Abstract
High-silicon cast steel exhibits good ductility and mechanical strength after microstructure transformation through an austempering heat treatment. The combination of these properties is outstanding in other steels, leading to emerging applications for high-silicon cast steel, such as in the railway sector. The Si content above 1.5% is a crucial factor for the formation of refined bainite and a dispersion of carbides in the matrix. This work involves the evaluation of the machinability of a steel alloy with 0.77% C and 1.77% Si using ceramic metal and ceramic tools. The alloy was cast, homogenized, austempered, and tempered. Subsequently, the high-silicon cast steel was characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), hardness, tensile strength, and elongation. Machinability tests were conducted by turning and varying the cutting speed under dry cutting conditions with a constant feed rate. The analyzed output parameters were surface roughness, tool wear, and wear mechanisms. The increase in cutting speed directly influenced tool wear for all tools. The predominant wear mechanisms observed during the tests were abrasion and diffusion. The hard metal tool exhibited chipping on the cutting edge.

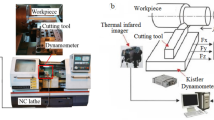
Source: elaborated by the author














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Georgiev MN, Simeonova TV (2018) Railroad rails from bainitic steel. Met Sci Heat Treat 60(7–8):464–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-018-0302-6
Gola AM, Ghadamgahi M, Ooi SW (2017) Microstructure evolution of carbide-free bainitic steels under abrasive wear conditions. Wear 376–377:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.12.038
Bhadeshia HKDH, Edmonds DV (1979) The bainite transformation in a silicon steel. Metall Trans A 10:895–907. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658309
Gopalsamy BM, Mondal B, Ghosh S et al (2010) Experimental investigations while hard machining of DIEVAR tool steel (50 HRC). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:853–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2688-1
Gille G, Szesny B, Dreyer K, Berg HVD, Schmidt J, Gestrich T, Leitner G (2002) Submicron and 224 ultrafine grained hardmetals for microdrills and metal cutting inserts. Int J Refract Metals Hard Mater 20:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-4368(01)00066-X
Khan M, Kumar A, Kumaran S et al (2019) Effect of tool wear on machining GFRP and AISI D2 steel using alumina based ceramic cutting tools. SILICON 11:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-018-9839-7
Machado ÁR, Abrão AM, Coelho RT, Silva MBD (2018) Teoria da usinagem dos materiais. São Paulo, Brazil
da Silva AE, de Melo INR, Pinheiro IP, da Silva LR (2021) Influence of Niobium addition on microstructure and machinability of high chromium cast iron. Mater Res 24:1. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2020-0429
American Society for Testing Materials - ASTM (2017) ASTM A781/A781M: standard specification for castings, steel and alloy, common requirements, for general industrial use. ASTM
Nassem S, Liu E et al (2020) Microstructure and mechanical properties of a high-carbon bainitic steel containing Si/Al by different heat treatment processes. Mater Express 10:1932–1940. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2020.1846
de Torres CT, Carmo DJ et al (2019) Evaluation of the steel obtaining process cast carbon low alloy with high mechanical resistance. In ABIFA Fundition Congress – CONAF, 18., 2019, São Paulo. São Paulo. ABIFA, São Paulo
Carmo DJ, Dias JF, Santos DB (2012) High cycle rotating bending fatigue property in high strength casting steel with carbide free bainite. Mater Sci Technol 28(8):991–993
Shimanov M, Korpala G, TerziC A, Kawalla R (2016) Bainitic steels, their characteristics and applications. Key Eng Mater 684:104–110. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.684.104
Ahmadi Miab S, Avishan B, Yazdani S (2016) Wear resistance of two nanostructural bainitic steels with different amounts of Mn and Ni. Acta Metall Sin 29:587–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-016-0424-z
Yuan L, Liu Q, Li H et al (2015) Effect of austenitizing temperature on the bainitic transformation in a high-carbon high-silicon steel. Metal Sci Heat Treat 57:156–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-015-9855-9
Adamczyk-CieślaK B, Koralnik M, Kuziak R et al (2022) The impact of retained austenite on the mechanical properties of bainitic and dual phase steels. J Mater Eng Perform 31:4419–4433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06547-w
Liu W, Jiang YH, Guo H et al (2020) Mechanical properties and wear resistance of ultrafine bainitic steel under low austempering temperature. Int J Miner Metall Mater 27:483–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1916-4
Chen Z, Lin Peng R, Zhou J et al (2019) Effect of machining parameters on cutting force and surface integrity when high-speed turning AD 730™ with PCBN tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:2601–2615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2792-1
Sharma MD, Sehgal R (2016) Modelling of machining process while turning tool steel with CBN tool. Arab J Sci Eng 41:1657–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1864-x
Cui X, Guo J, Zhao J et al (2015) Chip temperature and its effects on chip morphology, cutting forces, and surface roughness in high-speed face milling of hardened steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77:2209–2219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6635-4
Das SR, Dhupal D, Kumar A (2015) Study of surface roughness and flank wear in hard turning of AISI 4140 steel with coated ceramic inserts. J Mech Sci Technol 29(10):4329–4340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-0931-2
Reis BCM, Dos Santos AJ, Dos Santos NFP et al (2019) Cutting performance and wear behavior of coated cermet and coated carbide tools when turning AISI 4340 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:1655–1663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04392-9
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted with the support of the Federal Centre of Technological Education of Minas Gerais (CEFET-MG), SENAI Itaúna CETEF Marcelino Corradi and Sandvik Coromant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Caio César was responsible for the conceptualization, experimental work, and writing of the manuscript. Ernane Felipe was contributed to experimental work. Denilson José and Sandro Cardoso were responsible for the revision of the manuscript and contributed to the technical discussion of the results. Sandro Cardoso was responsible for the supervision of the work and the availability of resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All authors have previously approved this paper and judged that there is no ethical infringement.
Consent to participate and publication
All authors would like to declare that they have approved their participation and consent about the publication in this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Barroso, C.C.G.C., Dias, E.F., do Carmo, D.J. et al. Characterization and machinability of a high-silicon cast steel with ceramic and carbide tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 132, 167–178 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13206-6