Abstract
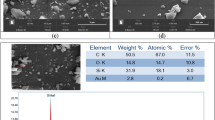
The present study embraces two-fold sustainability benefits where in first-fold, minimum power consumption (Pc) and machining time (Mt) escort one pillar of sustainability named as environmental sustainability. Moreover, the highest material removal rate (MRR) reduces manufacturing costs and embraces the second pillar of sustainability named as economic sustainability. The study is experimentally conducted on globally emerging Inconel 825 super alloy with a copper electrode in EDM. The sustainable machining is evaluated under a cluster of 8 input process parameters, i.e., spark gap (Sg), gap voltage (Vg), pulse on time (Ton), pulse off time (Toff), peak current (Ip), servo feed (Sf), depth of cut (Dc), and difficulty index (Di) under multi objective optimization (MOO) domain. The study has originally devised two novel approaches based on Taguchi, i.e., simple additive weighting (SAWTAG) and grey relational analysis (GRATAG). Toff is found as the chief significant parameter having p values of 0.005 and 0.002 respectively. Dc is found as the second significant parameter with p values of 0.061 and 0.071 respectively. Significant improvements of 0.16262 and 0.48371 are recognized in conformity experiment under GRATAG and SAWTAG approaches; optimal parametric setting is found as Sg2Vg3Ton1Toff1Ip3Sf1Dc1Di1, which is experimentally validated as robust decision. Furthermore, the proportional contribution of process parameters is estimated where GRATAG reflected 41.11% and SAWTAG reflected 47.29% of the contribution of pulse off time respectively. The study investigated surface topography for highlighting the effects of process parameters on heat-affected layers, machining debris, and surface cracks. It is examined with an increase in Ip and Vg; MRR increases and machining time decreases. Moreover, it is also noticed that an increase in Vg prevents irregularities such as micro voids and re-solidified droplets in machining.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Golshan A, Gohari S, Ayob A (2011) Modeling and optimization of cylindrical wire electro discharge machining of AISI D3 tool steel using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm. Int Conf Graph Image Process (ICGIP 2011), SPIE 82853V. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.914614
Kung KY, Chiang KT (2008) Modeling and analysis of machinability evaluation in the wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process of aluminum oxide-based ceramic. Mater Manuf Process 23:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910701860616
Yang SH, Srinivas J, Mohan S, Lee DM, Balaji S (2009) Optimization of electric discharge machining using simulated annealing. J Mater Process Technol 209:4471–4475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.10.053
Singh NK, Singh Y, Kumar S, Sharma A (2019) Comparative study of statistical and soft computing-based predictive models for material removal rate and surface roughness during helium-assisted EDM of D3 die steel. SN Appl Sci 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0545-x
Gaikwad V, Jatti VKS (2018) Optimization of material removal rate during electrical discharge machining of cryo-treated NiTi alloys using Taguchi’s method. J King Saud Univ - Eng Sci 30:266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2016.04.003
Shabgard M, Khosrozadeh B (2017) Investigation of carbon nanotube added dielectric on the surface characteristics and machining performance of Ti–6Al–4V alloy in EDM process. J Manuf Process 25:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.11.016
Singh AK, Mahajan R, Tiwari A, Kumar D, Ghadai RK (2018) Effect of dielectric on electrical discharge machining: a review. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 377:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/377/1/012184
Kumar DNM, Rao MPC (2019) Optimization of EDM process parameters using response surface methodology for AISI D3 steel. Int J Trend Sci Res Dev 3:1651–1656. https://doi.org/10.31142/ijtsrd23535
Chakraborty S, Chatterjee P, Das PP (2019) A DoE–TOPSIS method-based meta-model for parametric optimization of non-traditional machining processes. J Model Manag 14:430–455. https://doi.org/10.1108/JM2-08-2018-0110
Das PP, Chakraborty S (2020) Parametric analysis of a green electrical discharge machining process using DEMATEL and SIR methods. Opsearch 57:513–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12597-019-00410-2
