Abstract
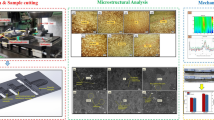
As typical ablation-resistant materials, carbon fiber–reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are widely used as hot-end components such as rocket launcher nozzles. Nevertheless, their characteristics of anisotropic and hard-brittle bring processing challenges. Rotary ultrasound–assisted machining (RUM) is an effective machining method for hard-brittle materials. In this paper, we established a single abrasive grit trajectory model and elucidated the trajectory characteristics of the grits under ultrasonic-assisted side grinding (UASG) and ultrasonic-assisted end grinding (UAEG). Then the effects of longitudinal ultrasonic vibration on the grinding force, and surface quality in UASG and UAEG of 2.5D Cf/SiC composites were investigated by the single-factor test. Finally, the grinding mechanism under the two processing methods was revealed. The experimental results showed that the longitudinal vibration in the two machining methods has different effects on the grinding force and surface roughness. After the application of longitudinal vibration, the reduction of grinding force in the side grinding process was the largest. However, the reduction of surface roughness in the end grinding process was the largest, which was 35.6%. For the removal of each phase of 2.5D Cf/SiC composites, the brittle fracture, fiber debonding, and breakage of the matrix could be reduced after applying ultrasonic vibration in both processing methods.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in this paper are all gained from experiments. All data generated are included in this article.
References
Chen L, Yao X, Cen S (2015) Predictions of elastic property on 2.5D C/SiC composites based on numerical modeling and semi-analytical method. Compos Part B 74:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.01.009
Du J, Zhang H, Geng Y, Ming W, He W, Ma J, Cao Y, Li X, Liu K (2019) A review on machining of carbon fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Ceram Int 45(15):18155–18166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.112
Luo L, Wang Y, Liu L, Zhao X, Lu Y, Wang G (2018) Carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide composite-based sharp leading edges in high enthalpy plasma flows. Compos Part B 135:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.09.060
Niu C, Zhang Q, Cheng L, Ye F, Zhang L (2023) Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cf/SiC composites with dispersed C-SiC interphase prepared by chemical vapor infiltration. Compos A: Appl Sci Manuf 165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107339
Sun Z, Shan Z, Shao T (2021) A comparative study for the thermal conductivities of C/SiC composites with different preform architectures fabricating by flexible oriented woven process. Int J Heat Mass Transf 170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.120973
Xue F, Zheng K, Liao W, Shu J, Dong S (2021) Investigation on fiber fracture mechanism of c/sic composites by rotary ultrasonic milling. Int J Mech Sci 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106054
Wang J, Zhang J, Feng P (2017) Effects of tool vibration on fiber fracture in rotary ultrasonic machining of C/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Compos Part B 129:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.07.081
Zhou K, Xu J, Xiao G, Huang Y (2022) A novel low-damage and low-abrasive wear processing method of Cf/SiC ceramic matrix composites: laser-induced ablation-assisted grinding. J Mater Process Technol 302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117503
Qu S, Yao P, Gong Y, Chu D, Yang Y, Li C, Wang Z, Zhang X, Hou Y (2022) Environmentally friendly grinding of C/SiCs using carbon nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication technology. J Clean Prod 366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132898
Yin J, Xu J, Ding W, Su H (2021) Effects of grinding speed on the material removal mechanism in single grain grinding of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composite. Ceram Int 47(9):12795–12802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.140
Li W, Long G, Shi F, Zhou S, Yin J, Yang J (2021) Influence of the fiber orientation on 3D C/C–SiC composite material and its formation mechanism of the machining surface. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118(7-8):2725–2743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08149-1
Du J, Ming W, Ma J, He W, Cao Y, Li X, Liu K (2018) New observations of the fiber orientations effect on machinability in grinding of C/SiC ceramic matrix composite. Ceram Int 44(12):13916–13928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.240
