Abstract
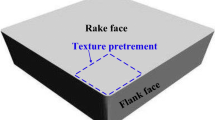
Titanium alloys have been widely used as an aerospace material owing to their excellent mechanical properties. However, ordinary tools can suffer from severe chip adhesion and surface abrasion when turning titanium alloys. To address these problems, micro-textured cutting tools have become a topic of significant research. Here, to improve the preparation process of textured tools, a novel tool prepared by an integrated molding process was proposed. The performance of this novel textured tool in terms of turning Ti-6Al-4 V was investigated under dry condition and minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Textured surfaces with four types of patterns and dimensions were used in the turning experiment to draw a comparison with traditional cutting tools. The results showed that the textured surface exhibited a uniform and smooth appearance with no obvious defects, indicating that the integrity of the textured surface was maintained. The combination of a micro-textured surface and the MQL method decreased the process temperature and cutting force. The narrower parallel type of textured tool exhibited the best performance. The process temperature reduced to 124 °C for the narrower parallel textured tool under MQL, decreasing by ~ 14.5% compared with the traditional tool; the lowest main cutting force and feed force were obtained for the narrower parallel textured tool, approximately 212 N and 171 N, respectively. Significant improvements in chip adhesion and tool wear were observed for the textured tool. Application of textured surface and MQL method are both decreased the adhesive scale layer area on the rake face of tools compared with ordinary tools.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawant MS, Jain NK, Palani IA (2018) Influence of dimple and spot-texturing of HSS cutting tool on machining of Ti-6Al-4V. J Materials Process Tech 261:1–11
Pramanik A (2014) Problems and solutions in machining of titanium alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70(2014):919–928
Fasasi AY, Mwenifumbo S, Rahbar N, Chen J, Li M, Beye AC, Arnold CB, Soboyejo WO (2009) Nano-second UV laser processed micro-grooves on Ti6Al4V for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C 2009(29):5–13
Kawasegi N, Sugimori H, Morimoto H, Morita N, Hori I (2009) Development of cutting tools with microscale and nanoscale textures to improve frictional behavior. Precis Eng 2009(33):248–254
Su Y, Li Z, Li L, Wang J, Gao H, Wang G (2017) Cutting performance of micro-textured polycrystalline diamond tool in dry cutting. J Manuf Process 2017(27):1–7
Arulkirubakaran D, Senthilkumar V, Lomesh V, Senthil P (2019) Performance of surface textured tools during machining of Al-Cu/TiB 2 composite. Measurement 2019(137):636–646
Fouathiya A, Meziani S, Sahli M, Barri`ere T (2021) Experimental investigation of microtextured cutting tool performance in titanium alloy via turning. J Manuf Process 69(2021):33–46
Deng J, Song W, Zhang H (2009) Design, fabrication and properties of a self-lubricated tool in dry cutting. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49(2009):66–72
Arulkirubakaran D, Senthilkumar V, Kumawat Vijay (2016) Effect of micro-textured tools on machining of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: an experimental and numerical approach. Int J Refractory Metals Hard Materials 54:165–177
Patel DS, Singh A, Jain VK, Ramkumar J, Shrivastava A (2019) Investigations into insertion force of electrochemically micro-textured hypodermic needles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(1311–1326):2019
Xie J, Luo MJ, Wu KK, Yang LF, Li DH (2013) Experimental study on cutting temperature and cutting force in dry turning of titanium alloy using a non-coated microgrooved tool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 2013(73):25–36
Wei Y, Kim MR, Lee DW, Park C, Park SS (2017) Effects of micro textured sapphire tool regarding cutting forces in turning operations. Int J Precis Eng Manuf - Green Technol 2017(4):141–147
Kawasegi N, Ozaki K, Morita N, Nishimura K, Yamaguchi M (2017) Development and machining performance of a textured diamond cutting tool fabricated with a focused ion beam and heat treatment. Precis Eng 2017(47):311–320
Ramesh A, Akram W, Mishra SP, Cannon AH, Polycarpou AA, King WP (2013) Friction characteristics of microtextured surfaces under mixed and hydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol Int 2013(57):170–176