Aich U, Pal AK, Laha D, Banerjee S (2013) Searching for a pareto optimal solution set of edm responses applying multi-objective simulated annealing on rsm model. Adv Mater Res 622:51–55. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.622-623.51
Werner A (2016) Method for enhanced accuracy in machining curvilinear profiles on wire-cut electrical discharge machines. Precis Eng 44:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.10.004
Arrabiyeh PA, Dethloff M, Müller C, Kirsch B, Aurich JC (2019) Optimization of micropencil grinding tools via electrical discharge machining. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans ASME 141:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4042110
Gunay M, Korkmaz ME, Yasar N (2020) Performance analysis of coated carbide tool in turning of nimonic 80A superalloy under different cutting environments. J Manuf Process 56:678–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.05.031
Sharma V, Misra JP, Singhal P (2019) Multi-optimization of process parameters for Inconel 718 while die-sink EDM using multi-criterion decision making methods. J Phys Conf Ser 1240:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1240/1/012166
Gunen A, Doleker KM, Korkmaz ME, Gok MS, Erdogan A (2021) Characteristics, high temperature wear and oxidation behavior of boride layer grown on nimonic 80A Ni-based superalloy. Surf Coatings Technol 409:126906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.126906
Sahu BK, Datta S, Mahapatra SS (2018) On electro-discharge machining of Inconel 718 super alloys: an experimental investigation. Mater Today Proc 5:4861–4869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.12.062
Jafarian F (2020) Electro discharge machining of Inconel 718 alloy and process optimization. Mater Manuf Process 35:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1711919
Erdogan A, Yener T, Doleker KM, Korkmaz ME, Gok MS (2021) Low-temperature aluminizing influence on degradation of nimonic 80A surface: microstructure, wear and high temperature oxidation behaviors. Surf Interfaces 25:101240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101240
Balasubramaniyan S, Selvaraj T (2017) Application of integrated Taguchi and TOPSIS method for optimization of process parameters for dimensional accuracy in turning of EN25 steel. J. Chinese Inst. Eng Trans Chinese Inst Eng A 40:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/02533839.2017.1308233
Ahmed N, Ishfaq K, Moiduddin K, Ali R, Shammary NA (2019) Machinability of titanium alloy through electric discharge machining. Mater Manuf Process 34:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1532092
Jafarian F (2018) A modified non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization of machining process. J Eng Sci Technol 13:4078–4093
Dang XP (2018) Constrained multi-objective optimization of EDM process parameters using kriging model and particle swarm algorithm. Mater Manuf Process 33:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1292037
Yurtkuran H, Korkmaz ME, Gunay M (2016) Modelling and optimization of the surface roughness in high speed hard turning with coated and uncoated CBN insert. Gazi Univ J Sci 29:987–995
Shah P, Khanna N, Maruda RW, Gupta MK, Krolczyk GM (2021) Life cycle assessment to establish sustainable cutting fluid strategy for drilling Ti-6Al-4V. Sustain Mater Technol 30:e00337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00337
Nadolny K, Kieras S (2020) New approach for cooling and lubrication in dry machining on the example of internal cylindrical grinding of bearing rings. Sustain Mater Technol 24:e00166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2020.e00166
Pellow MA, Ambrose H, Mulvaney D, Betita R, Shaw S (2020) Research gaps in environmental life cycle assessments of lithium ion batteries for grid-scale stationary energy storage systems: end-of-life options and other issues. Sustain Mater Technol 23:e00120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00120
Agarwal V, Khalid MK, Porvali A, Wilson BP, Lundström M (2019) Recycling of spent NiMH batteries: integration of battery leach solution into primary Ni production using solvent extraction. Sustain Mater Technol 22:e00121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00121
Thunman H, Vilches TB, Seemann M, Maric J, Vela IC, Pissot S, Nguyen HNT (2019) Circular use of plastics-transformation of existing petrochemical clusters into thermochemical recycling plants with 100% plastics recovery. Sustain Mater Technol 22:e00121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00124
