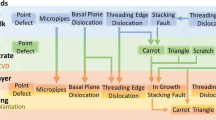
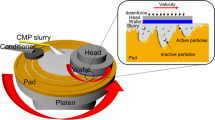
Abstract
When the integrated circuit (IC) feature size is reduced to 0.13 μm and below, copper (Cu) becomes the new wiring material in interconnect materials. The double damascene process is the only process for Cu patterning that is mature and has been successfully applied to IC manufacturing, so Cu interconnection chemical–mechanical polishing (CMP), which can achieve the surface nanoscale accuracy required by lithography level, is of great importance to the IC industry. The slurry is the most important component of the CMP materials and has a significant impact on the surface quality of the polished wafer. Therefore, how to select suitable additives to improve the chemical effect and obtain excellent post-polishing surface and good slurry stability while saving cost is an urgent issue to be considered. The research progress of each component in Cu interconnection slurry was discussed in this paper, mainly focusing on the advantages and disadvantages of acidic and alkaline slurries, and the research progress of oxidants, complexing agents, surfactants, and corrosion inhibitors as well as their respective action mechanisms were analyzed in detail, which will be a great contribution to the IC field. It will facilitate the optimization of the slurry for further development of new Cu interconnection CMP slurry.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This is not applicable.
Code availability
This is not applicable.
References
Nitta T, Ohmi T, Hoshi T, Sakai S, Sakaibara K, Imai S, Shibata T (1993) Evaluating the large electromigration resistance of copper interconnects employing a newly developed accelerated life-test method. J Electrochem Soc 140:1131–1137. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2056211
Nomura Y, Ono H, Terazaki H, Kamigata Y, Yoshida M (2004) Effect of abrasive in Cu-CMP slurry on global planarization. MRS Proc 816:451–455. https://doi.org/10.1557/proc-816-k4.5
Yan H, Niu X, Luo F, Qu M, Zhang Y (2022) Effect of OA and JFCE as surfactants on the stability of copper interconnection CMP slurry, 2022 China Semiconductor Technology International Conference (CSTIC): 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/CSTIC55103.2022.9856848
Du T, Luo Y, Desai V (2004) The combinatorial effect of complexing agent and inhibitor on chemical–mechanical planarization of copper. Microelectron Eng 71:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2003.08.008
Zhou J, Niu X, Wang Z, Cui Y, Wang J, Wang R (2019) Study on effective methods and mechanism of inhibiting removal rate in chemical mechanical polishing of GLSI low-tech node copper film. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8:P652–P660. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0271910jss
Manivannan R, Cho BJ, Hailin X, Ramanathan S, Park JG (2014) Characterization of non-amine-based post-copper chemical mechanical planarization cleaning solution. Microelectron Eng 122:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2014.02.034
Hong YK, Eom DH, Lee SH, Kim TG, Park JG, Busnaina AA (2004) The effect of additives in post-Cu CMP cleaning on particle adhesion and removal. J Electrochem Soc 151:756–761. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1802493
Zantye PB, Kumar A, Sikder AK (2004) Chemical mechanical planarization for microelectronics applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 45:89–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2004.06.002
Seah CH, You GZ, Wang SR, Li CY, Kumar R (2005) Impact of electroplated copper thickness on copper CMP and Cu/Coral™ BEOL integration. Microelectron Eng 81:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2005.03.040
Kondo S, Ichige Y, Otsuka Y (2017) Electrochemical study on metal corrosion in chemical mechanical planarization process, Japanese J Appl Phys 56.https://doi.org/10.7567/jjap.56.07ka01
Seo J (2021) A review on chemical and mechanical phenomena at the wafer interface during chemical mechanical planarization. J Mater Res 36:235–257. https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-020-00060-x
Zhao G, Wei Z, Wang W, Feng D, Xu A, Liu W, Song Z (2020) Review on modeling and application of chemical mechanical polishing. Nanotechnol Rev 9:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2020-0016
Wang MT, Tsai MS, Liu C, Tseng WT, Chang TC, Chen LJ, Chen MC (1997) Effects of corrosion environments on the surface finishing of copper chemical mechanical polishing. Thin Solid Films 308–309:518–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-6090(97)00500-2
