Abstract.
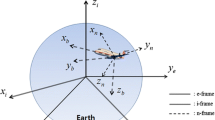
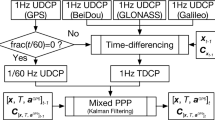
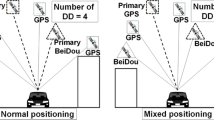
Integrated systems for kinematic positioning have been studied extensively from the perspective of the navigation problem. A model is presented for an integrated system that places greater emphasis on the geodetic problem. The model integrates global positioning system (GPS) carrier phase measurements with dead-reckoning (DR) sensor measurements from an odometer and three fibre-optic rate gyroscopes. Mathematical models are developed for a modified form of the triple-difference carrier-phase observable, odometer distance measurements and a transformation from vehicle axis rotations to changes in orientation in the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) coordinate system using a quaternion representation of rotations. Results from field tests show that the integration model achieves improved positioning performance during periods of limited satellite visibility (fewer than four satellites) over that provided by the dead-reckoned solution alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 February 2001 / Accepted: 15 April 2002
Correspondence to: S. A. Logan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logan, S., Leahy, F. & Kealy, A. Integration of GPS carrier phase and other measurements for kinematic mapping. Journal of Geodesy 76, 543–556 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-002-0281-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-002-0281-6