Ma J, Duong NH, Lei S (2015) Finite element investigation of friction and wear of microgrooved cutting tool in dry machining of AISI 1045 steel. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 2015(229):449–464
Gajrani KK, Suresh S, Sankar MR (2018) Environmental friendly hard machining performance of uncoated and MoS2coated mechanical micro-textured tungsten carbide cutting tools. Tribol Int 2018(125):141–155
Shokrani A, Dhokia V, Newman ST (2012) Environmentally conscious machining of difficult- to-machine materials with regard to cutting fluids. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 2012(57):83–101
He T, Liu N, Xia H, Wu L, Zhang Y, Li D, Chen Y (2023) Progress and trend of minimum quantity lubrication (MQL): a comprehensive review. J Cleaner Product 386:135809
Liu N, Liu B, Jiang H, Wu S, Yang C, Chen Y (2021) Study on vibration and surface roughness in MQCL turning of stainless steel. J Manuf Process 65(April):343–353
Anand N, Kumar AS, Paul S (2019) Effect of cutting fluids applied in MQCL mode on machinability of Ti-6Al-4V. J Manuf Process 43(May):154–163
Nguyen T, Zhang LC (2003) An assessment of the applicability of cold air and oil mist in surface grinding. J Mater Process Technol 140(1–3 SPEC.):224–230
Saberi A, Rahimi AR, Parsa H, Ashrafijou M, Rabiei F (2016) Improvement of surface grinding process performance of CK45 soft steel by minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) technique using compressed cold air jet from vortex tube. J Clean Prod 131:728–738
Sartori S, Ghiotti A, Bruschi S (2017) Hybrid lubricating/cooling strategies to reduce the tool wear in finishing turning of difficult-to-cut alloys. Wear 376–377:107–114
Zhao W, Gong L, Ren F, Li L, Xu Q, Khan AM (2018) Experimental study on chip deformation of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy in cryogenic cutting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96(9–12):4021–4027
Çetindağ HA, Çiçek A, Uçak N (2020) The effects of CryoMQL conditions on tool wear and surface integrity in hard turning of AISI 52100 bearing steel. J Manuf Process 56(May):463–473
Liu N, Zou X, Yuan J, Wu S, Chen Y (2020) Performance evaluation of castor oil-ethanol blended coolant under minimum quantity lubrication turning of difficult-to-machine materials. J Manuf Process 58(August):1–10
Wu YY, Tsui WC, Liu TC (2007) Experimental analysis of tribological properties of lubricating oils with nanoparticle additives. Wear 262(7–8):819–825
Rahmati B, Sarhan AAD, Sayuti M (2014) Morphology of surface generated by end milling AL6061-T6 using molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanolubrication in end milling machining. J Clean Prod 66:685–691
Yin Q, Li C, Zhang Y, Yang M, Jia D, Hou Y, Li R, Dong L (2018) Spectral analysis and power spectral density evaluation in Al2O3 nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication milling of 45 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97(1–4):129–145
Yuan SM, Han WL, Zhu GY, Hou XB, Wang L (2019) Recent progress on the efficiency increasing methods of minimum quantity lubrication technology in green cutting. J Mech Eng 55(5):175–185
Yang J, Yuan Y, Yuan S, Wang X, Liang C (2022) State of the art on MQL synergistic technologies and their applications. Cn Mech Eng 33(5):506–528
Kui GWA, Islam S, Reddy MM, Khandoker N, Chen VL (2022) Recent progress and evaluation of coolant usages in conventional machining methods: a comprehensive review. In J Adv Manuf Technol 119:3–40
Liu N, Liu B, Jiang H, Wu S, Yang C, Chen Y (2021) Study on vibration and surface roughness in MQCL turning of stainless steel. J Manufact Processes 65:343–353
Kazeem RA, Fadare DA, Ikumapayi OM, Adediran AA, Aliyu SJ, Akinlabi SA, Tc Jen, Akinlabi ET (2022) Advances in the application of vegetable-oil-based cutting fluids to sustainable machining operations-a review. Lubricants 10(69):1–43
Yuan J, Liu N, Zou X, Wu L, Zhang Y, He T, Xia H, Wang Y, Chen Y (2022) Processing characteristics and lubrication performance of castor oil-ethanol blended coolant-based minimal quantity lubrication. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 36:78–89
Kaynak Y (2014) Evaluation of machining performance in cryogenic machining of Inconel 718 and comparison with dry and MQL machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2014(72):919–933
