Abstract
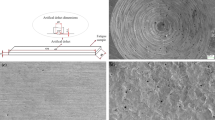
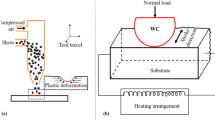
Shot peening is a well-known practical method for improving the surface performance of mechanical components. In this work, shot peening was applied to 42CrMo steel components as tie bars for a double platen injection molding machine. The microstructure and morphology of the samples were studied. The residual stress and phase identification of steel samples with and without shot peening were determined by X-ray diffractometer. At the same time, the numerical simulation was carried out and compared with the actual residual stress. Microhardness, mechanical properties, wear and corrosion resistances of the shot-peened samples were studied. The results showed that shot peening treatment influence surface microstructure and properties of the steel. Plastic deformation regions and residual stress layers were formed after shot peening. The presence of these plastic deformation regions, grain refinement, and residual stress layers improved the surface hardness, fatigue life, and wear resistance of the steel. Electrochemical analysis demonstrated a reduction in the corrosion resistance of the steel after shot peening. In order to improve the corrosion resistance of the steel after shot peening, it was subjected to phosphating treatment, and its corrosion resistance performance was studied.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sasikumar C, Srikanth S, Das SK (2006) Analysis of premature failure of a tie bar in an injection molding machine. Eng Fail Anal 13:1246–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2005.11.003
Dang H, Liang A, Feng R, Zhang J, Shao Y, Yam M (2022) Experiments on static and fatigue behaviour of corroded Q235B and 42CrMo steels. J Constr Steel Res 198:107535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2022.107535
Matsui M, Kakishima H (2006) Improvement of tribological performance of steel by solid lubricant shot-peening in dry rolling/sliding contact wear tests. Wear 260:669–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2005.03.030
Fridrici V, Fouvry S, Kapsa P (2001) Effect of shot peened on the fretting wear of Ti-6Al-4V. Wear 250:642–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(01)00671-8
Wang S, Li Y, Yao M, Wang R (1998) Compressive residual stress introduced by shot peened. J Mater Process Technol 73:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00213-6
Hashemi B, Rezaee Yazdi M, Azar V (2011) The wear and corrosion resistance of shot peened-nitrided 316L austenitic stainless steel. Mater Des 32:3287–3292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.02.037
Widmark M, Melander A (1999) Effect of material, heat treatment, grinding and shot peened on contact fatigue life of carburised steels. Int J Fatigue 21:309–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-1123(98)00077-2
Yan W, Fang L, Sun K, Xu Y (2007) Effect of surface work hardening on wear behavior of Hadfield steel. Mater Sci Eng A 460-461:542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.094
Unal O, Varol R (2014) Almen intensity effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon steel subjected to severe shot peened. Appl Surf Sci 290:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.184
Tekeli S (2002) Enhancement of fatigue strength of SAE 9245 steel by shot peened. Mater Lett 57:604–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(02)00838-8
Farrahi GH, Lebrijn JL, Couratin D (1995) Effect of shot peened on residual stress and fatigue life of a spring steel. Fatigue Fract Eng M 18:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2695.1995.tb00156.x
Umemoto M, Todaka Y, Tsuchiya K (2003) Formation of nanocrystalline structure in steels by air blast shot peened. Mater Trans 44:1488–1493. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.44.1488
Zhang P, Lindemann J (2005) Influence of shot peened on high cycle fatigue properties of the high-strength wrought magnesium alloy AZ80. Scr Mater 52:485–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.11.003