Zhong ZW (2020) Advanced polishing, grinding and finishing processes for various manufacturing applications: areview. Mater Manuf Processes 35:1279–1303. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1772481
Filatov YD (2020) Polishing of precision surfaces of optoelectronic device elements made of glass, sitall, and optical and semiconductor crystals: a review. J Superhard Mater 42:30–48. https://doi.org/10.3103/s1063457620010037
Srinivasan R, Dandu PVR, Babu SV (2015) Shallow trench isolation chemical mechanical planarization: a review. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 4:P5029–P5039. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0071511jss
Gao PL, Liu TT, Zhang ZY, Meng FN, Ye RP, Liu J (2021) Non-spherical abrasives with ordered mesoporous structures for chemical mechanical polishing. Sci China Mater 64:2747–2763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-021-1680-2
Xie WX, Zhang ZY, Liao LX, Liu J, Su HJ, Wang SD, Guo DM (2020) Green chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire wafers using a novel slurry. Nanoscale 12:22518–22526. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr04705h
Liu DD, Zhang ZY, Feng JJ, Yu ZB, Meng FN, Xu GH, Wang JM, Wen W, Liu W (2022) Atomic-level flatness on oxygen-free copper surface in lapping and chemical mechanical polishing. Nanoscale Adv 4:4263. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2na00405d
Lee H, Lee D, Jeong H (2016) Mechanical aspects of the chemical mechanical polishing process: a review. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 17:525–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-016-0066-0
Zhang Y, Niu X, Zhou J, Wang J, Yang C, Hou Z, Zhu Y, Huang L (2022) Surface corrosion inhibition mechanism of sarcosine as a green novel inhibitor on a novel barrier layer material of cobalt in copper film CMP for GLSI. Mater Sci Semicond Process 140:106402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2021.106402
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467–468:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.133
Liao LX, Zhang ZY, Meng FN, Liu DD, Wu B, Li YB, Xie WX (2021) A novel slurry for chemical mechanical polishing of single crystal diamond. Appl Surf Sci 564:150431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150431
Zhang ZY, Liao LX, Wang XZ, Xie WX, Guo DM (2020) Development of a novel chemical mechanical polishing slurry and its polishing mechanisms on a nickel alloy. Appl Surf Sci 506:144670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144670
Zhang ZY, Liu J, Hu W, Zhang LZ, Xie WX, Liao LX (2021) Chemical mechanical polishing for sapphire wafers using a developed slurry. J Manuf Process 62:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.01.004
Zhang ZY, Shi ZF, Du YF, Yu ZJ, Guo LC, Guo DM (2018) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry. Appl Surf Sci 427:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.064
Qu Z, Zhao Q, Meng Y, Wang T, Zhao D, Men Y, Lu X (2013) In-situ measurement of Cu film thickness during the CMP process by using eddy current method alone. Microelectron Eng 108:66–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2013.03.046
Kelly J, Surisetty C, Canaperi D (2013) Experimental study of copper leveling additives and their wafer and pattern-scale effect on copper planarization. C R Chim 16:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2012.03.013
Lee D, Lee H, Jeong H (2016) Slurry Components in metal chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process: a review. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 17:1751–1762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-016-0201-y
Nelabhotla DM, Jayaraman TV, Asghar K, Das D (2016) The optimization of chemical mechanical planarization process-parameters of c-plane gallium-nitride using Taguchi method and grey relational analysis. Mater Des 104:392–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.031
Deng C, Jiang L, Qin N, Qian L (2021) Effects of pH and H2O2 on the chemical mechanical polishing of titanium alloys. J Mater Process Technol 295:117204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117204
Badawy WA, Al-Kharafi FM, Al-Ajmi JR (2000) Electrochemical behaviour of cobalt in aqueous solutions of different pH. J Appl Electrochem 30:693–704. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003893122201
Du T, Desai V (2011) The pH effect on chemical mechanical planarization of copper, MRS Proceedings 767.https://doi.org/10.1557/proc-767-f6.6