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2020) ANFIS modelling of mean gap voltage variation to predict wire breakages during wire EDM of Inconel 718. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 31:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.10.007
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2021) Failure detection and control for wire EDM process using multiple sensors, CIRP. J Manuf Sci Technol 33:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.04.009
Ozkavak HV, Sofu MM, Duman B, Bacak S (2021) Estimating surface roughness for different EDM processing parameters on Inconel 718 using GEP and ANN. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 33:306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.04.007
Bucker M, Bartolomeis AD, Oezkaya E, Shokrani A, Biermann D (2020) Experimental and computational investigations on the effects of deep-temperature emulsion on the turning of Inconel 718 alloy. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 31:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.10.001
Chakraborty S, Das PP (2018) A multivariate quality loss function approach for parametric optimization of non-traditional machining processes. Manag Sci Lett 8:873–884. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2018.6.001
Tamiloli N, Venkatesan J, Ramnath BV (2016) A grey-fuzzy modeling for evaluating surface roughness and material removal rate of coated end milling insert. Meas J Int Meas Confed 84:68–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.02.008
Masoudi S, Mirabdolahi M, Dayyani M, Jafarian F, Vafadar A, Dorali MR (2019) Development of an intelligent model to optimize heat-affected zone, kerf, and roughness in 309 stainless steel plasma cutting by using experimental results. Mater Manuf Process 34:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1532579
Jafarian F (2019) 3D modeling of recrystallized layer depth and residual stress in dry machining of nickel-based alloy. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 41:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1707-x
Hribersek M, Pusavec F, Rech J, Kopac J (2018) Modeling of machined surface characteristics in cryogenic orthogonal turning of inconel 718. Mach Sci Technol 22:829–850. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2017.1415935
Behera BC, Ghosh CS, Paruchuri VR (2019) Study of saw-tooth chip in machining of Inconel 718 by metallographic technique. Mach Sci Technol 23:431–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2019.1575397
Lin YC, Yan BH, Huang FY (2001) Surface improvement using a combination of electrical discharge machining with ball burnish machining based on the Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manufact Technol 18:673–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001700170028
Lin YC, Yan BH, Huang FY (2001) Surface modification of Al-Zn-Mg aluminum alloy using the combined process of EDM with USM. J Mater Process Technol 115:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01017-2
Furutania K, Saneto A, Takezawa H, Mohri N, Miyake H (2001) Accretion of titanium carbide by electrical discharge machining with powder suspended in working fluid. Precis Eng 25:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-6359(00)00068-4
Scott D, Boyina S, Rajurkar KP (1991) Analysis and optimization of parameter combinations in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Prod Res 29:2189–2207. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207549108948078
Tarng YS, Ma SC, Chung LK (1995) Determination of optimal cutting parameters in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 35:1693–1701. https://doi.org/10.1016/0890-6955(95)00019-T
Jeswani ML (1981) Effect of the addition of graphite powder to kerosene used as the dielectric fluid in electrical discharge machining. Wear 70:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(81)90148-4
Mohri N, Saito N, Higashi MA (1991) A new process of finish machining on free surface by EDM methods. Ann CIRP 40:207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61969-6
Ming QY, He LY (1995) Powder-suspension dielectric fluid for EDM. J Mater Process Tech 52:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-0136(94)01442-4
Wong YS, Lim LC, Rahuman I, Tee WM (1998) Near-mirror-finish phenomenon in EDM using powder-mixed dielectric. J Mater Process Technol 79:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00450-0