Guagliano M (2001) Relating Almen intensity to residual stresses induced by shot peened: a numerical approach. J Mater Process Technol 110:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(00)00893-1
Kobayashi M, Matsui T, Murakami Y (1998) Mechanism of creation of compressive residual stress by shot peened. Int J Fatigue 20:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-1123(98)00002-4
Bagherifard S, Ghelichi R, Guagliano M (2012) Numerical and experimental analysis of surface roughness generated by shot peened. Appl Surf Sci 258:6831–6840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.03.111
Palacios M, Bagherifard S, Guagliano M, Fernández Pariente I (2014) Influence of severe shot peened on wear behaviour of an aluminium alloy. Fatigue Fract Eng M 37:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.12210
Maleki E, Unal O, Reza Kashyzadeh K (2018) Fatigue behavior prediction and analysis of shot peened mild carbon steels. Int J Fatigue 116:48–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.06.004
Amanov A, Karimbaev R, Maleki E, Unal O, Pyun Y, Amanov T (2019) Effect of combined shot peened and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification processes on the fatigue performance of AISI 304. Surf Coat Technol 358:695–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.11.100
Azar V, Hashemi B, Rezaee Yazdi M (2010) The effect of shot peened on fatigue and corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel in Ringer’s solution. Surf Coat Technol 204:3546–3551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.04.015
Wang T, Yu J, Dong B (2006) Surface nanocrystallization induced by shot peened and its effect on corrosion resistance of 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel. Surf Coat Technol 200:4777–4781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.04.046
Shen L, Wang L, Wang Y, Wang C (2010) Plasma nitriding of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel with pre-shot peened. Surf Coat Technol 204:3222–3227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.03.018
Wu W, Jiang J, Chen Z, Jiang P, Wang Z (2017) Morphology and mechanical characteristics of monolayer and multilayer Ir coating by double glow plasma. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci Ed 32:190–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-017-1579-9
Ghosh S, Singh AK, Mula S (2016) Effect of critical temperatures on microstructures and mechanical properties of Nb–Ti stabilized IF steel processed by multiaxial forging. Mater Des 100:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.03.107
Kovacı H, Bozkurt YB, Yetim AF, Aslan M, Çelik A (2019) The effect of surface plastic deformation produced by shot peened on corrosion behavior of a low-alloy steel. Surf Coat Technol 360:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.01.003
Maleki E, Unal O (2018) Roles of surface coverage increase and re-peening on properties of AISI 1045 carbon steel in conventional and severe shot peened processes. Surf Interfaces 11:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2018.03.003
Sivasankaran S, Sivaprasad K, Narayanasamy R, Satyanarayana PV (2011) X-ray peak broadening analysis of AA 6061100−x−xwt.% Al2O3 nanocomposite prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater Charact 62:661–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2011.04.017
Wu W, Huang J, Näther J, Omar NAB, Köster F, Lampke T, Liu Y, Pan H, Zhang Y (2021) Texture orientation, morphology and performance of nanocrystalline nickel coatings electrodeposited from a Watts-type bath: effects of H3BO3 concentration and plating time. Surf Coat Technol 424:127648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127648
Arifvianto B, Suyitnoa MM, Dewo P, Iswanto PT, Salim UA (2011) Effect of surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) on microhardness, surface roughness and wettability of AISI 316L. Mater Chem Phys 125:418–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.10.038
Williamson GK, Hall WH (1953) X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall 1:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(53)90006-6
Klug, H.P. and Alexander, L.E., X-ray Diffraction Procedures, 1954.
