Abstract
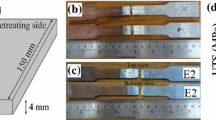
The objective of present research work is to improve the joint strength of dissimilar FSW of Al and Mg alloy. The method used for joining Al and Mg alloys is the application of Zn interlayer in different orientations in FSW process. The horizontal orientation of Zn interlayer has been used first time and compared for material mixing and strength with that of without interlayer and vertical Zn interlayer. The result shows that the maximum tensile strength of 126 MPa has been achieved for horizontal Zn interlayer as compared to the 85 MPa in the case of vertical Zn interlayer. It has been observed that cracking occurs when no interlayer was used due to formation of hard and brittle intermetallic compound (IMC) Al12Mg17. The two different types of eutectic structures and one eutectoid structure have been observed in FSW while using vertical Zn interlayer, whereas only one eutectic structure has been observed in case of horizontal Zn interlayer. New major phases identified in these FSW welds are Al5Mg11Zn4, Mg32(Al,Zn)49, MgZn, and MgZn2 in place of Al3Mg2 and Al12Mg17 phases. It has been concluded that orientation of Zn interlayer in the horizontal position has improved material flow and better mixing, which provided less hard intermetallic compounds and resulted in improved tensile strength.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials supporting the findings of this work are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdollahzadeh A, Shokuhfar A, Cabrera JM et al (2018) The effect of changing chemical composition on dissimilar Mg/Al friction stir welded butt joints using zinc interlayer. J Manuf Process 34:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.05.029
Bagheri B, Shamsipur A, Abdollahzadeh A, Mirsalehi SE (2023) Investigation of SiC nanoparticle size and distribution effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/SiC/Cu composite during the FSSW process: experimental and simulation. Met Mater Int 29:1095–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01284-8
Mishra RS, Ma ZY (2005) Friction stir welding and processing. Mater Sci Eng R 50:1–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2005.07.001
Hussein SA, Tahir AS, Hadzley AB (2015) Characteristics of aluminum-to-steel joint made by friction stir welding : a review. Mater Today Commun 5:32–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2015.09.004
Mehta KP, Badheka VJ (2016) A review on dissimilar friction stir welding of copper to aluminum : process, properties, and variants. Mater Manuf Process 31:233–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1025971
Jiang Z, Fan Z, Jiang W et al (2018) Interfacial microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg/Al bimetal produced by a novel liquid-liquid compound casting process. J Mater Process Tech 261:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.06.013
Singh AK, Sahlot P, Paliwal M, Arora A (2019) Heat transfer modeling of dissimilar FSW of Al 6061/AZ31 using experimentally measured thermo-physical properties. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:771–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04276-y
Yang P, Mao Y, Xu Y et al (2022) Interface characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical properties of friction stir lap welded dissimilar Al/Mg alloy joints: effect of pin-tip profile. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119:5251–5260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08611-0
Rai R, Bhadeshia HKDH, Debroy T et al (2011) Review: friction stir welding tools. Sci Technol Weld Join 16:325–342. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171811Y.0000000023
Kumar S, Wu CS, Zhen S, Ding W (2019) Effect of ultrasonic vibration on welding load, macrostructure, and mechanical properties of Al/Mg alloy joints fabricated by friction stir lap welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:1787–1799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2717-z
Malarvizhi S, Balasubramanian V (2012) Influences of tool shoulder diameter to plate thickness ratio (D/T) on stir zone formation and tensile properties of friction stir welded dissimilar joints of AA6061 aluminum-AZ31B magnesium alloys. Mater Des 40:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.04.008
Simoncini M, Forcellese A (2012) Effect of the welding parameters and tool configuration on micro- and macro-mechanical properties of similar and dissimilar FSWed joints in AA5754 and AZ31 thin sheets. Mater Des 41:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.04.057
Banjare PN, Dewangan SK, Manoj MK (2021) Study of material flow and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AA2024 with AA7075 dissimilar alloys using top-half-threaded pin tool. Trends Sci 18:28–31
Liu Z, Ji S, Meng X (2018) Improving joint formation and tensile properties of dissimilar friction stir welding of aluminum and magnesium alloys by solving the pin adhesion problem. J Mater Eng Perform 27:1404–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3216-y
Liu Z, Ji S, Meng X, Huang R (2017) Improving joint formation and tensile properties of friction stir welded ultra-thin Al/Mg alloy sheets using a pinless tool assisted by a stationary shoulder. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93:2071–2079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0682-6