Wong YS, Lim LC, Lee LC (1995) Effects of flushing on electro-discharge machined surfaces. J Mater Process Tech 48:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-0136(94)01662-K
Kunieda M, Yoshida M (1997) Electrical discharge machining in gas. CIRP Ann - Manuf Technol 46:143–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-8506(07)60794-x
Yoshida M, Kunieda M (1999) Study on mechanism for minute tool electrode wear in dry EDM. Seimitsu Kogaku Kaishi/Journal Japan Soc. Precis Eng 65:689–693. https://doi.org/10.2493/jjspe.65.689
Chow HM, Yan BH, Huang FY, Hung JC (2000) Study of added powder in kerosene for the micro-slit machining of titanium alloy using electro-discharge machining. J Mater Process Technol 101:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00458-6
Shao B, Rajurkar KP (2015) Modelling of the crater formation in micro-EDM. Procedia CIRP 33:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.06.085
Reddy PR, Reddy GJ, Prasanthi G (2020) Mathematical modeling of material removal rate using Buckingham Pi theorem in electrical discharge machining of hastelloy C276. Lect Notes Mech Eng Springer 2020:843–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1201-8_90
Tzeng YF, Lee CY (2001) Effects of powder characteristics on electrodischarge machining efficiency. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 17:586–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001700170142
Tzeng FY, Chen FU (2003) A simple approach for robust design of high speed electrical-discharge machining technology. Int J Mach Tools Manufact 43:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00261-4
Panda DK, Bhoi RJ (2005) Artificial neural network prediction of material removal rate in EDM. Mater Manuf Process 20:645–672. https://doi.org/10.1081/AMP-200055033
Tanveer A, Kapoor SG, Mujumdar SS (2019) Modeling of material removal in atomized dielectric-based electrical discharge machining (EDM). ASME 2019 14th Int. Manuf Sci Eng Conf MSEC 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1115/MSEC2019-3025
Luan ND, Minh ND, Thanh LTP (2019) Multi-Objective optimization of PMEDM process parameter by topsis method. Int J Trend Sci Res Dev 3:112–115. https://doi.org/10.31142/ijtsrd23169
Jain S, Parashar V (2020) Application of multi-objective BAT algorithm for EDM process parameters optimization. Int J Adv Sci Technol 29:5214–5225
Kansal HK, Singh S, Kumar P (2005) Parametric optimization of powder mixed electrical discharge machining by response surface methodology. J Mater Process Technol 169:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.03.028
Wang H, Zuo D, Miao H, Wang H, Wang M (2010) Effect of discharge parameters on micro-surface topography of NAK80 by mirror-like surface EDM. Key Eng Mater 2010:438–441. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.431-432.438
Li L, Niu Z, Yin F, Liu Y (2012) Surface integrity of sintered NdFeB permanent magnet after EDM. Adv Mater Res 2012:27–30. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.503-504.27
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Shen Y, Ji R, Li Z, Zheng C (2014) Investigation on the influence of the dielectrics on the material removal characteristics of EDM. J Mater Process Technol 214:1052–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.12.012
Payal H, Maheshwari S, Bharti PS (2019) Parametric optimization of EDM process for Inconel 825 using GRA and PCA approach. J Inf Optim Sci 40:291–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/02522667.2019.1578090
Sahu NK, Sahu AK, Sahu AK (2017) Optimization of weld bead geometry of MS plate (Grade: IS 2062) in the context of welding: a comparative analysis of GRA and PCA–Taguchi approaches. Indian Acad Sci 8:234–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-016-0589-1
Sahu AK, Sahu NK, Sahu AK, Rajput MS, Narang HK (2019) T-SAW methodology for parametric evaluation of surface integrity aspects in AlMg3 (AA5754) alloy: comparison with T-TOPSIS methodology. Measurement 132:309–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.09.037
Guo X, Sahu AK, Sahu NK, Sahu AK (2022) A novel integrated computational TRIFMRG approach with grey relational analysis toward parametric evaluation of weld bead geometry of MS-Grade: IS 2062. Grey Syst: Theory Appl 12:117–141. https://doi.org/10.1108/GS-09-2020-0124
Sahu NK, Singh MK, Mwanza BGM, Sahu AK (2022) Investigation of machinability characteristics of EDMed Inconel 825 alloy under multidimensional parametric modeling by using holistic grey-PCA statistical models. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2022:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3147586