Williamson GK, Smallman RE III (1956) Dislocation densities in some annealed and cold-worked metals from measurements on the X-ray Debye-Scherrer spectrum. Philos Mag 1:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786435608238074
Zhang J, Liu Z, Sun J, Zhao H, Shi Q, Ma D (2020) Microstructure and mechanical property of electropulsing tempered ultrafine grained 42CrMo steel. Mater Sci Eng A 782:139213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139213
Mansilla C, Ocelík V, De Hosson JTM (2015) Local residual stress measurements on nitride layers. Mater Sci Eng A 636:476–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.04.023
Wawszczak R, Baczmański A, Marciszko M, Wróbel M, Czeppe T, Sztwiertnia K, Braham C, Berent K (2016) Evolution of microstructure and residual stress during annealing of austenitic and ferritic steels. Mater Charact 112:238–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.12.019
Dieter GE, Bacon D (1976) Mechanical metallurgy. McGraw-hill, New York
Fujita K, Tsuboi H, Kikuchi S (2023) Grain size effect on near-threshold fatigue crack propagation in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Eng Fract Mech 286:109317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2023.109317
Hassani-Gangaraj SM, Cho KS, Voigt HJL, Guagliano M, Schuh CA (2015) Experimental assessment and simulation of surface nanocrystallization by severe shot peened. Acta Mater 97:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.06.054
Hassani-Gangaraj SM, Moridi A, Guagliano M, Ghidini A (2014) Nitriding duration reduction without sacrificing mechanical characteristics and fatigue behavior: the beneficial effect of surface nano-crystallization by prior severe shot peened. Mater Des 55:492–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.015
Hassani-Gangaraj SM, Moridi A, Guagliano M, Ghidini A, Boniardi M (2014) The effect of nitriding, severe shot peened and their combination on the fatigue behavior and micro-structure of a low-alloy steel. Int J Fatigue 62:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2013.04.017
Wang Y, Choo H (2014) Influence of texture on Hall-Petch relationships in an Mg alloy. Acta Mater 81:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.08.023
Tjong SC, Chen H (2004) Nanocrystalline materials and coatings. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 45:1–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2004.07.001
Bozkurt YB, Kovacı H, Yetim AF, Çelik A (2022) Tribocorrosion properties and mechanism of a shot peened AISI 4140 low-alloy steel. Surf Coat Technol 440:128444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128444
Yan H, Zhu P, Chen Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y (2022) Effect of shot peening on the surface properties and wear behavior of heavy-duty-axle gear steels. J Mater Res Technol 17:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.12.126
Peral LB, Ebrahimzadeh P, Gutiérrez A, Fernández-Pariente I (2023) Effect of tempering temperature and grain refinement induced by severe shot peened on the corrosion behavior of a low alloy steel. J Electroanal Chem 932:117207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2023.117207
Aparicio C, Javier Gil F, Fonseca C, Barbosa M, Planell JA (2003) Corrosion behaviour of commercially pure titanium shot blasted with different materials and sizes of shot particles for dental implant applications. Biomaterials 24:263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00314-9
Hara N, Kobayashi Y, Kagaya D, Akao N (2007) Formation and breakdown of surface films on magnesium and its alloys in aqueous solutions. Corros Sci 49:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2006.05.033
Liu C, Zheng H, Gu X, Jiang B, Liang J (2019) Effect of severe shot peened on corrosion behavior of AZ31 and AZ91 magnesium alloys. J Alloys Compd 770:500–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.141
Guo S, Xu D, Jiang G, Guo Y, Jing Z (2022) Sulfate corrosion and phosphate passivation of Ni-based alloy in supercritical water. J Supercrit Fluids 184:05564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2022.105564
Wang J, Yang H, Du M, Hou J, Peng W, Lin C (2021) Corrosion mechanism of 5083 aluminum alloy in seawater containing phosphate. J Ocean Univ China 20:372–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-021-4545-2
Wu W, Jiang J (2017) Effect of plating temperature on electroless amorphous Ni-P film on Si wafers in an alkaline bath solution. Appl Nanosci 7:325–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0575-x
Lee H, Kim D, Jung J, Pyoun Y, Shin K (2009) Influence of peening on the corrosion properties of AISI 304 stainless steel. Corros Sci 51:2826–2830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.08.008
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Guang Yang from the Analysis and Testing Center, NERC Biomass of Changzhou University, for the discussion and for helping in the XRD measurement and thank Mr. Xiaodong Xu from Changzhou University for the support with the fatigue life testing.
Funding
This work was supported by the funding of project (Contract number 2022K2653) from the Engel Injection Molding Machinery (Changzhou) Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization, review and comments, software, and supervision were performed by Dr. WW. Measurements, material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Mr. GS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 73 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, G., Wu, W. The influence of shot peening on mechanical properties, wear, and corrosion resistance of 42CrMo steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 130, 5299–5313 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13052-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13052-6