Pourbaix M (1967) Atlas of electrochemical equilibria in aqueous solutions. J Electroanal Chem 13:471–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(67)80059-7
Steigerwald JM, Murarka SP, Gutmann RJ, Duquette DJ (1995) Chemical processes in the chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Mater Chem Phys 41:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/0254-0584(95)01516-7
Kulkarni M, Baker M, Greisen D, Ng D, Griffin R, Liang H (2006) Effects of electrochemistry on surface roughness during chemical-mechanical polishing of copper. Tribol Lett 25:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-006-9134-4
Li J, Liu Y, Pan Y, Lu X (2014) Chemical roles on Cu-slurry interface during copper chemical mechanical planarization. Appl Surf Sci 293:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.150
Yao C, Niu X, Wang C, Liu Y, Jiang Z, Wang Y, Tian S (2017) Study on the weakly alkaline slurry of copper chemical mechanical planarization for GLSI. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 6:P499–P506. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0071708jss
Zhou J, Wang J, Niu X, Zhang K, Wang Z, Cui Y, Wang R (2019) Chemical interactions and mechanisms of different pH regulators on copper and cobalt removal rate of copper film CMP for GLSI. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology 8:P99–P105. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0101902jss
Xu R, Wang YS, Wang YP, Liu HX, Su JX (2020) Study on oxidant in chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Trans Electr Electron Mater 21:580–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-020-00208-w
Shukla A, Victoria SN, Manivannan R (2021) A review on chemical mechanical planarization of barrier layer metals. Key Eng Mater 882:171–180. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.882.171
Thomas L, Gratton R, Marino B, Betelú S, Diez J, Simon J (1996) Measurement of the slope of an unsteady liquid surface along a line by an anamorphic Schlieren system. Meas Sci Technol 7:1134. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/7/8/008
Poddar MK, Jalalzai P, Sahir S, Yerriboina NP, Kim TG, Park JG (2021) Tungsten passivation layer (WO3) formation mechanisms during chemical mechanical planarization in the presence of oxidizers. Appl Surf Sci 537:147862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147862
Du T, Vijayakumar A, Desai V (2004) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on oxidation of copper in CMP slurries containing glycine and Cu ions. Electrochim Acta 49:4505–4512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2004.05.008
Hernandez J, Wrschka P, Oehrlein GS (2001) Surface chemistry studies of copper chemical mechanical planarization. J Electrochem Soc 148:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1377595
Zhou J, Niu X, Cui Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Wang R (2020) Study on the film forming mechanism, corrosion inhibition effect and synergistic action of two different inhibitors on copper surface chemical mechanical polishing for GLSI. Appl Surf Sci 505:144507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144507
Nishizawa H, Nojo H, Isobe A (2010) Fundamental study of chemical–mechanical polishing slurry of cobalt barrier metal for the next-generation interconnect process, Japanese. J Appl Phys 49.https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.49.05fc03
Kawaguchi K, Ito H, Kuwahara T, Higuchi Y, Ozawa N, Kubo M (2016) Atomistic mechanisms of chemical mechanical polishing of a Cu surface in aqueous H2O2: tight-binding quantum chemical molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:11830–11841. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b11910
Yun SS, Son YH, Jeong GP, Lee JH, Jeong JH, Bae JY, Kim SI, Park JH, Park JG (2021) Dishing-free chemical mechanical planarization for copper films. Colloids Surf, A 616:126143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126143
Zhao T, Jiang L, Liu J, Wu H, Qin N, Qian L (2021) Potassium persulfate as an effective oxidizer for chemical mechanical polishing of GCr15 bearing steel. J Appl Electrochem 51:803–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01540-6
Kanki T, Kimura T, Nakamura T (2013) Chemical and mechanical properties of Cu surface reaction layers in Cu-CMP to improve planarization. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 2:P375–P379. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.023309jss