Gaurav G, Sharma A, Dangayach GS, Meena ML (2020) Assessment of jojoba as a pure and nano-fluid base oil in minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) hard-turning of Ti–6Al–4V: A step towards sustainable machining. J Clean Prod 272:122553
Elsheikh AH, Elaziz MA, Das SR, Muthuramalingam T, Lu S (2021) A new optimized predictive model based on political optimizer for eco-friendly MQL-turning of AISI 4340 alloy with nano-lubricants. J Manuf Process 67(2021):562–578
Sarıkaya M, Şirin S, Yıldırım V, Kivak T, Gupta MK (2021) Performance evaluation of whisker-reinforced ceramic tools under nano-sized solid lubricants assisted MQL turning of Co-based Haynes 25 superalloy. Ceramics International 47(11):15542–15560
Saleem MQ, Mehmood A (2022) Eco-friendly precision turning of superalloy Inconel 718 using MQL based vegetable oils: tool wear and surface integrity evaluation. J Manufact Processes 73:112–127
Yıldırım CV, Sankaya M, Kıvak T, Şirin S (2019) The effect of addition of hBN nanoparticles to nanofluid-MQL on tool wear patterns, tool life, roughness and temperature in turning of Ni-based Inconel 625. Tribology International 134:443–456
Lawal SA, Choudhury IA, Nukman Y (2012) Application of vegetable oil-based metalworking fluids in machining ferrous metals - a review. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 52:1–12
Ranjan P, Hiremath SS (2019) Role of textured tool in improving machining performance: a review. J Manuf Process 43(2019):47–73
Siju AS, Gajrani KK, Joshi SS (2021) Dual textured carbide tools for dry machining of titanium alloys. Int J Refract Metal Hard Mater 94(2021):105403
Siju AS, Waigaonkar SD (2021) Effects of rake surface texture geometries on the performance of single-point cutting tools in hard turning of titanium alloy. J Manuf Process 69(2021):235–252
Wang X, Li C, Zhang Y, Ding W, Yang M, Gao T, Cao H, Xu X, Wang D, Said Z, Debnath S, Jamil M, Ali HM (2020) Vegetable oil-based nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning: academic review and perspectives. J Manuf Process 59(September):76–97
Wang X, Li C, Zhang Y, Said Z, Debnath S, Sharma S, Yang M, Gao T (2022) Influence of texture shape and arrangement on nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119(1–2):631–646
Duan R, Deng J, Lei S, Ge D, Liu Y, Li X (2019) Effect of derivative cutting on machining performance of micro textured tools. J Manuf Process 45(July):544–556
Lei C, Tai BL, Chaudhari RG, Xiaozhong S, Shih AJ (2017) Machined surface temperature in hard turning. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 121(2017):10–21
Ueda T, Huda MA, Yamada K, Nakayama K, Kudo H (1999) Temperature measurement of CBN tool in turning of high hardness steel. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 48(1):63–66
Leshock CE, Shin YC (1997) Investigation on cutting temperature in turning by a toolwork thermocouple technique. J Manuf Sci Eng 119(4A):502–508
Battaglia JL, Puigsegur L, Cahuc O (2005) Estimated temperature on a machined surface using an inverse approach. Exp Heat Transf 18(1):13–32
Sen B, Mia M, Mandal UK, Mondal SP (2020) Synergistic effect of silica and pure palm oil on the machining performances of Inconel 690: a study for promoting minimum quantity nano doped-green lubricants. J Clean Prod 258:120755
Yin J, Bai Q, Goel S, Zhou P, Zhang B (2021) An analytical model to predict the depth of sub-surface damage for grinding of brittle materials. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 33(2021):454–464
Fang Z, Obikawa T (2017) Cooling performance of micro-texture at the tool flank face under high pressure jet coolant assistance. Precis Eng 49:41–51
Colwell LV (1954) Predicting the angle of chip flow for single-point cutting tools. Trans ASME 76:199–204
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51775469, 91860133) and the Open Project of Engineering Research Center of Ministry of Education (Grant No. FZGJ2020-001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and GZ designed this study. JL, GW, and BC conducted the experiments. GW summarized the data and wrote the manuscript. JL drew the schematic and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, G., Wu, G. et al. Application of micro-textured surface prepared by an integrated molding process in sustainable turning of titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 129, 5029–5045 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12569-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12569-6