Abstract
Understanding and optimizing mechanical manufacturing processes is essential for sustainable industrial development. Among unconventional machining methods, electrical discharge machining (EDM) distinguishes itself by its capability to remove material through successive electrical discharges submerged in a dielectric fluid. EDM encompasses intricate phenomena influenced by machine parameters, dielectric choice, and the materials involved. Unlike conventional machining, EDM operates with the tool electrode in close proximity to, but not in physical contact with, the workpiece, achieving material removal through localized overheating. This study focuses on monitoring EDM phenomena during the machining of AISI H13 steel, exploring variations in machining parameters and electrode materials (electrolytic copper and graphite). Acoustic emission (AE) signals and machine learning (ML) are employed for experimental characterization and data analysis. Spectral entropy is applied to AE signals, quantifying inherent signal uncertainty. The findings reveal remarkable accuracy (97.7%) and underscore the superior control achieved with graphite electrodes in managing machining phenomena compared to electrolytic copper electrodes.
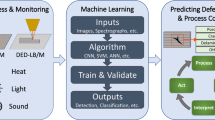
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not available.
References
Banu A, Ali MY (2016) Electrical discharge machining (EDM): a review. Int J Eng Mater Manuf 1:3–10. https://doi.org/10.26776/ijemm.01.01.2016.02
Jain S, Parashar V (2021) Critical review on the impact of EDM process on biomedical materials. Mater Manuf Processes 36:1701–1724. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2021.1942907
Ablyaz TR, Shlykov ES, Muratov KR, Zhurin AV (2022) Study of the edm process of bimetallic materials using a composite electrode tool. Materials 15:750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030750
Erman B, Kalyon A (2023) Multi objective optimization of parameters in EDM of Mirrax steel. Mater Manuf Processes 38:848–858. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2022.2149780
Luzia CAO, Laurindo CAH, Soares PC, Torres RD, Mendes LA, Amorim FL (2019) Recast layer mechanical properties of tool steel after electrical discharge machining with silicon powder in the dielectric. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03549-w
Mouralova K, Bednar J, Benes L, Plichta T, Prokes T, Fries J (2022) Production of precision slots in copper foil using micro EDM. Sci Rep 12:5023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08957-9
Chen Z, Zhan S, Zhao Y (2021) Electrochemical jet-assisted precision grinding of single-crystal SiC using soft abrasive wheel. Int J Mech Sci 195:106239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106239
Cesarotti C, Lu Q, Nakai Y, Parikh A, Reece M (2019) Interpreting the electron EDM constraint. J High Energy Phys 2019:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP05(2019)059
Sisodiya MS, Shukla S, Bajpai V (2022) Feasibility analysis of novel Maglev EDM by comparing with conventional micro EDM. Sci Rep 12:2613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06662-1
Ferreira SS, Amorim FL, Júnior JL, Maia LHA, Machado ÁR, Sales WF (2022) A new technique for identification and evaluation of wear in copper electrodes in electrical discharge machining using acoustic emission signals. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08071-6
Malek O, González-Julián J, Vleugels J, Vanderauwera W, Lauwers B, Belmonte M (2011) Carbon nanofillers for machining insulating ceramics. Mater Today 14:496–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(11)70214-0
Muttamara A, Fukuzawa Y, Mohri N, Tani T (2009) Effect of electrode material on electrical discharge machining of alumina. J Mater Process Technol 209:2545–2552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.06.018
Tsai HC, Yan BH, Huang FY (2003) EDM performance of Cr/Cu-based composite electrodes. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00238-9
Tsai MY, Fang CS, Yen MH (2018) Vibration-assisted electrical discharge machining of grooves in a titanium alloy (Ti-6A-4V). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1904-2
Bonfá MM, Costa ÉS, Sales WF, Amorim FL, Maia LHA, Machado ÁR (2019) Evaluation of tool life and workpiece surface roughness in turning of AISI D6 hardened steel using PCBN tools and minimum quantity of lubricant (MQL) applied at different directions. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:971–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03619-z
Wang P, Li B, Shi G, Lin T, Wang B (2018) Non-linear mechanism in electrical discharge machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97:1687–1696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1888-y
Zhang L, Du J, Zhuang X, Wang Z, Pei J (2015) Geometric prediction of conic tool in micro-EDM milling with fix-length compensation using simulation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 89:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2014.11.007
Mollik MS, Saleh T, bin Md Nor KA, Ali MSM (2022) A machine learning-based classification model to identify the effectiveness of vibration for μEDM. Alexandria Eng J 61:6979–6989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.12.048
Maia LHA, Abrao AM, Vasconcelos WL, Sales WF, Machado AR (2015) A new approach for detection of wear mechanisms and determination of tool life in turning using acoustic emission. Tribol Int 92:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.07.024