Zhang W, Lu X, Liu Y, Pan G, Luo J (2009) Effect of pH on material removal rate of Cu in abrasive-free polishing. J Electrochem Soc 156:176–180. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3055985
Kanki T, ShirasuT Takesako S, Sakamoto M (2008) On the elements of high throughput Cu-CMP slurries compatible with low step heights. Int Interconnect Technol Conf IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/IITC.2008.4546931
Hazarika J, Patil CS, Rajaraman PV (2021) Formulation of slurry for chemical mechanical polishing of Cu substrates. Mater Today: Proc 39:1781–1785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.545
Zhang L, Wang T, Lu X (2020) Potassium persulfate as an oxidizer in chemical mechanical polishing slurries relevant for copper interconnects with cobalt barrier layers. J Mater Sci 55:8992–9002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04579-6
He YG, Wang JX, Gan XW, Li WJ, Liu YL (2012) Effect of complex agent on copper dissolution in alkaline slurry for chemical mechanical planarization. Adv Mater Res 455–456:1145–1148. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.455-456.1145
Kwon O, Bae K, Byun J, Lim T, Kim JJ (2020) Study on effect of complexing agents on Co oxidation/dissolution for chemical-mechanical polishing and cleaning process. Microelectron Eng 227:111308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2020.111308
Zhou J, Niu X, Zhang T, Wang H, Yang C, Zhang Y, Wang W, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Hou Z, Wang R (2021) Prediction of planarization property in copper film chemical mechanical polishing via response surface methodology and convolutional neural network. Nano Select 3:688–702. https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202100028
Patri UB, Pandija S, Babu SV (2005) Role of molecular structure of complexing/chelating agents in copper CMP slurries. MRS Proceedings 867.https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-867-W1.11
Yang G, He P, Qu XP (2018) Inhibition effect of glycine on molybdenum corrosion during CMP in alkaline H2O2 based abrasive free slurry. Appl Surf Sci 427:148–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.140
Gorantla VRK, Matijević E, Babu SV (2005) Amino acids as complexing agents in chemical−mechanical planarization of copper. Chem Mater 17:2076–2080. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm048478f
Zhang P, Chen G, Ni Z, Wang Y, Teng K, Qian S, Bian D, Zhao Y (2021) The effect of Cu2+ ions and glycine complex on chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) performance of SiC substrates. Tribol Lett 69.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01468-0
Oraby EA, Eksteen JJ (2014) The selective leaching of copper from a gold–copper concentrate in glycine solutions. Hydrometallurgy 150:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.09.005
Zhang YC, Niu XH, Zhou JK, Yang CH, Feng ZX, Chang JR, Hou ZY, Zhu YB (2021) Study on the application of amino acid chemical additives represented by glycine in the CMP process. Appl Chem Ind 50:2249–2253. https://doi.org/10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20210526.028
Jang S, Jeong H, Yuh M, Park I, Park J (2016) Effect of glycine on copper CMP. Int J Precis Eng Manuf-Green Technol 3:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-016-0019-1
Wen J, Ma T, Zhang W, Duin ACTV, Duin DMV, Hu Y, Lu X (2019) Atomistic insights into Cu chemical mechanical polishing mechanism in aqueous hydrogen peroxide and glycine: ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem C 123:26467–26474. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b08466
Guo X, Yuan S, Gou Y, Wang X, Guo J, Jin Z, Kang R (2020) Study on chemical effects of H2O2 and glycine in the copper CMP process using ReaxFF MD. Appl Surf Sci 508:145262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145262
Zhou J, Niu X, Yang C, Huo Z, Lu Y, Wang Z, Cui Y, Wang R (2020) Surface action mechanism and planarization effect of sarcosine as an auxiliary complexing agent in copper film chemical mechanical polishing. Appl Surf Sci 529:147109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147109
Zhang Y, Niu X, Zhou J, Wang J, Zhu Y, Hou Z, Yan H, Luo F, Qu M (2022) Effect and mechanism analysis of sarcosine on the chemical mechanical polishing performance of copper film for GLSI. Mater Sci Semicond Process 151:107003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.107003
Selvam NV, Srinivasan R (2010) Electrochemical characterization of copper chemical mechanical polishing in L-glutamic acid–hydrogen peroxide-based slurries. J Solid State Electrochem 15:837–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-010-1164-z
