Abstract
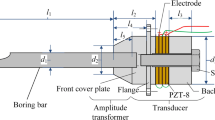
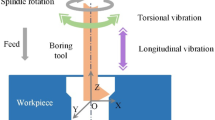
Due to the low rigidity of the boring bar with a large length-to-diameter ratio, chatter easily occurs during deep hole boring. In this paper, an ultrasonic vibration boring bar with a length-to-diameter ratio greater than 10 is designed to suppress the chatter during the boring operation of deep holes. First, the dynamic model of the boring operation is built to guide the design of the ultrasonic vibration boring bar. Then, the optimal design of structure parameter of the ultrasonic vibration boring bar is performed by the finite element method, and then the optimized boring bar is manufactured. Finally, the vibration performance test and cutting experiments are carried out to verify the machining capability of the bar. The experimental results show that the ultrasonic vibration boring bar can reduce the cutting force by about 35%, improve the system stability, and increase the quality of the relative machined surface by about 43%, which demonstrate the feasibility of chatter suppression of the developed ultrasonic vibration boring bar.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quintana G, Ciurana J (2011) Chatter in machining processes: a review. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51(5):363–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2011.01.001
Taylor FW (1906) On the art of cutting metals. ASME 28:31–279. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4060388
Zhang CJ, Ren YS, Ji SJ, Zhang JF (2020) Analysis of the vibration and chatter stability of a tapered composite boring bar. Shock Vib 2020:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4190806
Hayati S, Hajaliakbari M, Rajabi Y, Rasaee S (2018) Chatter reduction in slender boring bar via a tunable holder with variable mass and stiffness. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 232(12):2098–2108. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405417690554
Ghorbani S, Rogov VA, Carluccio A, Belov PS (2019) The effect of composite boring bars on vibration in machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105(1):1157–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04298-6
Chen F, Hanifzadegan M, Altintas Y, Lu X (2015) Active damping of boring bar vibration with a magnetic actuator. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron 20(6):2783–2794. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2015.2393364
Bak C, Son H (2018) Magnetostrictive actuator for chatter vibration suppression of boring bar. Inter Confere AIM: Auckland, New Zealand, pp 103–106. https://doi.org/10.1109/AIM.2018.8452250
Matsubara A, Maeda M, Yamaji I (2014) Vibration suppression of boring bar by piezoelectric actuators and LR circuit. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 63(1):373–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.132
Saleh MK, Nejatpour M, Acar HY, Lazoglu I (2021) A new magnetorheological damper for chatter stability of boring tools. J Mater Process Technol 289:116931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116931
Li L, Sun B, Hua H (2019) Analysis of the vibration characteristics of a boring bar with a variable stiffness dynamic vibration absorber. Shock Vib 2019(9):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5284194
Ding K, Li QL, Lei WN, Zhang CD, Xu MZ, Wang X (2022) Design of a defined grain distribution brazed diamond grinding wheel for ultrasonic assisted grinding and experimental verification. Ultrasonics 118:106577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2021.106577
Zou P, Xu YS, He Y, Chen MF, Wu H (2015) Experimental investigation of ultrasonic vibration assisted turning of 304 austenitic stainless steel. Shock Vib 2015:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/817598
Zhou M, Ngoi BKA, Yusoff MN, Wang XJ (2006) Tool wear and surface finish in diamond cutting of optical glass. J Mater Process Technol 174(1–3):29–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.02.248
Kim GD, Loh BG (2007) An ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting device for micro V-groove machining: kinematical analysis and micro V-groove machining characteristics. J Mater Process Technol 190(1–3):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.02.047
Dong GJ, Wang L, Li C, Yu YF (2020) Investigation on ultrasonic elliptical vibration boring of deep holes with large depth–diameter ratio for high-strength steel 18Cr2Ni4WA. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108(5):1527–1539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05531-3
Lotfi M, Amini S, Aghayar Z, Sajjady S, Farid A (2020) Effect of 3D elliptical ultrasonic assisted boring on surface integrity. Measurement 163:108008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108008
Kurniawan R, Kumaran ST, Ko TJ (2021) Finite element analysis in ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting (UEVC) during micro-grooving in AISI 1045. Int J Precis Eeg Manuf 22:1497–1515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-021-00554-6
Ma C, Ma J, Shamoto E, Moriwaki T (2011) Analysis of regenerative chatter suppression with adding the ultrasonic elliptical vibration on the cutting tool. Precis Eng 35(2):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2010.12.004
Li X, Zhang DY (2006) Ultrasonic elliptical vibration transducer driven by single actuator and its application in precision cutting. J Mater Process Technol 180(1–3):91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.05.007
Ma CX, Shamoto E, Moriwaki T (2004) Study on the thrust cutting force in ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Mater Sci 471:396–400. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.471-472.396
Zuo CM, Zhou XQ, Liu Q, Wang RQ, Lin JQ, Xu P, Zhang X (2018) Analytical topography simulation of micro/nano textures generated on freeform surfaces in double-frequency elliptical vibration cutting based diamond turning. J Manuf Sci Eng 140(10):101010. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4040616
Xiao M, Karube S, Soutome T, Sato K (2002) Analysis of chatter suppression in vibration cutting. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42(15):1677–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00077-9
Jung H, Hayasaka T, Shamoto E (2016) Mechanism and suppression of frictional chatter in high-efficiency elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 65(1):369–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2016.04.103
Merchant ME (1944) Basic mechanics of the metal-cutting process. J Appl Mech 11(3):A168–A175. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4009380
Sui H, Zhang DY, Chen HW, Zhang XY (2016) Effect of ultrasonic vibration cutting on coupled chatter. Journal of Aeronautics and Astronautics 37(5):1696–1704. https://doi.org/10.7527/S1000-6893,2015.0230
Jiao F, Liu X, Zhao CY, Zhang X (2011) Experimental study on the surface micro-geometrical characteristics of quenched steel in ultrasonic assisted turning. Adv Materials Res 189:4059–4063
Yin S, Dong Z, Bao Y, Kang R, Du W, Pan Y, Jin Z (2021) Development and optimization of ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting device based on single excitation. J Manuf Sci Eng 143(8):081005. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4049965
Ma CX, Shamoto E, Moriwaki T, Zhang YH, Wang LJ (2005) Suppression of burrs in turning with ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(11):1295–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.01.011
Wang WK, Wan M, Zhang WH, Yang Y (2022) Chatter detection methods in the machining processes: a review. J Manuf Process 77:240–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.03.018
Funding
The authors would like to thank the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52075275, 51675289), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022QE241, ZR2021QE230), the Talent Research Project of Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences) (2023RCKY124), and the Basic Research Project of Science, Education and Industry Integration Pilot Project of Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences) (2022PX044, 2022PY007, 2023PX026, 2023PY021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. YX: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, project administration. GS: validation. BL: methodology. JD: methodology.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Xia, Y., Su, G. et al. Ultrasonic vibration–assisted chatter suppression for deep hole boring of stainless steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 1691–1703 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13016-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-024-13016-w