Yan J, Xu Z, Li Z et al (2005) Microstructure characteristics and performance of dissimilar welds between magnesium alloy and aluminum formed by friction stirring. Scr Mater 53:585–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.04.022
Liang Z, Chen KE, Wang X et al (2013) Effect of tool offset and tool rotational speed on enhancing mechanical property of Al/Mg dissimilar FSW joints. Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 44:3721–3731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1700-4
Deng Y, Qiu Z, Zuo D et al (2020) Influence of tool offset on microstructure and properties of Mg/Al dissimilar alloys by friction stir welding joints at low heat input. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109:2845–2853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05788-8
Dewangan SK, Tripathi MK, Manoj MK (2019) Effect of welding speeds on microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welding of AA7075 and AA5083 alloy. Mater Today Proc 27:2713–2717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.12.190
Morishige T, Kawaguchi A, Tsujikawa M et al (2008) Dissimilar welding of Al and Mg alloys by FSW. Mater Trans 49:1129–1131. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MC200768
Verma J, Taiwade RV, Reddy C, Khatirkar RK (2018) Effect of friction stir welding process parameters on Mg-AZ31B/Al-AA6061 joints. Mater Manuf Process 33:308–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1291957
Shah LH, Othman NH, Gerlich A (2017) Review of research progress on aluminium–magnesium dissimilar friction stir welding. Sci Technol Weld Join 23:256–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2017.1370193
Singh VP, Patel SK, Ranjan A et al (2020) Recent research progress in solid state friction-stir welding of aluminium-magnesium alloys: a critical review. J Mater Res Technol 9:6217–6256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.008
Ji S, Meng X, Liu Z et al (2017) Dissimilar friction stir welding of 6061 aluminum alloy and AZ31 magnesium alloy assisted with ultrasonic. Mater Lett 201:173–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.05.011
Liu Z, Ji S, Meng X (2018) Joining of magnesium and aluminum alloys via ultrasonic assisted friction stir welding at low temperature. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97:4127–4136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2255-8
Bagheri B, Abbasi M, Sharifi F, Abdollahzadeh A (2022) Different attempt to improve friction stir brazing: effect of mechanical vibration and rotational speed. Met Mater Int 28:2239–2251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01121-4
Li D, Cui ZQ, Yang QX et al (2012) Microstructure and property of friction stir welding joint of 7075Al and AZ31BMg. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ 17:679–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-012-1345-2
Hernández-García D, Saldaña-Garcés R, García-Vázquez F et al (2017) Friction stir welding of dissimilar AA7075-T6 to AZ31B-H24 alloys. Mater Res Soc 2:4055–4066. https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2017
Bilgin M, Karabulut Ş, Özdemir A (2018) Study on the mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welding of AA 7075 T6 and AZ31B alloys. Proc 2018 9th Int Conf Mech Aerosp Eng ICMAE 2018 467–471. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMAE.2018.8467679
Zhang Y, Luo Z, Li Y et al (2015) Microstructure characterization and tensile properties of Mg/Al dissimilar joints manufactured by thermo-compensated resistance spot welding with Zn interlayer. Mater Des 75:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.03.030
Bagheri B, Alizadeh M, Mirsalehi SE et al (2022) The effect of rotational speed and dwell time on Al/SiC/Cu composite made by friction stir spot welding. Weld World 66:2333–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01376-4
Liu F, Liu Y, Wu Y (2017) Effect of lattice matching degree and intermetallic compound on the properties of Mg/Al dissimilar material welded joints. Sci Technol Weld Join 22:719–725. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2017.1313584
Vaneghi AH, Bagheri B, Shamsipur A et al (2022) Investigations into the formation of intermetallic compounds during pinless friction stir spot welding of AA2024-Zn-pure copper dissimilar joints. Weld World 66:2351–2369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01366-6
Dewangan SK, Tripathi MK, Manoj MK (2021) Material flow behavior and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welded Al 7075 and Mg AZ31 alloys using Cd interlayer. Met Mater Int 28:1169–1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-00980-1
Karimi-dermani O, Abbasi A, Azimi G, Javad M (2021) Dissimilar friction stir lap welding of AA7075 to AZ31B in the presence of Sn interlayer. J Manuf Process 68:616–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.068
Dong S, Lin S, Zhu H et al (2022) Effect of Ni interlayer on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/Mg dissimilar friction stir welding joints. Sci Technol Weld Join. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2021.2014742
Zheng B, Zhao L, Lv Q et al (2020) Effect of Sn interlayer on mechanical properties and microstructure in Al/Mg friction stir lap welding with different rotational speeds. Mater Res Express 7. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab9fbb