Gorantla V, Babu SV (2011) Comparison of glycine and citric acid as complexing agents in copper chemical-mechanical polishing slurries. MRS Proceedings 767.https://doi.org/10.1557/proc-767-f6.7
Gorantla VRK, Assiongbon KA, Babu SV, Roy D (2005) Citric acid as a complexing agent in CMP of copper. J Electrochem Soc 152:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1890786
Lee H (2018) Effect of citric acid in Cu chemical mechanical planarization slurry on frictional characteristics and step height reduction of Cu pattern. Tribol Lubricants 34:226–234. https://doi.org/10.9725/kts.2018.34.6.226
Gorantla VRK, Babel A, Pandija S, Babu SV (2005) Oxalic acid as a complexing agent in CMP slurries for copper. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8:G131–G134. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1883873
Janjam SVSB, Peddeti S, Roy D, Babu SV (2008) Tartaric acid as a complexing agent for selective removal of tantalum and copper in CMP. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 11:327–330. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2980345
Zhou J, Niu X, Wang Z, Cui Y, Wang J, Yang C, Huo Z, Wang R (2020) Roles and mechanism analysis of chitosan as agreen additive in low-tech node copper film chemical mechanical polishing. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 586:124293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124293
Jiang L, Lan Y, He Y, Li Y, Luo J (2014) Functions of Trilon® P as apolyamine in copper chemical mechanical polishing. Appl Surf Sci 288:265–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.020
Hong J, Niu X, Liu Y, He Y, Zhang B, Wang J, Han L, Yan C, Zhang J (2016) Effect of a novel chelating agent on defect removal during post-CMP cleaning. Appl Surf Sci 378:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.230
Zhang B, Liu Y, Wang C (2015) BTA free alkaline slurries developed for copper and barrier CMP. ECS J Solid State Sci and Technol 4:P5112–P5117. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0171511jss
Luan X, Liu Y, Wang C, Niu X, Wang J, Zhang W (2016) A study on exploring the alkaline copper CMP slurry without inhibitors to achieve high planarization efficiency. Microelectron Eng 160:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2016.02.044
Zhang K, Niu X, Wang C, Wang J, Yin D, Wang R (2018) Effect of chelating agent and ammonium dodecyl sulfate on the interfacial behavior of copper CMP for GLSI. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 7:P509–P517. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0231809jss
Yin D, WangQ ZS, Tan B, Yang F, Wang R, Sun X, Liu M (2021) Effect of EDTA-based alkaline cleaning solution on TAZ removal in post CMP cleaning of copper interconnection. Mater Res Bull 137:111202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.111202
Miao Y, Wang S, Wang C, Liu Y, Sun M, Chen Y (2014) Effect of chelating agent on benzotriazole removal during post copper chemical mechanical polishing cleaning. Microelectron Eng 130:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2014.08.012
Wang Q, Yin D, Gao B, Tian S, Sun X, Liu M, Zhang S, Tan B (2020) Effect of arginine-based cleaning solution on BTA residue removal after Cu-CMP. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 586:124286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124286
Yang L, Tan B, Liu Y, Gao B, Liu Y, Han C, Wang Q, Tian, S (2018) Effect of organic amine alkali and inorganic alkali on benzotriazole removal during post Cu-CMP cleaning. J Semicond 39. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/39/12/126003
Seo J, Vegi SSRKH, Babu SV (2019) Post-CMP cleaning solutions for the removal of organic contaminants with reduced galvanic corrosion at copper/cobalt interface for advanced Cu interconnect applications. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8:P379–P387. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0011908jss
Yin D, Yang L, Ma T, Xu Y, Tan B, Yang F, Sun X, Liu M (2020) Synergistic effect of composite complex agent on BTA removal in post CMP cleaning of copper interconnection. Mater Chem Phys 252.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123230
Hu CY, Lo SL, Li CM, Kuan WH (2005) Treating chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) wastewater by electro-coagulation-flotation process with surfactant. J Hazard Mater 120:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.12.038
