Abstract
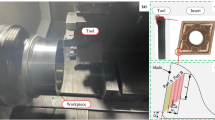
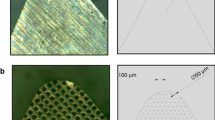
Difficult-to-machine materials such as Ni-based superalloy suffer from severe tool wear and poor surface quality; therefore, the cooling mechanism is the key to improving machining performance and reducing the environmental pollution in manufacturing. In the past, plenty of studies verified that the micro-texture on the cutting insert improved the cutting performance under the same cooling condition. The main explanation is that the second generated cracks caused the capillary siphon phenomenon and increased the wettability of the subsurface of the workpiece. In order to investigate the effect of surface wettability differences on the cutting performance of the tool under different micro-textured morphologies, three types of micro-textured CBN tools with pit, linear, and sinusoidal morphologies were fabricated by laser machining technology. Through cutting experiments on Inconel 718 Ni-based superalloy, the cutting force, tool wear, and machined surface roughness of different micro-textured tools were compared and analyzed. The relationship between cutting performance and wettability of different shaped micro-texture was obtained by measuring the contact angle using PT-705B optical angular contact meter. The experimental results show that the presence of surface micro-textures enhances the surface wettability of the tool. It effectively reduces the cutting force and slows down the rake face’s wear and the machined part’s surface roughness. Compared with other morphologies, sinusoidal micro-textured tools show the best cutting performance. Among the four morphologies of micro-textured tools, cutting performance improvement increases with surface wettability. More generally, these primary findings are consistent with research showing that wettability is critical in micro-texture generation for high-performance machining. The conclusion is very much the key component in future attempts to overcome the assumption of the capillary siphon phenomenon on the subsurface of the workpiece.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Criado V, Díaz-Álvarez J, Cantero JL, Miguélez MH (2018) Study of the performance of PCBN and carbide tools in finishing machining of Inconel 718 with cutting fluid at conventional pressures. Procedia CIRP 77:634–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.08.189
Slipchenko K, Petrusha I, Turkevich V, Johansson J, Bushlya V, Ståhl JE (2018) Investigation of the mechanical properties and cutting performance of cBN-based cutting tools with Cr3C2 binder phase. Procedia CIRP 72:1433–1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2018.03.180
Sheng J, Zhang H, Hu X, Huang S (2020) Influence of laser peening on the high-temperature fatigue life and fracture of Inconel 718 nickel-based alloy. Theoret Appl Fract Mech 109:102757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2020.102757
Tan N, Li Y, Lou L, Zhang G, Xing Z, Wang H (2021) Influence of micro-nano multiscale surface texture on wettability of Ni-based droplets at high temperature. Surf Coat Technol 418:127103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127103
Divin-Mariotti S, Amieux P, Pascale-Hamri A, Auger V, Kermouche G, Valiorgue F, Valette S (2019) Effects of micro-knurling and femtosecond laser micro texturing on aluminum long-term surface wettability. Appl Surf Sci 479:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.025
Qin L, Lin P, Zhang Y, Dong G, Zeng Q (2013) Influence of surface wettability on the tribological properties of laser textured Co-Cr-Mo alloy in aqueous bovine serum albumin solution. Appl Surf Sci 268:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.003
Kubiak KJ, Wilson MCT, Mathia TG, Carval P (2011) Wettability versus roughness of engineering surfaces. Wear 271:523–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.03.029
Ding Y, Jia L, Yin L, Dang C, Liu X, Xu J (2022) Anisotropic wetting characteristics of droplet on micro-grooved surface. Colloids Surf A 633:127850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127850
Hao X, Cui W, Li L, Li H, Khan AM, He N (2018) Cutting performance of textured polycrystalline diamond tools with composite lyophilic/lyophobic wettabilities. J Mater Process Technol 260:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.04.049
Sakthivel G, Sathiya Narayanan N, Vedha Hari BN, Sriraman N, Aanandhamanikandan G, Suraj Nanduru VSP (2021) Performance of surface textured PCD inserts with wettability chemical solutions for machining operation. Mater Today Proc 46:8283–8287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.252
Zhang L, Guo X, Zhang K, Wu Y, Huang Q (2020) Enhancing cutting performance of uncoated cemented carbide tools by joint-use of magnetic nanofluids and micro-texture under magnetic field. J Mater Process Technol 284:116764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116764
Wang Q, Yang Y, Yao P, Zhang Z, Yu S, Zhu H, Huang C (2021) Friction and cutting characteristics of micro-textured diamond tools fabricated with femtosecond laser. Tribol Int 154:106720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106720
Wang Y, Mo Y, Zhu M, Bai M (2008) Wettability of metal coatings with biomimic micro textures. Surf Coat Technol 203:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.08.040
Pratap T, Patra K (2018) Fabrication of micro-textured surfaces using ball-end micromilling for wettability enhancement of Ti-6Al-4V. J Mater Process Technol 262:168–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.06.035
Sun Z, Zhang T, Li P, Wang S, To S, Wang H (2021) Analytical modelling of the trans-scale cutting forces in diamond cutting of polycrystalline metals considering material microstructure and size effect. Int J Mech Sci 204:106575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106575
Gupta MK, Korkmaz ME, Sarıkaya M, Krolczyk GM, Günay M, Wojciechowski S (2022) Cutting forces and temperature measurements in cryogenic assisted turning of AA2024-T351 alloy: an experimentally validated simulation approach. Meas J Int Meas Confederation 188:110594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110594
Fan Z, Zhao J, Yin J, Hu D, Fu W, Yan H, Song X (2022) Wetting behavior of Al on the surface of SiC textured by nanosecond laser. Opt Laser Technol 146:107596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107596
Du Q, Zhou P, Pan Y, Qu X, Liu L, Yu H, Hou J (2022) Influence of hydrophobicity and roughness on the wetting and flow resistance of water droplets on solid surface: a many-body dissipative particle dynamics study. Chem Eng Sci 249:117327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2021.117327
Wang F, Cao Z, Liang A, Zhang X, Qiang L, Zhang J (2018) Surface structure and wettability tuning of porous silicon films by capillary-driven surface texturing under different current densities of electrochemical etching. Mater Lett 218:249–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.01.161
Al-Anssari S, Wang S, Barifcani A, Lebedev M, Iglauer S (2017) Effect of temperature and SiO2 nanoparticle size on wettability alteration of oil-wet calcite. Fuel 206:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.05.077
Yang C, Mei X, Tian Y, Zhang D, Li Y, Liu X (2016) Modification of wettability property of titanium by laser texturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87:1663–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8601-9
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research & Development Projects (Grant Agreement No. 2020ZDZX0025) of Sichuan Province, China and the Key Research & Development Projects (Grant Agreement No. 22DYF3466) of Sichuan Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, methodology, cutting experiments, writing—original draft, data collection, and analysis were performed by Zengfeng Duan. Validation, investigation, and data curation were performed by Binbin Li. Experimental method guidance and writing — review and editing were performed by Ling Chen. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Therefore, ethics approval is not applicable.
Consent to participate
Consent to participate in this study was obtained from all the authors.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from all the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, Z., Chen, L. & Li, B. Effect of micro-textured morphology with different wettabilities on tool cutting performance. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 123, 1745–1754 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10284-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10284-2