Xiaoqing J, Yongyong L, Tao Y et al (2022) Enhanced mechanical properties of dissimilar Al and Mg alloys fabricated by pulse current assisted friction stir welding. J Manuf Process 76:123–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.02.007
Deng H, Chen Y, Zhang T et al (2019) Effect of Zn-brazed-interface on microstructures and mechanical properties of dissimilar 2A12/AZ31 alloys friction stir lap welds. Mater Lett 255:126543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126543
Abbasi M, Bagheri B, Sharifi F (2021) Simulation and experimental study of dynamic recrystallization process during friction stir vibration welding of magnesium alloys. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 31:2626–2650. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65681-9. English Ed
Yu-ping R, Gao-wu QIN, Wen-li PEI et al (2012) Phase equilibria of Mg-rich corner in Mg−Zn−Al ternary system at 300 ° C. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 22:241–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61166-7
Cheng J, Zheng D, He K, Guo Y (2021) Effect of the vacuum heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the galvanized‑Q235/AZ91D bimetal material produced by solid–liquid compound casting. Met Mater Int 545–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00503-z
Li S, Zheng Z, Chang L et al (2021) A two-step bonding process for preparing 6061/AZ31 bimetal assisted with liquid molten zinc interlayer : the process and microstructure. J Adhes Sci Technol 0:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2021.1999713
Liu LM, Zhao LM, Wu ZH (2011) Influence of holding time on microstructure and shear strength of Mg–Al alloys joint diffusion bonded with Zn–5Al interlayer. Mater Sci Technol 27:1372–1376. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708310X12699498462887
Liu L, Liu F, Zhu M (2014) Study on Mg/Al weld seam based on Zn–Mg–Al ternary alloy. Materials 7:1173–1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7021173
Kevorkov D, Pekguleryuz M (2009) Experimental study of the Ce-Mg-Zn phase diagram at 350 °C via diffusion couple techniques. J Alloys Compd 478:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.119
Ma L, He D, Li X, Jiang J (2010) Microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium alloy AZ31B brazed joint using a Zn-Mg-Al filler metal. J Mater Sci Technol 26:743–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-0302(10)60117-X
Shi Z, Zhang W (2013) Intermetallics prediction of the morphology of Mg 32 (Al, Zn) 49 precipitates in a Mg–Zn–Al alloy. Intermetallics 39:34–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2013.02.023
Feuerbacher M, Thomas C, Roitsch S (2008) Single-crystal growth of the complex metallic alloy phase Mg32(Al, Zn)49. Intermetallics 16:943–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2008.04.012
Abdollahzadeh A, Bagheri B, Abassi M et al (2021) Comparison of the weldability of AA6061-T6 joint under different friction stir welding conditions. J Mater Eng Perform 30:1110–1127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05379-4
Zhong X, Zhao Y, Pu J et al (2020) Microstructure characterization and mechanical properties of Mg/Al dissimilar joints by friction stir welding with Zn interlayer. Phys Met Metallogr 121:1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X20130190
Naeem HT, Mohammed KS (2013) Microstructural evaluation and mechanical properties of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-alloy after addition of nickel under RRA conditions. Mater Sci Appl 2013:704–711. https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2013.411088
Guo W, You G, Yuan G, Zhang X (2017) Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar inertia friction welding of 7A04 aluminum alloy to AZ31 magnesium alloy. J Alloys Compd 695:3267–3277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.218
Tabasi M, Farahani MTM, Givi MKB et al (2016) Dissimilar friction stir welding of 7075 aluminum alloy to AZ31 magnesium alloy using SiC nanoparticles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86:705–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-8211-y
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the facility provided by IIT Delhi for TEM analysis and thanks to the Director NIT Raipur, India for providing necessary facilities and constant encouragement for publication of the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Satya Kumar Dewangan: methodology, characterizations, and writing—first draft. P. N. Banjare: formatting and editing. Dr. M. K. Tripathi: review and editing. Dr. Manoranjan Kumar Manoj: supervision and final draft. All authors have read and agreed to publish the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The article follows all the guidelines for Publication in the journal.
Consent to participate
All authors are agreeing to participate in this research study.
Consent for publication
All authors are agreeing to publish this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dewangan, S.K., Banjare, P.N., Tripathi, M.K. et al. Effect of vertical and horizontal zinc interlayer on material flow, microstructure, and mechanical properties of dissimilar FSW of Al 7075 and Mg AZ31 alloys. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 126, 4453–4474 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11348-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11348-7