Cao S, Li HN, Huang W, Zhou Q, Lei T, Wu C (2022) A delamination prediction model in ultrasonic vibration assisted drilling of CFRP composites. J Mater Process Technol 302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117480
Liu J, Chen G, Ren C, Qin X, Zou Y, Ge J (2020) Effects of axial and longitudinal-torsional vibration on fiber removal in ultrasonic vibration helical milling of CFRP composites. J Manuf Process 58:868–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.08.071
Wang H, Pei ZJ, Cong W (2020) A feeding-directional cutting force model for end surface grinding of CFRP composites using rotary ultrasonic machining with elliptical ultrasonic vibration. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2020.103540
Chen J, An Q, Ming W, Chen M (2020) Investigation on machined surface quality in ultrasonic-assisted grinding of Cf/SiC composites based on fracture mechanism of carbon fibers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109(5-6):1583–1599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05739-3
Yao L, Liu Z, Song Q, Wang B, Cai Y (2023) Prediction modelling of cutting force in rotary ultrasonic end grinding 2.5D woven SiO2f/SiO2 ceramic matrix composite. Compos Struct 304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116448
Ding K, Li Q, Zhang C (2021) Experimental studies on material removal mechanisms in ultrasonic assisted grinding of SiC ceramics with a defined grain distribution brazed grinding wheel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 116(11-12):3663–3676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07612-3
Huang C, Zhou M, Zhang H (2021) A cutting force prediction model in axial ultrasonic vibration end grinding for BK7 optical glass considering protrusion height of abrasive grits. Measurement 180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109512
Huang C, Zhou M, Zhang H (2022) Investigations on the micro-interactions of grit-workpiece and forces prediction in ultrasonic vibration side grinding of optical glass. J Mater Process Technol 300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117415
Liu C, Li C, Gao L, Shen R (2022) Micro-hole drilling of 2.5D C/SiC composite with picosecond laser: numerical modeling and experimental validation on hole shape evolution. J Manuf Process 81:852–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.07.040
Zhao C, Tu Z, Mao J, Chen P, Li L (2022) The design of special woven-preformed structures for the high-performance film cooling with undamaged fibers based on 2.5D ceramic matrix composites. Compos Struct 283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.115114
Qu S, Gong Y, Yang Y, Cai M, Xie H, Zhang H (2019) Grinding characteristics and removal mechanism of 2.5D-needled Cf/SiC composites. Ceram Int 45(17):21608–21617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.156
Xie Z, Liu Z, Han L, Wang B, Xin M, Cai Y, Song Q (2022) Optimizing amplitude to improve machined surface quality in longitudinal ultrasonic vibration-assisted side milling 2.5D C/SiC composites. Compos Struct 297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115963
Li Z, Yuan S, Ma J, Shen J, Batako ADL (2021) Study on the surface formation mechanism in scratching test with different ultrasonic vibration forms. J Mater Process Technol 294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117108
Xie Z, Liu Z, Wang B, Xin M, Song Q, Jiang L (2021) Longitudinal amplitude effect on material removal mechanism of ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling 2.5D C/SiC composites. Ceram Int 47(22):32144–32152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.08.106
Qu S, Yao P, Gong Y, Yang Y, Chu D, Zhu Q (2022) Modelling and grinding characteristics of unidirectional C–SiCs. Ceram Int 48(6):8314–8324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.036
Funding
This work was financially sponsored by the Applied Innovation Program (Grant numbers: 6230113001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Zhenyan Duan: Methodology, Experiments, Writin—Original draft preparation. Tao Chen: Writing—Review & editing, Supervision. Hongbo Li: Writing—Original draft preparation, Validation, Image processing. Chuandian Zhang: Data curation. Fengyu Liu: Measurement and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Our research does not involve ethical issues.
Consent for publication
All the authors agreed to publish this paper.
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, Z., Chen, T., Li, H. et al. Longitudinal ultrasonic vibration effects on grinding mechanism in side and end grinding of 2.5D Cf/SiC composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 129, 4185–4199 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12585-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12585-6