Abstract
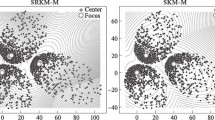
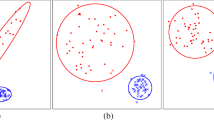
The k points that optimally represent a distribution (usually in terms of a squared error loss) are called the k principal points. This paper presents a computationally intensive method that automatically determines the principal points of a parametric distribution. Cluster means from the k-means algorithm are nonparametric estimators of principal points. A parametric k-means approach is introduced for estimating principal points by running the k-means algorithm on a very large simulated data set from a distribution whose parameters are estimated using maximum likelihood. Theoretical and simulation results are presented comparing the parametric k-means algorithm to the usual k-means algorithm and an example on determining sizes of gas masks is used to illustrate the parametric k-means algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham C, Cornillon PA, Matzner-Lober E, Molinari N (2003) Unsupervised curve clustering using B-splines. Scand J Stat 30:1–15
Connor R (1972) Grouping for testing trends in categorical data. J Am Stat Assoc 67:601–604
Cox DR (1957) A note on grouping. J Am Stat Assoc 52:543–547
Dalenius T (1950) The problem of optimum stratification. Skandinavisk Aktuarietidskrift 33: 203–213
Dalenius T, Gurney M (1951) The problem of optimum stratification ii. Skandinavisk Aktuarietidskrift 34:133–148
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J Am Stat Assoc 39:1–38
Eubank RL (1988) Optimal grouping, spacing, stratification, and piecewise constant approximation. Siam Rev 30:404–420
Fang K, He S (1982) The problem of selecting a given number of representative points in a normal population and a generalized mill’s ratio. Technical report, Department of Statistics, Stanford University
Fang KT, Kotz S, Ng KW (1990) Symmetric multivariate and related distributions. Chapman and Hall, London
Flury B (1990) Principal points. Biometrika 77:33–41
Flury B (1993) Estimation of principal points. Appl Stat 42:139–151
Flury B (1997) A first course in multivariate statistics. Springer, New York
Flury BD, Tarpey T (1993) Representing a large collection of curves: a case for principal points. Am Stat 47:304–306
Graf L Luschgy H (2000) Foundations of quantization for probability distributions. Springer, Berlin
Gu XN, Mathew T (2001) Some characterizations of symmetric two-principal points. J Stat Plann Infer 98:29–37
Hand DJ, Krzanowski WJ (2005) Optimising k-means clustering results with standard software packages. Comput Stat Data Anal 49:969–973
Hartigan JA (1975) Clustering algorithms. Wiley, New York
Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) A k-means clustering algorithm. Appl Stat 28:100–108
Iyengar S, Solomon H (1983) Selecting representative points in normal populations. In recent advances in statistics: papers in honor of Herman chernoff on his 60th Birthday, Academic, New York, pp 579–591
James G, Sugar C (2003) Clustering for sparsely sampled functional data. J Am Stat Assoc 98: 397–408
Li L, Flury B (1995) Uniqueness of principal points for univariate distributions. Stat Probab Lett 25:323–327
Luschgy H, Pagés G (2002) Functional quantization of Gaussian processes. J Func Anal 196:486–531
MacQueen J (1967) Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In:Proceedings 5th Berkeley symposium on mathematics, statistics and probability 3:281–297
McLachlan GJ, Krishnan T (1997) The EM algorithm and extensions. Wiley, New York
Mease D, Nair VN, Sudjianto A (2004) Selective assembly in manufacturing: statistical issues and optimal binning strategies. Technometrics 46:165–175
Pollard D (1981) Strong consistency of k-means clustering. Ann Stat 9:135–140
Pollard D (1982) A central limit theorem for k-means clustering. Ann Probab 10:919–926
Pötzelberger K, Felsenstein K (1994) An asymptotic result on principal points for univariate distributions. Optimization 28:397–406
R Development Core Team (2003) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-00-3
Ramsay JO, Silverman BW (1997) Functional data analysis. Springer, New York
Rowe S (1996) An algorithm for computing principal points with respect to a loss function in the unidimensional case. Stat Comput 6:187–190
Stampfer E, Stadlober E (2002) Methods for estimating principal points. Commun Stat—Ser B, Simul Comput 31:261–277
Su Y (1997) On the asymptotics of qunatizers in two dimensions. J Multivariate Anal 61:67–85
Sugar C, James G (2003) Finding the number of clusters in a data set: an information theoretic approach. J Am Stat Assoc 98:750–763
Tarpey T (1994) Two principal points of symmetric, strongly unimodal distributions. Stat Probab Lett 20:253–257
Tarpey T (1995) Principal points and self–consistent points of symmetric multivariate distributions. J Multivariate Anal 53:39–51
Tarpey T (1997) Estimating principal points of univariate distributions. J Appl Stat 24:499–512
Tarpey T (1998) Self-consistent patterns for symmetric multivariate distributions. J Class 15:57–79
Tarpey T, Flury B (1996) Self-consistency: a fundamental concept in statistics. Stat Sci 11:229–243
Tarpey T, Kinateder KJ (2003) Clustering functional data. J Class 20:93–114
Tarpey T, Li L, Flury B (1995) Principal points and self–consistent points of elliptical distributions. Ann Stat 23:103–112
Tarpey T, Petkova E, Ogden RT (2003) Profiling placebo responders by self-consistent partitions of functional data. J Am Stat Assoc 98:850–858
Titterington DM, Smith AFM, Makov UE (1985) Statistical analysis of finite mixture distributions. Wiley, New York
Wei GCG, Tanner MA (1990) A Monte Carlo implementation of the EM algorithm and the poor man’s algorithms. J Am Stat Assoc 85:699–704
Yamamoto W, Shinozaki N (2000a) On uniqueness of two principal points for univariate location mixtures. Stat Probab Lett 46:33–42
Yamamoto W, Shinozaki N (2000b) Two principal points for multivariate location mixtures of distributions. J Japan Stat Soc 30:53–63
Zoppé A (1995) Principal points of univariate continuous distributions. Stat Comput 5:127–132
Zoppé A (1997) On uniqueness and symmetry of self-consistent points of univariate continuous distributions. J Class 14:147–158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarpey, T. A parametric k-means algorithm. Computational Statistics 22, 71–89 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-007-0022-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-007-0022-7