He Z, Ma X, Luo J, Sahu AK, Sahu AK, Sahu NK (2021) Exploitation of the advanced manufacturing machine tool evaluation model under objective-grey information: a knowledge-based cluster with the grey relational analysis approach. Grey Syst: Theory Appl 11:394–417. https://doi.org/10.1108/GS-03-2020-0028
Sahu NK, Singh MK, Sahu AK, Sahu AK (2022) Surface topography and optimal machining characteristics investigation for advanced engineering material Inconel 825 alloy exploring statistical TGRA accompanied with T-Topsis methodology. Surf Rev Lett 29:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218625X22501499
Muthuramalingam T, Babu LG, Sridharan K, Geethapriyan T, Srinivasan KP (2020) Multi-response optimization of WEDM process parameters of Inconel 718 alloy using TGRA method. Lect Notes Networks Syst 2020:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-37497-6_56
Gostimirovic M, Pucovsky V, Sekulic M, Radovanovic M, Madic M (2018) Evolutionary multi-objective optimization of energy efficiency in electrical discharge machining. J Mech Sci Technol 32:4775–4785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0925-y
Choudhury SD, Saharia NJ, Surekha B, Mondal G (2018) Study on the influence of hybridized powder mixed dielectric in electric discharge machining of alloy steels. Mater Today Proc 5:18410–18415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.181
Baldin V, Baldin CRB, Machado AR, Amorim FL (2020) Machining of Inconel 718 with a defined geometry tool or by electrical discharge machining. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02358-7
Zhou S, Yang Y, Zhou M, Sun H (2020) Electrical discharge machining Inconel 718 with adaptively regulating gap servo-voltage. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 109:2575–2585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05835-4
Suji D, Adesina A, Mirdula R (2021) Optimization of self-compacting composite composition using Taguchi-Grey relational analysis. Materialia 15:101027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2021.101027
Geethapriyan T, Kalaichelvan K, Muthuramalingam T (2016) Multi performance optimization of electrochemical micro-machining process surface related parameters on machining Inconel 718 using Taguchi-grey relational analysis. Metall Ital 108:13–19
Alinezhad A, Amini A, Alinezhad A (2009) Sensitivity analysis of simple additive weighting method (SAW): the results of change in the weight of one attribute on the final ranking of alternatives. J Ind Eng 4:13–18
Afshari A, Mojahed M, Yusuff R (2010) Simple additive weighting approach to personnel selection problem. Int J Innov, Manag Technol 1:511–515. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784413265.043
Dhakar K, Dvivedi A (2017) Influence of glycerin-air dielectric medium on near-dry EDM of titanium alloy. Int J Addit Subtractive Mater Manuf 1:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijasmm.2017.10010933
Jafarian F, Masoudi S, Umbrello D, Filice L (2019) New strategies for improvement of numerical model accuracy in machining of nickel-based alloy. Simul Model Pract Theory 94:134–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2019.02.006
Rajyalakshmi G, Ramaiah PV (2013) Multiple process parameter optimization of wire electrical discharge machining on Inconel 825 using Taguchi grey relational analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69:1249–1262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5081-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first author, i.e., Nitin Kumar Sahu, has developed the theoretical content of the paper. He has also performed the experimental investigations related to the study. Mukesh Kumar Singh has developed the methodological aspects and performed the computations. Atul Kumar Sahu and Anoop Kumar Sahu have assisted in framing decision modeling, descriptions, and findings of this study. All authors have discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, N.K., Singh, M.K., Sahu, A.K. et al. Employment of cylindrical electrolytic copper grade electrode under EDMed Inconel 825 super alloy: emphasis on machining behavior accompanied with surface topography for sustainability. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 131, 2207–2233 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10967-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10967-4