Xu Q, Yang F, Chen L, Cao H (2018) Effect of non-ionic surfactant on chemical mechanical planarization performance in alkaline copper slurry. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 19:1585–1595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-018-0186-9
Tsai TH, Wu YF (2006) Effects of Nonionic surfactants on performance of copper chemical mechanical polishing. Chem Eng Commun 193:702–714. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986440500265901
Yin D, Tian S, Zhang N, Wang Q, Sun X, Liu M, Zhang S, Tan B (2021) Synergistic effect of LABSA/JFCE combined surfactant system on the removal of particles on copper wafer surface. Mater Chem Phys 257:123841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123841
Deng H, Tan B, Gao B, Wang C, Gu Z, Zhang Y (2015) A novel cleaner for colloidal silica abrasive removal in post-Cu CMP cleaning. J Semicond 36.https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/36/10/106002
Qu L, Gao B, Wang X, Wu T, Tan B (2021) Effect of intermolecular interaction of compound surfactant on particle removal in post-Cu CMP cleaning. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 10:064007. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac08d2
Luo C, Xu Y, Zeng N, Ma T, Wang C, Liu Y (2020) Synergy between dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid and isomeric alcohol polyoxyethylene ether for nano-scale scratch reduction in copper chemical mechanical polishing. Tribol Int 152:106576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106576
Zhang Y, Niu X, Zhou J, Yang C, Hou Z, Zhu Y (2021) Effect of FA/O II surfactant as a complex non-ionic surfactant on copper CMP. 2021 China Semicond Technol Int Conf (CSTIC). https://doi.org/10.1109/CSTIC52283.2021.9461470
Zhang W, Liu Y, Wang C, Gao J, Niu X, Wang J (2017) Effect of non-ionic surfactant on copper dishing and dielectric erosion correction in alkaline barrier CMP solution free of inhibitors. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 6:P270–P275. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0191705jss
Tansuğ G, Tüken T, Giray ES, Fındıkkıran G, Sığırcık G, Demirkol O, Erbil M (2014) A new corrosion inhibitor for copper protection. Corros Sci 84:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2014.03.004
Karcher EL, Bayles DO, Bannantine JP, Beitz DC, Stabel JR (2008) Osteopontin: a novel cytokine involved in the regulation of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection in periparturient dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci 91:3079–3091. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1061
Hong Y, Devarapalli VK, Roy D, Babu SV (2007) Synergistic Roles of dodecyl sulfate and benzotriazole in enhancing the efficiency of CMP of copper. J Electrochem Soc 154:H444–H453. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1061
Liu L, Zhang Z, Wu B, Hu W, Meng F, Li Y (2021) A review: green chemical mechanical polishing for metals and brittle wafers. J Phys D Appl Phys 54:373001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac0c4a
Huang W, Tamilmani S, Raghavan S, Small R (2003) Dissolution of Copper thin films in hydroxylamine-based solutions. Int J Miner Process 72:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-7516(03)00111-x
Turk MC, Shi X, Gonyer DAJ, Roy D (2015) Chemical and mechanical aspects of a Co-Cu planarization scheme based on an alkaline slurry formulation. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 5:P88–P99. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0271602jss
Li F, Wang Z, Jiang Y, Li C, Sun S, Chen S, Hu S (2021) DFT Study on the adsorption of deprotonated benzotriazole on the defective copper surfaces. Corros Sci 186:109458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109458
Deshpande S, Kuiry SC, Klimov M, Obeng Y, Seal S (2004) Chemical mechanical planarization of copper: role of oxidants and inhibitors. J Electrochem Soc 151:788–794. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1806395
Xu Q, Chen L, Yang F, Cao H (2017) Influence of slurry components on copper CMP performance in alkaline slurry. Microelectron Eng 183–184:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2017.10.002
Li J, Lu XC, Zhang ZB (2014) Inhibition mechanism of benzotriazole in copper chemical mechanical planarization. Appl Mech Mater 607:74–78. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.607.74
Li W, Ma T, Tan B, Zhang S, Yan M, Ji J, Wang F, Du H, Wang X (2022) The effect of structural properties of benzo derivative on the inhibition performance for copper corrosion in alkaline medium: experimental and theoretical investigations. Colloids Surf, A 649:129531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129531
