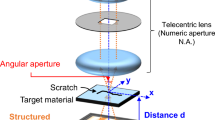
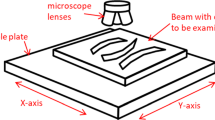
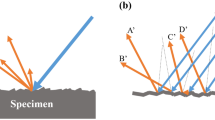
Abstract
Illumination estimation is crucial for surface detection methods based on visual image reconstruction. The luminance of the machined surface topography with desertification fractal structure is difficult to accurately describe using existing illumination models, which depend on the macrosurface geometric features and reflection characteristics. Therefore, machined surface topography illumination model under coaxial light microscopic vision is proposed in this paper for the online detection of complex surfaces and special functional surface topography in the manufacturing field. Based on light scattering theory, the luminance of the surface topography is studied under the coaxial light microscopic vision; the influencing factors of luminance of surface topography are revealed and the illumination model of machined surface topography is established. The experimental results show that less calculation error occurs when using the proposed illumination model, which can be used to more accurately describe the luminance of machined surface topography. The research results will lay a foundation for online detection and monitoring of machined surfaces.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ning PX, Zhao JJ, Ji SJ, Li JJ, Dai HD (2021) Simulation and experiment on surface topography of complex surface in single point diamond turning based on determined tool path. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 113(9–10):2555–2562
Pu YZ, Zhao YG, Zhang HY, Zhao GY, Meng JB, Song PP (2020) Study on the three-dimensional topography of the machined surface in laser-assisted machining of Si3N4 ceramics under different material removal modes. Ceram Int 45(5):5695–5705
Zhang H, Liu J, Lu EH, Suo XY, Chen N (2019) A novel surface roughness measurement method based on the red and green aliasing effect. Tribol Int 131:579–590
Zhou YJ, Wu YC, Luo C (2018) A fast dimensional measurement method for large hot forgings based on line reconstruction. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 99(5–8):1713–1724
Herrero FJD, Garcia DF, Usamentiaga R (2020) Surface defect system for long product manufacturing using differential topographic images. Sensors 20(7):2142
Ma L, Lyu Y, Hu YM, Sun FM (2018) Scaled SFS method for Lambertian surface 3D measurement under point source lighting. Opt Express 26(11):14251–14258
Zhang AJ, Zhao Y, Wang SG (2019) Illumination estimation for augmented reality based on a global illumination model. Multimed Tools Appl 78(23):33487–33503
Yang L, Li E, Long T, Fan JF, Mao YJ, Fang ZJ, Liang ZZ (2018) A welding quality detection method for arc welding robot based on 3D reconstruction with SFS algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(1–4):1209–1220
Torrance KE (1967) Theory for Off-Specular reflection from roughened surfaces. Optics Society 57(3):1105–1114
Cook RL, Torrance KE (1982) A Reflectance Model for Computer Graphic. ACM Transactions on Graphics 1(1):7–24
Hirayama H, Kaneda K, Yamashita H, Monden Y (2001) An accurate illumination model for objects coated with multilayer films. Computers & Graphics 25(3):391–400
Jager K, Tillmann P, Becker C (2020) Detailed illumination model for bifacial solar cells. Opt Express 28(4):4751–4762
Grzesik W (2016) Prediction of the functional performance of machined components based on surface topography: state of the art. J Mater Eng Perform 25(10):4460–4468
Wang FB, Sun ZL, Wang SZ, Zhang BL (2020) Micro-vision image measurement for spot arrays on silicon wafer ablated by femtosecond laser. Optik 203:163894
Ikgeun J, Liu Y, Kwangnam R, Hoon S (2019) Online melt pool depth estimation during directed energy deposition using coaxial infrared camera, laser line scanner, and artificial neural network. Addit Manuf 47:102295
Liu YK, Guo L, Gao HL, You ZC, Ye YG, Zhang B (2022) Machine vision based condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of machine tools using information from machined surface texture: a review. Mech Syst Signal Process 164:108068
Nammi SAU, Ramamoorthy B (2014) Effect of surface lay in the surface roughness evaluation using machine vision. Optik 125(15):3954–3960
McGunnigle G, Dong J (2011) Augmenting photometric stereo with coaxial illumination. IET Comput Vision 5(1):33–49
Ewing BE, Butler SD, Marciniak MA (2018) Improved grazing angle bidirectional reflectance distribution function model using Rayleigh-Rice polarization factor and adaptive surface topography distribution function. Opt Eng 57(10):105102
Shi WC, Zheng JM, Wang QL, Wang LJ, Li Q (2021) Characterization of machined surface topography based on the normal declination angle of surface topographys. Micromachines 12(3):228
Li JC, Lei L (2020) A Hybrid genetic algorithm based on information entropy and game theory. IEEE Access 8:36602–36611
Chen MJ, Bovik AC (2011) Fast structural similarity index algorithm. J Real-Time Image Proc 6(4):281–287
Yoo JC, Ahn CW (2012) Image matching using peak signal-to-noise ratio-based occlusion detection. IET Image Proc 6(5):483–495
Funding
Financial support for this work was received from the Natural Science Foundation Research Project of Shaanxi Province (2021JQ-488) and the Doctor’s Research Foundation of Xi’an University of Technology (Grant Number 102–451120014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design, to the search in the literature and to the reading of the relevant retrieved papers. WeiChao Shi proposed the method and conducted the numerical simulation. He also drafted the manuscript. JianMing Zheng and Qiang Sheng discussed the prediction model and revised the manuscript. Qilong Wang, Lijie Wang and Qi Li conducted the experiment and processed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors declare that this manuscript was not submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration. The submitted work is original and has not been published elsewhere in any form or language.
Consent to participate
All the authors consented to participate in this research and contribute to the research.
Consent for publication
All the authors consented to publish the research. There are no potential copyright/plagiarism issues involved in this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, W., Zheng, J., Sheng, Q. et al. Illumination modelling for reconstructing the machined surface topography. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 125, 4975–4987 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10925-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10925-0