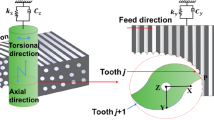
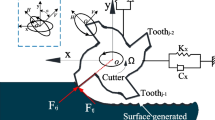
Abstract
With their successful applications in handling, spraying, arc welding and other processing fields, industrial robots are gradually replacing traditional CNC machine tools to complete machining tasks due to the wider working envelope and the higher flexibility. Aiming at the chatter problem, a robotic longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic milling method with variable force coefficient is proposed in this paper. Taking carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) as the processing object, the influence of the fiber layup angle on the milling force is analyzed first; then, the robot milling force parameters are determined, and the robot milling kinematics model is established. Furthermore, the ultrasonic function angle is defined, and the cutting layer thickness model, the dynamic milling force model, and the dynamic differential equation under ultrasonic vibration are established to analyze the stability of robotic longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic milling of CFRP. Finally, the full discrete method is used to obtain stability lobe diagrams.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
References
Li B, Tian W, Zhang CF, Hua FF, Cui GY, Li YF (2021) Positioning error compensation of an industrial robot using eural networks and experimental study. Chinese J of Aeronaut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2021.03.027
Wang W, Tian W, Liao WH, Li B (2021) Pose accuracy compensation of mobile industry robot with binocular vision measurement and deep belief network. Optik 238(8):166716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166716
Bu Y, Liao WH, Tian W, Zhang L, Li DW (2017) Modeling and experimental investigation of cartesian compliance characterization for drilling robot. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:3253–3264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-9991-z
Zhang L, Tian W, Li DW, Hong P, Li ZY(2018) Design of drilling and riveting multi-functional end effector for cfrp and aluminum components in robotic aircraft assembly. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics 35(3):529–538. https://doi.org/10.16356/j.1005-1120.2018.03.529
Ning FD, Wang H, Cong WL (2019) Rotary ultrasonic machining of carbon fiber reinforced plastic composites: a study on fiber material removal mechanism through single-grain scratching. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03433-7
Chen T, Lu YJ, Wang YS, Liu G, Liu GJ (2021) Comparative study on cutting performance of conventional and ultrasonic-assisted bi-directional helical milling of CFRP. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 115:3701–3711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07418-3
Takeyama H, Iijima N (1988) Machinability of glassfiber reinforced plastics and application of ultrasonic machining. CIRP Ann-Manuf Techn 37(1):93–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)61593-5
Kim JD, Lee ES (1994) A study of the ultrasonic-vibration cutting of carbon-fiber reinforced plastics. J Mater Process Tech 43(2–4):259–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-0136(94)90025-6
Zhao B, Liu CS, Zhu XS, Xu KW (2002) Research on the vibration cutting performance of particle reinforced metallic matrix composites SiCp/Al. J Mater Process Tech 129(1–3):380–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00696-9
Guo WH, Zheng K, Liao WH, Liu JS, Feng JD (2019) Experimental research on rotating ultrasonic milling aluminum alloy by robot. Journal of Nanjing University of Science Technology 43(02):159–164
Sun LJ, Zheng K, Liao WH, Liu JS, Feng JD, Dong S (2020) Investigation on chatter stability of robotic rotary ultrasonic milling. Robot Cim-Int Manuf 63:101911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2019.101911
He YL, Sheikh-Ahmad J, Zhu SW, Zhao CL (2020) Cutting force analysis considering edge effects in the milling of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite. J Mater Process Tech 279:116541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116541
Ding Y, Zhu LM, Zhang XJ, Ding H (2010) Second-order full-discretization method for milling stability prediction. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(10):926–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.05.005
Funding
The study was co-supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Nos. 52075256 and 52005254, and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK20190417.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianlong Zhang: Test design, Test execution, Software, Data analysis, and Writing-original draft preparation. Wenhe Liao: Test design, Data analysis, Writing, and Editing. Wei Zhao: Validation, Project administration, Writing-reviewing, and Editing. Wei Tian: Test design, Investigation, Reviewing and editing, and Project administration. Kan Zheng: Investigation, Supervision, Reviewing, and Editing. Bo Li: Writing-reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
We confirm that this work is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere. All the authors listed have agreed to publish the manuscript that is enclosed.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liao, W., Zhao, W. et al. Research on stability of robotic longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic milling with variable cutting force coefficient. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 121, 1707–1715 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09321-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-09321-x