Wang Y, Zhang S, Tan B, Li W, Ji J, Yan M, Cui Z (2022) Effect of corrosion inhibitor BTA on silica particles and their adsorption on copper surface in copper interconnection CMP. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 11:044002. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac627c
Liu M, Yin D, Tan B, Yang F, Sun X, Gao P, Zhang S, Wang Y (2020) Toward understanding the adsorption and inhibition mechanism of Cu-MBTA passivation film on copper surface: a combined experimental and DFT investigation. Electron Mater Lett 17:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-020-00255-8
Ryu HY, Cho BJ, Yerriboina NP, Lee CH, Hwang JK, Hamada S, Wada Y, Hiyama H, Park JG (2019) Selection and optimization of corrosion inhibitors for improved Cu CMP and post-Cu CMP cleaning. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8:P3058–P3062. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0101905jss
Wang N, Pan G, Liu Y (2011) Synergistic roles of mixed inhibitors and the application of mixed complexing ligands in copper chemical mechanical polishing. Microelectron Eng 88:3372–3374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2011.06.029
Tian Y, Zhou J, Wang C, Li H, Xu C, Li Y, Liu Q (2022) Role of potassium tolyltriazole as an inhibitor in H2O2-based slurry on Cu/Ru patterned wafer CMP. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 11:034006. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac5eac
Jiang L, Lan Y, He Y, Li Y, Li Y, Luo J (2014) 1,2,4-Triazole as a corrosion inhibitor in copper chemical mechanical polishing. Thin Solid Films 556:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2013.12.047
Wang Q, Tan B, Gao B, Tian S, Han C, Yang L (2019) Study on the adsorption and inhibition mechanism of 1,2,4-triazole on copper surface in copper interconnection CMP. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8:P313–P318. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0121906jss
Muniz-Miranda M, Muniz-Miranda F, Caporali S (2014) SERS and DFT study of copper surfaces coated with corrosion inhibitor. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 5:2489–2497. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.5.258
Li W, Tan B, Zhang S, Guo L, Ji J, Yan M, Wang R (2022) Insights into triazole derivatives as potential corrosion inhibitors in CMP process: experimental evaluation and theoretical analysis. Appl Surf Sci 602:154165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154165
Hu L, Pan G, Zhang X, He P, Wang C (2019) Inhibition effect of TT-LYK on Cu corrosion and galvanic corrosion between Cu and Co during CMP in alkaline slurry. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8:P437–P447. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0181908jss
Ma T, Tan B, Xu Y, Yin D, Liu G, Zeng N, Song G, Kao Z, Liu Y (2020) Corrosion control of copper wiring by barrier CMP slurry containing azole inhibitor: combination of simulation and experiment. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Asp 599:124872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124872
Hu L, Pan G, Wang H, Xu Y, Wang R (2020) The synergistic inhibitory effect and density functional theory study of 2,2’-[[(methyl-1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]imino]bisethanol and potassium oleate on copper in H2O2 based alkaline slurries. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Asp 603:125275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125275
Wu T, Gao B, Zheng Q, Liu S, Wang J (2022) Corrosion inhibition and the synergistic effect of three different inhibitors on copper surface. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 11:054009. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ac6d75
Guo X, Huang H, Liu D (2021) The inhibition mechanism and adsorption behavior of three purine derivatives on the corrosion of copper in alkaline artificial seawater: structure and performance. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Asp 622:126644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126644
Petrović Mihajlović MB, Radovanović MB, Simonović AT, Tasić ŽZ, Antonijević MM (2019) Evaluation of purine based compounds as the inhibitors of copper corrosion in simulated body fluid. Results in Physics 14:102357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102357
Zeng N, Zhao H, Luo C, Liu Y, Wang C, Ma T, Wang W (2021) Roles and mechanistic analysis of adenine as a green inhibitor in chemical mechanical polishing. J Appl Electrochem 51:1479–1489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-021-01587-5
