC over Europe obtained from GPS observations. Ann Geophys 22:405–415
Wielgosz P., Grejner-Brzezinska DA., Kashani I. (2004b). Network approach to precise medium range GPS navigation. Navigation 51(3):213–220
Wielgosz P, Grejner-Brzezinska DA, Kashani I (2004c) High-accuracy DGPS and precise point positioning based on Ohio CORS network. In: Proceedings of the ION 60th AM, Dayton, OH, pp 754–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wielgosz, P., Kashani, I. & Grejner-Brzezinska, D. Analysis of long-range network RTK during a severe ionospheric storm. J Geodesy 79, 524–531 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-005-0003-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-005-0003-y