De La Rosa JJG, Pérez AA, Salas JCP, Fernández JMS (2015) A novel measurement method for transient detection based in wavelets entropy and the spectral kurtosis: an application to vibrations and acoustic emission signals from termite activity. Measurement (Lond) 68:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.02.044
Pham DT, Pham PTN (1999) Artificial intelligence in engineering. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 39:937–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(98)00076-5
Fan Y-S, Bai J-C (2018) Study on volt-ampere characteristics of spark discharge for transistor resistor pulse power of EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96:3019–3031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1702-x
Marrocco V, Modica F, Fassi I (2019) Analysis of discharge pulses in micro-EDM milling of Si3N4-TiN composite workpiece by means of power spectral density (PSD). J Manuf Process 43:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.05.017
Ferreira DFS, Vieira JS, Rodrigues SP, Miranda G, Oliveira FJ, Oliveira JM (2022) Dry sliding wear and mechanical behaviour of selective laser melting processed 18Ni300 and H13 steels for moulds. Wear 488–489:204179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2021.204179
Chen J-P, Gu L, Zhao W-S, Guagliano M (2020) Modeling of flow and debris ejection in blasting erosion arc machining in end milling mode. Adv Manuf 8:508–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-020-00328-9
V. des V.D. Ingenieure, VDI 3402 (1994) Application of electrical discharge machining (EDM), 1994
Krishnakumar P, Rameshkumar K, Ramachandran KI (2018) Machine learning based tool condition classification using acoustic emission and vibration data in high speed milling process using wavelet features. Intell Decis Technol 12:265–282. https://doi.org/10.3233/IDT-180332
Chen H-Y, Lee C-H (2021) Deep learning approach for vibration signals applications. Sensors 21:3929. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113929
Gill AS, Kumar S (2015) Surface alloying of H11 die steel by tungsten using EDM process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78:1585–1593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6743-1
Lee H-T, Hsu F-C, Tai T-Y (2004) Study of surface integrity using the small area EDM process with a copper–tungsten electrode. Mater Sci Eng A 364:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.08.046
S. P., M. B (2017) Investigation on the influence of different types of dielectrics in electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:277–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0039-1
Liao Z, la Monaca A, Murray J, Speidel A, Ushmaev D, Clare A, Axinte D, M’Saoubi R (2021) Surface integrity in metal machining - Part I: Fundamentals of surface characteristics and formation mechanisms. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 162:103687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2020.103687
Hyndman RJ, Koehler AB (2006) Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int J Forecast 22:679–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2006.03.001
Valentinčič J, Filipič B, Junkar M (2009) Machine learning induction of a model for online parameter selection in EDM rough machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41:865–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1532-3
Chen G, Li Y, Liu X (2019) Pose-dependent tool tip dynamics prediction using transfer learning. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 137:30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2018.10.003
Ming W, Xie Z, Ma J, Du J, Zhang G, Cao C, Zhang Y (2021) Critical review on sustainable techniques in electrical discharge machining. J Manuf Process 72:375–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMAPRO.2021.10.035
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge (i) CAPES and (ii) PUC Minas, especially PROPPG Mecânica, for their continuous support of research and development (R&D), crucial for technological development, and these work achievements.
Funding
This research is funded by Pontifical Catholic University of Minas Gerais and CAPES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: S.S.F., F.L.A., L.H.A.M. Methodology: S.S.F., F.L.A., L.H.A.M. Software: S.S.F., L.H.A.M. Validation: S.S.F., F.L.A., L.H.A.M. Data curation: S.S.F., F.L.A., L.H.A.M. Writing-original draft preparation: S.S.F. Writing-review and editing: S.S.F., L.H.A.M. All authors have participated in the manuscript preparation and have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Analysis of acoustic emission (AE) signals contain rich information that provides insights into the phenomena and behaviors of a process.
• Electrical discharge machining (EDM) parameters significantly affect these phenomena, subsequently influencing AE signal responses.
• More aggressive parameters in EDM have lower process efficiency.
• Graphite electrode promotes better control of electrical sparks compared to electrolytic copper electrodes.
• Spectral entropy shows promise in characterizing the various phenomena observed in EDM, especially when considering the variation in parameters and electrode materials.
• Machine learning serves as a powerful tool for data analysis and predicting machining process responses.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, S.S., Maia, L.H.A. & Amorim, F.L. Effects of machining parameters on spectral entropy of acoustic emission signals in the electro erosion. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 289–299 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13129-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13129-2