Abstract
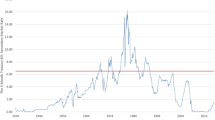
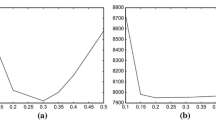
Financial data are often assumed to be generated by diffusions. Using recent results of Fan et al. (J Am Stat Assoc, 102:618–631, 2007; J Financ Econometer, 5:321–357, 2007) and a multiple comparisons procedure created by Benjamini and Hochberg (J R Stat Soc Ser B, 59:289–300, 1995), we develop a test for non-stationarity of a one-dimensional diffusion based on the time inhomogeneity of the diffusion function. The procedure uses a single sample path of the diffusion and involves two estimators, one temporal and one spatial. We first apply the test to simulated data generated from a variety of one-dimensional diffusions. We then apply our test to interest rate data and real exchange rate data. The application to real exchange rate data is of particular interest, since a consequence of the law of one price (or the theory of purchasing power parity) is that real exchange rates should be stationary. With the exception of the GBP/USD real exchange rate, we find evidence that interest rates and real exchange rates are generally non-stationary. The software used to implement the estimation and testing procedure is available on demand and we describe its use in the paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuaf N, Jorion P (1990) Purchasing power parity in the long run. J Financ 45: 157–174
Banon G (1978) Nonparametric identificaton for diffusion processes. SIAM J Cont Optim 16(3): 380–395
Basher S, i Silvestre JC (2007) Another look at the null of stationary real exchange rates: panel data with structural breaks and cross-section dependence, iREA working papers 200710, University of Barcelona, Research Institute of Applied Economics
Beirne J, Hunter J, Simpson M (2007) Is the real exchange rate stationary? A similar sized test approach for the univariate and panel cases, research paper, Brunel Business School, West London
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Statist Soc Ser B 59: 289–300
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29: 1165–1188
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y, Kling Y (1997) False discovery rate control in multiple hypotheses testing using dependent test statistics, research paper 97-1, Department of Statistics and O.R., Tel Aviv University
Black F, Scholes M (1973) The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. J Polit Econ 81: 637–654
Cassel G (1922) Money and foreign exchanges after 1914. Constable, London
Chortareas G, Kapetanios G (2006) The yen real exchange rate may be stationary after all: evidence from nonlinear unit-root tests. Working paper no. 311, Bank of England
Cox J, Ingersoll J, Ross S (2005) A theory of the term structure of interest rates. Econometrica 53: 385–407
Craiu R, Sun L (2005) Choosing the lesser evil: trade-off between false discovery rate and non-discovery rate, research paper, University of Toronto, Toronto
Dutt S, Ghosh D (1995) Purchasing power parity doctrine: weak and strong form tests. Appl Econ Lett 2: 316–320
Ethier S, Kurtz T (1986) Markov processes: characterization and convergence. Wiley, New York
Fan J, Gijbels I (1996) Local polynomial modelling and its applications. Chapman & Hall, London
Fan J, Yao Q (2005) Nonlinear time series: nonparametric and parametric methods. Springer series in statistics, Springer, New York
Fan J, Zhang C (2003) A reexamination of diffusion estimators with applications to financial model validation. J Am Statist Assoc 98: 118–134
Fan J, Fan Y, Jiang J (2007a) Dynamic integration of time- and state-domain methods for volatility estimation. J Am Statist Assoc 102: 618–631
Fan J, Fan Y, Lv J (2007b) Aggregation of nonparametric estimators for volatility matrix. J Financ Economet 5: 321–357
Glasserman P (2004) Monte Carlo methods in financial engineering. Springer, New York
Hansen L, Sheinkman J (1995) Back to the future: generating moment implications for continuous-time Markov processes. Econometrica 63: 767–804
Härdle W (1991) Smoothing techniques with implementation in S. Springer series in statistics, Springer, New York
Jong FD, Drost F, Werker B (2001) A jump-diffusion model for exchange rates in a target zone. Stat Neerl 55(3): 270–300
Karatzas I, Shreve S (1991) Brownian motion and stochastic calculus. Springer, New York
Larsen K, Sorensen M (2007) Diffusion models for exchange rates in a target zone. Math Financ 17(2): 285–306
Liew VKS, Baharumshah A, Chong TTL (2004) Are Asian real exchange rates stationary? Econ Lett 83: 3–313316
Merton R (1992) Continuous-time finance. Blackwell Publishing, Malden
Narayan P (2006) Are bilateral real exchange rates stationary? Evidence from Lagrange multiplier unit root tests from India. App Econ 38(1): 63–70
Nelson D (1990) ARCH models as diffusion approximations. J Economet 45: 7–38
Nicolau J (1999) Modelling the DEM/USD exchange rate as a stationary continuous time process, research Paper, Instituto Superior de Economia e Gestao
RiskMetrics (1996) Technical document, 4th edn. J.P. Morgan, New York
Rosenblatt M (1970) Density estimates and Markov sequences. In: Pun ML (eds) Nonparametric techniques in statistical inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 199–213
Silverman B (1986) Density estimation for statistics and data analysis. Chapman & Hall, London
Skorokhod A (1989) Asymptotic methods in the theory of stochastic differential equations. Translation of mathematical monographs, vol 78. American Mathematical Society, New York
Stanton R (1997) Nonparametric models of term structure dynamics and the market price of interest rate risk. J Financ 52: 1973–2002
Stroock D (2003) Markov processes from K. Itô’s perspective, vol 155. Annals of Math. Studies Series, Princeton University Press
Trede M, Wilfling B (2004) Estimating exchange rate dynamics with diffusion processes: an application to Greek EMU data, hWAA discussion paper no. 267
Wang Y (2002) Asymptotic nonequivalence of GARCH models and diffusions. Ann Stat 30: 754–783
Wilmott P (2000) Paul Wilmott on quantitative finance. Wiley, West Sussex
Wu J, Chen S (1999) Are real exchange rates stationary based on panel unit-root tests? Evidence from Pacific Basin countries. Int J Financ Econ 4(3): 243–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamrick, J., Taqqu, M.S. Testing diffusion processes for non-stationarity. Math Meth Oper Res 69, 509–551 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-008-0250-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00186-008-0250-9