Prasad YN, Ramanathan S (2007) Chemical mechanical planarization of copper in alkaline slurry with uric acid as inhibitor. Electrochim Acta 52:6353–6358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.04.044
Pandija S, Roy D, Babu SV (2009) Achievement of high planarization efficiency in CMP of copper at a reduced down pressure. Microelectron Eng 86:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2008.11.047
Goonetilleke PC, Roy D (2008) Relative roles of acetic acid, dodecyl sulfate and benzotriazole in chemical mechanical and electrochemical mechanical planarization of copper. Appl Surf Sci 254:2696–2707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.10.005
Hong Y, Patri UB, Ramakrishnan S, Roy D, Babu SV (2005) Utility of Dodecyl sulfate surfactants as dissolution inhibitors in chemical mechanical planarization of copper. J Mater Res 20:3413–3424. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2005.0419
Yang G, Wang H, Wang N, Sun R, Wong CP (2019) Integrated electrochemical analysis of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) as the inhibitor for copper chemical mechanical planarization (Cu-CMP). J Alloy Compd 770:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.101
Jang S, Song J, Amalnerkar D, Qin H, Kim T (2016) Effect of secondary inhibitors on material removal rate and nano-roughness of Cu chemical mechanical planarization. Mater Express 6:383–393. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2016.1323
Klug BK, Pettit CM, Pandija S, Babu SV, Roy D (2008) Investigation of dissolution inhibitors for electrochemical mechanical planarization of copper using beta-alanine as a complexing agent. J Appl Electrochem 38:1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-008-9570-y
Yang C, Niu X, Zhou J, Wang J, Huo Z, Lu Y (2020) Synergistic action mechanism and effect of ammonium dodecyl sulfate and 1,2,4-triazole in alkaline slurry on step height reduction for Cu CMP. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology 9:034010. https://doi.org/10.1149/2162-8777/ab80b3
Ma T, Tan B, Liu Y, Niu X, Liu G, Wang C, Luo C, Xu Y, Kao Z (2019) Role of 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one (BIT) in the improvement of barrier CMP performance with alkaline slurry. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 8:P449–P456. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0041909jss
Abelev E, Smith AJ, Hassel AW, Ein-Eli Y (2007) Potassium sorbate solutions as copper chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) based slurries. Electrochim Acta 52:5150–5158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.02.010
Nagar M, Starosvetsky D, Vaes J, Ein-Eli Y (2010) Potassium sorbate as an inhibitor in copper chemical mechanical planarization slurry. Part I. Elucidating Slurry Chem, Electrochim Acta 55:3560–3571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.12.088
Nagar M, Vaes J, Ein-Eli Y (2010) Potassium sorbate as an inhibitor in copper chemical mechanical planarization slurries. Part II: Effects Sorbate Chem Mech Planarization Perform, Electrochim Acta 55:2810–2816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.10.086
Sekhar MS, Ramanathan S (2006) Characterization of copper chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) in nitric acid–hydrazine based slurry for microelectronic fabrication. Thin Solid Films 504:227–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.09.128
Funding
This work was supported by the Major National Science and Technology Special Projects (No. 2016ZX02301003-004–007), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62074049), Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No. F2021202009), Scientific Research Program of Tianjin Education Commission (No. 2019KJ094), and Key Laboratory of Electronic Materials and Devices of Tianjin, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors discussed each reference paper together and contributed useful ideas for this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
The authors consent to participate.
Consent for publication
The authors consent to publish.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Niu, X., Qu, M. et al. A review: research progress of chemical–mechanical polishing slurry for copper interconnection of integrated circuits. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 125, 47–71 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10775-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10775-2