Abstract
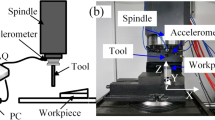
Chatter is a self-excited vibration that reduces the quality of the workpiece surface and accelerates tool wear, it is a phenomenon that is difficult to monitor and control. In order to achieve high-performance manufacturing, a reliable online monitoring system for chatter needs to be developed. This paper proposes a chatter identification method based on optimized variational modal decomposition (OVMD) and fuzzy entropy to achieve online monitoring of chatter accurately. The method embeds the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) into the VMD method, and the chattering features are extracted for both simulated and experimental signals to achieve the optimal decomposition of the force signal in a rapid way. In order to solve the problem that sample entropy and approximate entropy are not sensitive to chatter detection, fuzzy entropy is introduced to monitor the chatter feature components. Experimental results show that the fuzzy entropy is particularly sensitive to the occurrence of chatter in specific embedding dimensions, and this method can monitor the dynamics of milling with higher sensitivity and stability.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that all data and materials reported in this paper are available. The data set supporting the results of this paper comes from the actual processing process.
References
Sun Y, Xiong Z (2017) Modeling, analysis, and removal of chatter marks in flexible turning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93:4187–4196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0856-2
Zhu L, Liu C (2020) Recent progress of chatter prediction, detection and suppression in milling. Mech Syst Signal Process 143:106840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106840
Albertelli P, Braghieri L, Torta M, Monno M (2019) Development of a generalized chatter detection methodology for variable speed machining. Mech Syst Signal Process 123:26–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.01.002
Wang GF, Yang YW, Zhang YC, Xie QL (2014) Vibration sensor based tool condition monitoring using ν support vector machine and locality preserving projection. Sens Actuators A 209:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2014.01.004
Zhu K, Vogel-Heuser B (2014) Sparse representation and its applications in micro-milling condition monitoring: noise separation and tool condition monitoring. Inte J Adv Manuf Technol 70:185–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5258-5
Chen D, Zhang X, Zhao H, Ding H (2021) Development of a novel online chatter monitoring system for flexible milling process. Mech Syst Signal Process 159:107799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.107799
Li X, Yao ZH, Chen ZC (2010) An effective EMD-based feature extraction method for boring chatter recognition. Appl Mech Mater 34–35:1058–1063. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.34-35.1058
Shrivastava Y, Singh B (2021) Tool chatter prediction based on empirical mode decomposition and response surface methodology. Measurement 173:108585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108585
Ji Y, Wang X, Liu Z, Wang H, Jiao L, Wang D, Leng S (2018) Early milling chatter identification by improved empirical mode decomposition and multi-indicator synthetic evaluation. J Sound Vib 433:138–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.07.019
Shrivastava Y, Singh B, Sharma A (2018) Identification of chatter in turning operation using WD and EMD. Mater Today Proc 5:23917–23926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.10.184
Shrivastava Y, Singh B (2019) A comparative study of EMD and EEMD approaches for identifying chatter frequency in CNC turning. Eur J Mech - A/Solids 73:381–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2018.10.004
Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D (2014) Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62:531–544. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675
Ni Q, Ji JC, Feng K, Halkon B (2022) A fault information-guided variational mode decomposition (FIVMD) method for rolling element bearings diagnosis. Mech Syst Signal Process 164:108216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.108216
Wang Y, Markert R, Xiang J, Zheng W (2015) Research on variational mode decomposition and its application in detecting rub-impact fault of the rotor system. Mech Syst Signal Process 60–61:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.02.020
Feng G, Wei H, Qi T, Pei X, Wang H (2021) A transient electromagnetic signal denoising method based on an improved variational mode decomposition algorithm. Measurement 184:109815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109815
Li K, He S, Luo B, Li B, Liu H, Mao X (2019) Online chatter detection in milling process based on VMD and multiscale entropy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:5009–5022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04478-4
Liu C, Zhu L, Ni C (2018) Chatter detection in milling process based on VMD and energy entropy. Mech Syst Signal Process 105:169–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.046
Yang K, Wang G, Dong Y, Zhang Q, Sang L (2019) Early chatter identification based on an optimized variational mode decomposition. Mech Syst Signal Process 115:238–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.052
Fu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou H, Li D, Liu H, Qiao H, Wang X (2016) Timely online chatter detection in end milling process. Mech Syst Signal Process 75:668–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.01.003
Zhang Z, Li H, Meng G, Tu X, Cheng C (2016) Chatter detection in milling process based on the energy entropy of VMD and WPD. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 108:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.06.002
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008
Chen W, Wang Z, Xie H, Yu W (2007) Characterization of surface EMG signal based on fuzzy entropy. IEEE Transact Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 15:266–272. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2007.897025
Funding
The authors are very grateful for the support of the Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Funds (2021JJ12GX011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Defeng Peng proposed the recognition method of chatter and wrote the paper; Hongkun Li guided the writing of the paper and acquired funding support; Jiayu Ou and Zhaodong Wang engaged in project promotion and administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The manuscript has been read and approved by the authors.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, D., Li, H., Ou, J. et al. Milling chatter identification by optimized variational mode decomposition and fuzzy entropy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121, 6111–6124 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09666-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09666-3